Optical Fiber communication
... through the core. The index of the cladding is less than 1%, lower than that of the core. Light injected into the Fiber and striking core to cladding interface at greater than the critical angle, reflects back into core, since the angle of incidence and reflection are equal, the reflected light will ...
... through the core. The index of the cladding is less than 1%, lower than that of the core. Light injected into the Fiber and striking core to cladding interface at greater than the critical angle, reflects back into core, since the angle of incidence and reflection are equal, the reflected light will ...
The nature of light - FIU Faculty Websites
... When light rays pass from hotter to colder, they bend toward the direction of the temperature increase. If the air near the ground is warmer than that higher up, the light ray bends in a concave, upward trajectory. ...
... When light rays pass from hotter to colder, they bend toward the direction of the temperature increase. If the air near the ground is warmer than that higher up, the light ray bends in a concave, upward trajectory. ...
Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani and Elite School of Optometry
... Definition of radiometric units - radiant energy, radiant energy density, radiant flux, radiant exitance, irradiance, radiant intensity, radiance. 8.3 R2 fall of irradiance with distance R; Lambert’s law: I(θ) = I(0) cosθ. 8.4 Retinal sensitivity functions; photopic and scotopic V(λ) curve. 8.5 Defi ...
... Definition of radiometric units - radiant energy, radiant energy density, radiant flux, radiant exitance, irradiance, radiant intensity, radiance. 8.3 R2 fall of irradiance with distance R; Lambert’s law: I(θ) = I(0) cosθ. 8.4 Retinal sensitivity functions; photopic and scotopic V(λ) curve. 8.5 Defi ...
n - LSU Physics
... distances (like the thickness of a soap bubble), since we are able to resolve distances of the order of the wavelength of the light (for instance, for yellow light, we are talking about 0.5 of a millionth of a meter, 500nm). This has therefore technological applications. In the Michelson interferome ...
... distances (like the thickness of a soap bubble), since we are able to resolve distances of the order of the wavelength of the light (for instance, for yellow light, we are talking about 0.5 of a millionth of a meter, 500nm). This has therefore technological applications. In the Michelson interferome ...
P5G
... P5G Refraction Light waves change speed when they pass across the boundary between two substances with different densities, such as air and glass. This causes them to change direction and this effect is called refraction. ...
... P5G Refraction Light waves change speed when they pass across the boundary between two substances with different densities, such as air and glass. This causes them to change direction and this effect is called refraction. ...
TEACHER RESOURCE NETWORK/TEACHER CHANNEL®
... 4. How does the sun's heating of water in the tropics affect climate in the rest of the world? 5. What happens to water after it evaporates from the ocean and land? 6. How does the sun's energy cause winds and hurricanes? Concepts: a. The student will know that weather is the effect of the condition ...
... 4. How does the sun's heating of water in the tropics affect climate in the rest of the world? 5. What happens to water after it evaporates from the ocean and land? 6. How does the sun's energy cause winds and hurricanes? Concepts: a. The student will know that weather is the effect of the condition ...
Refraction Practice Problems
... 9. A laser beam is incident at an angle of 30.0° to the vertical onto a solution of corn syrup in water. If the beam is refracted to 19.24° to the vertical, (a) what is the index of refraction of the syrup solution? Suppose the light is red, with wavelength 632.8 nm in a vacuum. Find its (b) wavelen ...
... 9. A laser beam is incident at an angle of 30.0° to the vertical onto a solution of corn syrup in water. If the beam is refracted to 19.24° to the vertical, (a) what is the index of refraction of the syrup solution? Suppose the light is red, with wavelength 632.8 nm in a vacuum. Find its (b) wavelen ...
Waves and Optics One
... When light passes from one medium to another, e.g. air to glass, there will be a change of __________. This is due to the __________ of light being less in glass than air. The light ray will bend _________ the normal. When the light ray moves from glass to air it will bend _________ __________ the n ...
... When light passes from one medium to another, e.g. air to glass, there will be a change of __________. This is due to the __________ of light being less in glass than air. The light ray will bend _________ the normal. When the light ray moves from glass to air it will bend _________ __________ the n ...
PHYS_3342_120611
... The eye consists of pupil that allows light into the eye - it controls the amount of light allowed in through the lens - acts like a simple glass lens which focuses the light on the retina - which consists of light sensitive cells that send signals to the brain via the optic nerve. An eye with perfe ...
... The eye consists of pupil that allows light into the eye - it controls the amount of light allowed in through the lens - acts like a simple glass lens which focuses the light on the retina - which consists of light sensitive cells that send signals to the brain via the optic nerve. An eye with perfe ...
visible spectroscopy - Purdue University Chemistry Department
... PURDUE UNIVERSITY INSTRUMENT VAN PROJECT ...
... PURDUE UNIVERSITY INSTRUMENT VAN PROJECT ...
living with the lab
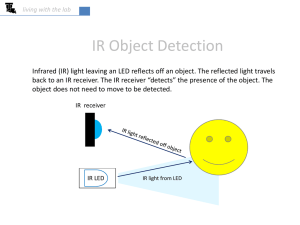
... It is important to install the LED in an enclosure to properly direct the IR light. Your kit includes the black pieces shown. Insert the legs of the LED through the holes in the longer black cylinder, and then install the smaller top piece over the exposed end of the LED. If you don’t have a shield, ...
... It is important to install the LED in an enclosure to properly direct the IR light. Your kit includes the black pieces shown. Insert the legs of the LED through the holes in the longer black cylinder, and then install the smaller top piece over the exposed end of the LED. If you don’t have a shield, ...
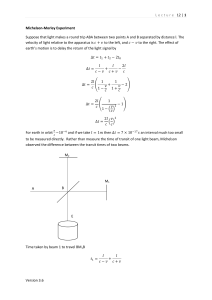
Lecture 12 | 1 Version 3.6 Michelson
... Thus time difference for two beams to reach the same spot according to ether hypothesis ...
... Thus time difference for two beams to reach the same spot according to ether hypothesis ...
PPT - National Radio Astronomy Observatory
... Objects which are very close to the Earth may be in the near-field of the interferometer. In this case, there is the additional complexity that the received e-m radiation cannot be assumed to be a plane wave. Because of this, an additional phase term in the relationship between the visibility and sk ...
... Objects which are very close to the Earth may be in the near-field of the interferometer. In this case, there is the additional complexity that the received e-m radiation cannot be assumed to be a plane wave. Because of this, an additional phase term in the relationship between the visibility and sk ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.