Interference I - Galileo and Einstein
... Mirages • Mirages are caused by light bending back when it encounters a decreasing refractive index: the hot air just above the desert floor (within a few inches) has a lower n then the colder air above it: ...
... Mirages • Mirages are caused by light bending back when it encounters a decreasing refractive index: the hot air just above the desert floor (within a few inches) has a lower n then the colder air above it: ...
Problem 2
... 2A. Optical properties of an unusual material (7 points) The optical properties of a medium are governed by its relative permittivity ( r ) and relative permeability ( r ). For conventional materials like water or glass, which are usually optically transparent, both of their r and r are posi ...
... 2A. Optical properties of an unusual material (7 points) The optical properties of a medium are governed by its relative permittivity ( r ) and relative permeability ( r ). For conventional materials like water or glass, which are usually optically transparent, both of their r and r are posi ...
Optical Mineralogy: Introduction
... earlier, the reasons being that the two waves are vibrating in perpendicular directions, and that we still have to deal with an additional layer represented by the analyzer. When white light is used instead of monochromatic light, a retardation of full wavelength ( = n) would not result in complet ...
... earlier, the reasons being that the two waves are vibrating in perpendicular directions, and that we still have to deal with an additional layer represented by the analyzer. When white light is used instead of monochromatic light, a retardation of full wavelength ( = n) would not result in complet ...
Semiconductor Devices
... the NDR region to produce a Gunn-domain. Once a domain has formed, the electric field in the rest of the sample falls below the NDR region and will therefore inhibit the formation of a second Gunn-domain. As soon as the domain is absorbed by the anode contact region, the average electric field in th ...
... the NDR region to produce a Gunn-domain. Once a domain has formed, the electric field in the rest of the sample falls below the NDR region and will therefore inhibit the formation of a second Gunn-domain. As soon as the domain is absorbed by the anode contact region, the average electric field in th ...
CT_optics
... A planar wave is incident on a single slit and forms a diffraction pattern on a screen. The pattern has a central, zeroth-order maximum and a number of secondary maxima. The first order maximum is formed in a direction where light from the top third (a) of the slit cancels light from the middle thi ...
... A planar wave is incident on a single slit and forms a diffraction pattern on a screen. The pattern has a central, zeroth-order maximum and a number of secondary maxima. The first order maximum is formed in a direction where light from the top third (a) of the slit cancels light from the middle thi ...
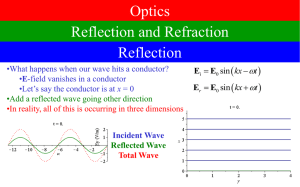
Reflect/Refract
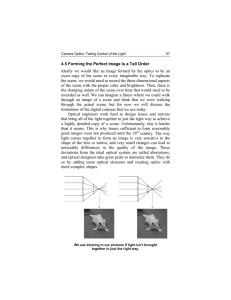
... •Prisms are rarely used in research •Diffraction gratings work better •Lenses are a lot like prisms •They focus colors unevenly •Blurring called chromatic dispersion •High quality cameras use a combination of lenses to cancel this effect ...
... •Prisms are rarely used in research •Diffraction gratings work better •Lenses are a lot like prisms •They focus colors unevenly •Blurring called chromatic dispersion •High quality cameras use a combination of lenses to cancel this effect ...
Unit X: Light Phenomena - Bremen High School District 228
... persuade the viewing audience how lenses or mirrors have had a tremendous influence in scientific areas of study and research. It is important to touch upon historical implications of lenses in your report. You must prepare a visual aid, such as PowerPoint, poster, video, etc, and you will present y ...
... persuade the viewing audience how lenses or mirrors have had a tremendous influence in scientific areas of study and research. It is important to touch upon historical implications of lenses in your report. You must prepare a visual aid, such as PowerPoint, poster, video, etc, and you will present y ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS In geometric
... index of the prism is then related to the apex angle, σ of the prism and δ as in the equation above. δ can be found by adjusting the angle of the incident light so that the light passes through the prism parallel to the base of the prism. ...
... index of the prism is then related to the apex angle, σ of the prism and δ as in the equation above. δ can be found by adjusting the angle of the incident light so that the light passes through the prism parallel to the base of the prism. ...
Chapter 33E Worksheet - Rose
... diameter. (A) Find the apparent position of the fish to an observer outside the bowl. The effect of the thin walls of the bowl may be ignored. (B) Find the magnification of the fish to an observer outside the bowl. (C) A friend advised the owner of the bowl to keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid ...
... diameter. (A) Find the apparent position of the fish to an observer outside the bowl. The effect of the thin walls of the bowl may be ignored. (B) Find the magnification of the fish to an observer outside the bowl. (C) A friend advised the owner of the bowl to keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid ...
physics
... 6. Draw the well labeled dig for the astronomical telescope, when the image formed at the least distance of distinct vision. 7. State and prove Prism Formula. 8. A ray of light falls normally on a refracting face of a prism of refractive index (1.5) . Find the angle of the prism if the ray just fail ...
