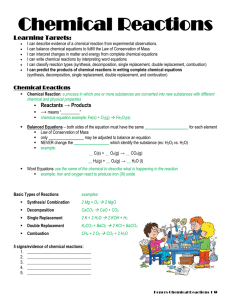
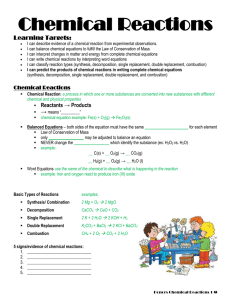
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Asbestos was used for years as an insulating material in buildings until prolonged exposure to asbestos was demonstrated to cause lung cancer. Asbestos is a mineral containing magnesium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen. One form of asbestos, chrysotile (520.27 g/mol), has the composition 28.03% magnes ...
... Asbestos was used for years as an insulating material in buildings until prolonged exposure to asbestos was demonstrated to cause lung cancer. Asbestos is a mineral containing magnesium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen. One form of asbestos, chrysotile (520.27 g/mol), has the composition 28.03% magnes ...
Chapter 7 Review
... For the reaction CO(g) + 2 H2(g) <---> CH3OH(g) + heat; [CO(g)] = 0.025 mol/L, [H2(g) ] = 0.050 mol/L and [CH3OH(g)] = 0.0063 mol/L a) b) ...
... For the reaction CO(g) + 2 H2(g) <---> CH3OH(g) + heat; [CO(g)] = 0.025 mol/L, [H2(g) ] = 0.050 mol/L and [CH3OH(g)] = 0.0063 mol/L a) b) ...
Document
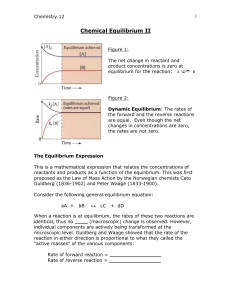
... adjusts itself such that, after some time, the reaction rates of the direct and inverse reactions are equal, i.e., the number of moles of CO2 that dissociate, according to the direct reaction, is equal to the number of moles that are formed, according to the inverse reaction, per unit of time. A che ...
... adjusts itself such that, after some time, the reaction rates of the direct and inverse reactions are equal, i.e., the number of moles of CO2 that dissociate, according to the direct reaction, is equal to the number of moles that are formed, according to the inverse reaction, per unit of time. A che ...
Naming Binary Molecular Compounds
... Significance of a chemical formula The chemical formula indicates the relative number of atoms of each element in a chemical compound. ...
... Significance of a chemical formula The chemical formula indicates the relative number of atoms of each element in a chemical compound. ...
Solving Equilibrium Problems
... Now, fill the table with all known concentrations These are the concentrations that are given in the problem Example - Suppose for the equilibrium reaction below, the initial concentrations of A and B were given as 0.750 M in A and 1.500 M in B The table will look as follows: aA I C E ...
... Now, fill the table with all known concentrations These are the concentrations that are given in the problem Example - Suppose for the equilibrium reaction below, the initial concentrations of A and B were given as 0.750 M in A and 1.500 M in B The table will look as follows: aA I C E ...
Lab 3. Chemical Reactions
... rolled into pellets, or pounded into sheets and foil). It conducts heat and electricity but is not magnetic. It has a high melting point (it takes a lot of energy to make it turn from a solid to a liquid) and it is not soluble (doesn’t dissolve) in water. These characteristics are physical propertie ...
... rolled into pellets, or pounded into sheets and foil). It conducts heat and electricity but is not magnetic. It has a high melting point (it takes a lot of energy to make it turn from a solid to a liquid) and it is not soluble (doesn’t dissolve) in water. These characteristics are physical propertie ...
Chemistry and the material world
... Enthalpy favours the reaction. It is exothermic, heat is released. Entropy dis-favours the reaction. Order is increased, the number of particles decreases. The questions remains: Will the reaction occur spontaneously? ...
... Enthalpy favours the reaction. It is exothermic, heat is released. Entropy dis-favours the reaction. Order is increased, the number of particles decreases. The questions remains: Will the reaction occur spontaneously? ...
L-12 Spontaneity of chemical reactions
... Spontaneity of Chemical Reactions When the valve between the two bulbs is opened [Fig 12.1 (b)], the two gases mix spontaneously. The mixing of gases continues until the partial pressure of each gas becomes equal to 0.5 bar in each bulb i.e., the equilibrium is attained. We know from experience tha ...
... Spontaneity of Chemical Reactions When the valve between the two bulbs is opened [Fig 12.1 (b)], the two gases mix spontaneously. The mixing of gases continues until the partial pressure of each gas becomes equal to 0.5 bar in each bulb i.e., the equilibrium is attained. We know from experience tha ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... 1) If given the initial concentrations of all parts and the change in concentration of 1+ parts (reactants or products), you can use stoichiometry to find the change in the other parts. 2) If not given, let x be the change in concentration of the reactant with the smallest coefficient (to avoid frac ...
... 1) If given the initial concentrations of all parts and the change in concentration of 1+ parts (reactants or products), you can use stoichiometry to find the change in the other parts. 2) If not given, let x be the change in concentration of the reactant with the smallest coefficient (to avoid frac ...