Soft X-ray spectroscopy of single sized CdS nanocrystals: size
... diffraction. To extend the size range into a truly molecular regime, we also studied a pure Cadmium thiolate whose single crystal structure consists of Cd8(SR)16 units [8]. So far, only optical absorption measurements of these samples have been possible in solution and on thin films after dissolutio ...
... diffraction. To extend the size range into a truly molecular regime, we also studied a pure Cadmium thiolate whose single crystal structure consists of Cd8(SR)16 units [8]. So far, only optical absorption measurements of these samples have been possible in solution and on thin films after dissolutio ...
M. Sc. in Industrial Chemistry Centre for Applied Chemistry Syllabus
... Industries Accreditation of QC laboratories: Tools and Mechanisms ICH Guidelines on Drug substances and Products. Quantum Chemistry, Symmetry and Group Theory ...
... Industries Accreditation of QC laboratories: Tools and Mechanisms ICH Guidelines on Drug substances and Products. Quantum Chemistry, Symmetry and Group Theory ...
Absorption of low-loss optical materials measured at 1064 nm by a
... nm and continues to decrease. Detection of such a low absorption level is difficult because the thickness of the silica substrates shaped to become optical components is usually not larger than a few centimeters, so the total absorption integrated over the sample thickness never exceeds a few ppm. T ...
... nm and continues to decrease. Detection of such a low absorption level is difficult because the thickness of the silica substrates shaped to become optical components is usually not larger than a few centimeters, so the total absorption integrated over the sample thickness never exceeds a few ppm. T ...
Imaging and Non-imaging System Modeling in ASAP
... weight, and cost requirements. The principal performance requirements of the LCD projector are total screen lumens, screen illumination uniformity, color balance, color uniformity, and image quality, which are usually expressed as resolution (modulation transfer function (MTF) and image size (magnif ...
... weight, and cost requirements. The principal performance requirements of the LCD projector are total screen lumens, screen illumination uniformity, color balance, color uniformity, and image quality, which are usually expressed as resolution (modulation transfer function (MTF) and image size (magnif ...
Clays form a class of technologically important - Eu
... quantification, according to the ZAF procedure and to the “standardless” approach (namely, using computed pure element intensity factors). Analytical accuracy was checked using secondary standards, i.e. samples with known composition; an agreement better than 10 % was achieved. The analytical precis ...
... quantification, according to the ZAF procedure and to the “standardless” approach (namely, using computed pure element intensity factors). Analytical accuracy was checked using secondary standards, i.e. samples with known composition; an agreement better than 10 % was achieved. The analytical precis ...
Optical properties of the human tissue
... This method includes inverse adding-doubling (IAD) method developed by Prahl et al (Prahl S.A., et al. // Appl. Opt., 1993, Vol. 32(4), P. 559-568) and inverse Monte Carlo simulations. The IAD method is widely used in tissue optics for processing the experimental data of spectrophotometry with integ ...
... This method includes inverse adding-doubling (IAD) method developed by Prahl et al (Prahl S.A., et al. // Appl. Opt., 1993, Vol. 32(4), P. 559-568) and inverse Monte Carlo simulations. The IAD method is widely used in tissue optics for processing the experimental data of spectrophotometry with integ ...
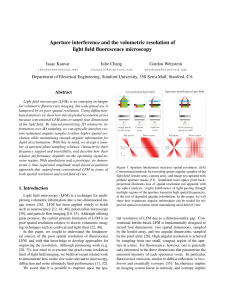
Interferometric near-infrared spectroscopy directly quantifies optical
... [Eqs. (2) and (3)] and parametric (e.g., temporal) averages within a sample. DSCL techniques have two main limitations. Firstly, the photon time-of-flight (TOF) is not measured. Accurate determination of particle dynamics from multiply scattered light is challenging if the TOF distribution is unknow ...
... [Eqs. (2) and (3)] and parametric (e.g., temporal) averages within a sample. DSCL techniques have two main limitations. Firstly, the photon time-of-flight (TOF) is not measured. Accurate determination of particle dynamics from multiply scattered light is challenging if the TOF distribution is unknow ...
Multi-photon absorption and third-order
... (MPA) processes has increased over the past decade, because of their importance for ultrafast all-optical signal processing. Near-infrared (near-IR) and short wave infrared (SWIR) nonlinear optical properties of silicon, namely, the third-order susceptibility χ(3), have been widely studied in the pa ...
... (MPA) processes has increased over the past decade, because of their importance for ultrafast all-optical signal processing. Near-infrared (near-IR) and short wave infrared (SWIR) nonlinear optical properties of silicon, namely, the third-order susceptibility χ(3), have been widely studied in the pa ...
``Interaction-free`` imaging - Vienna Center for Quantum Science and
... of 90%! because both beams undergo the same spatial inversion at their respective mirrors. However, as for system 2, it is not possible to image exactly at the waist. The Michelson systems were investigated chiefly because of the perceived advantages of their relative ease of alignment. However, reg ...
... of 90%! because both beams undergo the same spatial inversion at their respective mirrors. However, as for system 2, it is not possible to image exactly at the waist. The Michelson systems were investigated chiefly because of the perceived advantages of their relative ease of alignment. However, reg ...
PDF
... requires a high power pump laser which makes the light source expensive and bulky. In addition, the microstructure fiber requires a free space coupling to the interferometer, which limits the optical power at the sample and the stability of the system. Finally, in order to achieve broad bandwidth, h ...
... requires a high power pump laser which makes the light source expensive and bulky. In addition, the microstructure fiber requires a free space coupling to the interferometer, which limits the optical power at the sample and the stability of the system. Finally, in order to achieve broad bandwidth, h ...
1 Indentifying Unknown #M20 via Infrared Spectroscopy, Mass
... formula was discovered. When looking at the mass spectra (Figure 2) the molecular ion peak (A in Figure 2), which was determined to be an even numbered value because the unknown was determined to have no nitrogen atoms, appears at approximately 98 g/mol. To calculate the molecular formula, the molec ...
... formula was discovered. When looking at the mass spectra (Figure 2) the molecular ion peak (A in Figure 2), which was determined to be an even numbered value because the unknown was determined to have no nitrogen atoms, appears at approximately 98 g/mol. To calculate the molecular formula, the molec ...