... 6. Draw the well labeled dig for the astronomical telescope, when the image formed at the least distance of distinct vision. 7. State and prove Prism Formula. 8. A ray of light falls normally on a refracting face of a prism of refractive index (1.5) . Find the angle of the prism if the ray just fail ...
Light Microscopy
... • Salmon, E. D. and J. C. Canman. 1998. Proper Alignment and Adjustment of the Light Microscope. Current Protocols in Cell Biology 4.1.1-4.1.26, John Wiley and Sons, N.Y. • Murphy, D. 2001. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging. Wiley-Liss, N.Y. • Keller, H.E. 1995. Objective le ...
... • Salmon, E. D. and J. C. Canman. 1998. Proper Alignment and Adjustment of the Light Microscope. Current Protocols in Cell Biology 4.1.1-4.1.26, John Wiley and Sons, N.Y. • Murphy, D. 2001. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging. Wiley-Liss, N.Y. • Keller, H.E. 1995. Objective le ...
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... Find the angular width of the first-order spectrum produced by a grating ruled with 800 lines/cm. Solution: The slit space d that corresponding to 800 line/cm is d=(10-2 m/cm)/(8x103 lines/cm)=1.25x10-6 m Since m=1, sinΘb=λb/d = 4x10-7m/1.25x10-6m = 0.32, Θb=19o sinΘr=λr/d = 7x10-7m/1.25x10-6m = 0.5 ...
... Find the angular width of the first-order spectrum produced by a grating ruled with 800 lines/cm. Solution: The slit space d that corresponding to 800 line/cm is d=(10-2 m/cm)/(8x103 lines/cm)=1.25x10-6 m Since m=1, sinΘb=λb/d = 4x10-7m/1.25x10-6m = 0.32, Θb=19o sinΘr=λr/d = 7x10-7m/1.25x10-6m = 0.5 ...
Single Pixel Cameras wall panels
... process. The text and diagrams show the experimental layout and mathematical equations used in computational imaging techniques, as well as other writings from different experiments ...
... process. The text and diagrams show the experimental layout and mathematical equations used in computational imaging techniques, as well as other writings from different experiments ...
UNIT 5_THE ATMOSPHERE
... In the first place, the atmosphere contains oxygen which is necessary for living beings. We all need air to breathe. Secondly, the temperature of the Earth depends on the atmosphere. The atmosphere favours the warming of the Earth. It absorbs a great part of solar radiation and prevents this from es ...
... In the first place, the atmosphere contains oxygen which is necessary for living beings. We all need air to breathe. Secondly, the temperature of the Earth depends on the atmosphere. The atmosphere favours the warming of the Earth. It absorbs a great part of solar radiation and prevents this from es ...
Practical Laboratory #2: Emission Spectra 2
... Do the following steps for the unknown light source after you’ve set it up: 1. Start data collection on the Logger Pro software. An emission spectrum will be graphed. 2. When you achieve a satisfactory graph, stop data collection. If the highest peak in the emission spectrum is > 1, then the sensor ...
... Do the following steps for the unknown light source after you’ve set it up: 1. Start data collection on the Logger Pro software. An emission spectrum will be graphed. 2. When you achieve a satisfactory graph, stop data collection. If the highest peak in the emission spectrum is > 1, then the sensor ...
Unit 5 Test - Ms. Williams
... b. they temporarily change the volume of material they pass through by compression and expansion c. they shake particles at right angles to their direction of travel – side to side, like a snake d. they cannot be transmitted through water or air 43. Where do most earthquakes occur? a. in the mountai ...
... b. they temporarily change the volume of material they pass through by compression and expansion c. they shake particles at right angles to their direction of travel – side to side, like a snake d. they cannot be transmitted through water or air 43. Where do most earthquakes occur? a. in the mountai ...
What is light? For the purposes of this class, light will refer to visible
... For the purposes of this class, light will refer to visible light - light that can be seen by the human eye. Like all electromagnetic waves, light has a particlewave duality: it exhibits features of both a particle and a wave. ...
... For the purposes of this class, light will refer to visible light - light that can be seen by the human eye. Like all electromagnetic waves, light has a particlewave duality: it exhibits features of both a particle and a wave. ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... Chapter 36 Image Formation (Lens and Mirrors) Using the ray approximation of geometric optics, we can now study how images are formed with mirrors and lens Then we can apply these principles to practical optical devices: the eye, telescopes, … First consider the common flat mirror to make some defin ...
... Chapter 36 Image Formation (Lens and Mirrors) Using the ray approximation of geometric optics, we can now study how images are formed with mirrors and lens Then we can apply these principles to practical optical devices: the eye, telescopes, … First consider the common flat mirror to make some defin ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.