Light Scattering Spectroscopy
... Summary of LSS • LSS contrasts: • Polarization: single vs. multiple scattering • Angle: small vs. large particles • Spectrum: size and refractive index • Advantages: • Strong signal - allows use of lower cost components components. • Sensitive to important chromophores that are not fluorescent: e.g ...
... Summary of LSS • LSS contrasts: • Polarization: single vs. multiple scattering • Angle: small vs. large particles • Spectrum: size and refractive index • Advantages: • Strong signal - allows use of lower cost components components. • Sensitive to important chromophores that are not fluorescent: e.g ...
TAP 704- 7: Red shifts of quasars
... By what factor has the Universe expanded since light now reaching us left 3C273? ...
... By what factor has the Universe expanded since light now reaching us left 3C273? ...
Behavior Of Waves
... Waves refract when they change direction upon entering another medium. In order to refract the wave must: 1. Change speed when it hits the new medium 2. The wave must strike the new medium at an angle other than perpendicular ...
... Waves refract when they change direction upon entering another medium. In order to refract the wave must: 1. Change speed when it hits the new medium 2. The wave must strike the new medium at an angle other than perpendicular ...
Paper Chromatography of a Spinach Leaf Lab
... 8. Observe as the alcohol gets absorbed and travels up the paper by capillary action. This may take up to 20 minutes. Do not touch your experiment during this time. 9. When the alcohol has absorbed to approximately 1-cm below the pencil, you may remove the pencil/paper strip from the beaker to dry ...
... 8. Observe as the alcohol gets absorbed and travels up the paper by capillary action. This may take up to 20 minutes. Do not touch your experiment during this time. 9. When the alcohol has absorbed to approximately 1-cm below the pencil, you may remove the pencil/paper strip from the beaker to dry ...
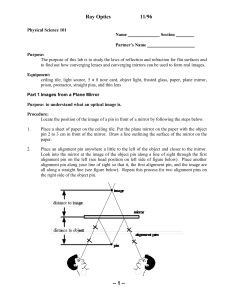
AP Physics Ch 24 : Physical Optics
... He placed a screen that had two slits cut into it in front of a monochromatic (single color) light. The results of Young's Double Slit Experiment should be very different if light is a wave or a particle. Let’s look at what the results would be in both situations, and then see how this experiment su ...
... He placed a screen that had two slits cut into it in front of a monochromatic (single color) light. The results of Young's Double Slit Experiment should be very different if light is a wave or a particle. Let’s look at what the results would be in both situations, and then see how this experiment su ...
Topic 5 Core Questions
... wave as it passes between different materials. It is caused by the slowing down or speeding up of the wave as it travels from one density to a different density. Away from the normal line. They will be parallel to each other. You might also notice the incident ray is slightly brighter than the emerg ...
... wave as it passes between different materials. It is caused by the slowing down or speeding up of the wave as it travels from one density to a different density. Away from the normal line. They will be parallel to each other. You might also notice the incident ray is slightly brighter than the emerg ...
Chapter 23: Electromagnetic waves What will we learn in this chapter?
... Total internal reflection contd. For a glass-air surface θcrit = arcsin(1/1.52) = 41.1◦. The fact that this angle is smaller than 45º makes it possible to use triangular prisms as a totally reflecting surface. This has advantages over metallic mirrors since the latter oxidize and do not reflect ...
... Total internal reflection contd. For a glass-air surface θcrit = arcsin(1/1.52) = 41.1◦. The fact that this angle is smaller than 45º makes it possible to use triangular prisms as a totally reflecting surface. This has advantages over metallic mirrors since the latter oxidize and do not reflect ...
lightandeye - Leon County Schools
... reflects light rays traveling in the same direction at the same angle. • Because the light rays travel the same way relative to each other before and after reflection, the reflected light rays form a sharp image. • Diffuse reflection occurs when light rays traveling in the same direction hit a rough ...
... reflects light rays traveling in the same direction at the same angle. • Because the light rays travel the same way relative to each other before and after reflection, the reflected light rays form a sharp image. • Diffuse reflection occurs when light rays traveling in the same direction hit a rough ...
Chapter 22 - The Nature of Light
... or _______________ and consists of changing ________________ and _____________________ fields. •A field is a __________ around an object that can exert a _________ on another object without actually ______________ the object. •Electromagnetic waves are __________________ waves with the electric and ...
... or _______________ and consists of changing ________________ and _____________________ fields. •A field is a __________ around an object that can exert a _________ on another object without actually ______________ the object. •Electromagnetic waves are __________________ waves with the electric and ...
Light Rays FACILITATOR NOTES
... Prepare the SAM robot, calculator and CBL2 or LabPRO interface and load the three calculator programs. For Part 1 on Reflection Identify clear boundaries (such as the ends of a white or black board or the front corners of the classroom) which can mark the edges of the simulated roll of steel. If nec ...
... Prepare the SAM robot, calculator and CBL2 or LabPRO interface and load the three calculator programs. For Part 1 on Reflection Identify clear boundaries (such as the ends of a white or black board or the front corners of the classroom) which can mark the edges of the simulated roll of steel. If nec ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.