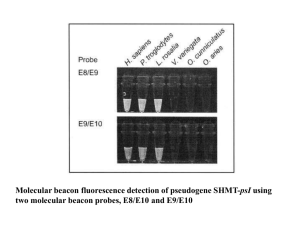
White-light diffraction tomography of unlabelled live cells
... rather than a scattering geometry. Note that this is a departure from the far-zone, angular scattering that is traditionally used in X-ray diffraction. When dealing with transparent objects, measuring the complex field at the image plane yields higher sensitivity than measuring in the far-zone38. Thi ...
... rather than a scattering geometry. Note that this is a departure from the far-zone, angular scattering that is traditionally used in X-ray diffraction. When dealing with transparent objects, measuring the complex field at the image plane yields higher sensitivity than measuring in the far-zone38. Thi ...
Laboratory Exercise 3: Microscopy The microscope is a tool for the
... immersion objective. This lens has high resolution and high N.A., since the lens gathers in a great amount of light. High resolving power is enhanced by clear mineral oil between the objective and the slide. The oil has a refractive (light-bending) index similar to glass; it reduces the amount of li ...
... immersion objective. This lens has high resolution and high N.A., since the lens gathers in a great amount of light. High resolving power is enhanced by clear mineral oil between the objective and the slide. The oil has a refractive (light-bending) index similar to glass; it reduces the amount of li ...
Microscope
... Numerical Aperture (N.A.): This is a number that expresses the ability of a lens to resolve fine detail in an object being observed. It is derived by a complex mathematical formula and is related to the angular aperture of the lens and the index of refraction of the medium found between the lens and ...
... Numerical Aperture (N.A.): This is a number that expresses the ability of a lens to resolve fine detail in an object being observed. It is derived by a complex mathematical formula and is related to the angular aperture of the lens and the index of refraction of the medium found between the lens and ...
Rejection of two-photon fluorescence background in
... simply W (z). If we assume that all the ballistic light travels approximately the same optical path-length through the tissue to attain depth z, then W (z) is subject to Beer’s law and decays exponentially with increasing z. This small-angle assumption is equivalent to the paraxial approximation, wh ...
... simply W (z). If we assume that all the ballistic light travels approximately the same optical path-length through the tissue to attain depth z, then W (z) is subject to Beer’s law and decays exponentially with increasing z. This small-angle assumption is equivalent to the paraxial approximation, wh ...
Correlative Imaging of Fluorescent Proteins in Resin
... Figure 1. En bloc imaging of FPs using confocal microscopy. A, Unprocessed, free-hand section of a tobacco petiole expressing pSEO2.HDEL:GFP (shown in green; Knoblauch and Peters, 2010). In this construct, GFP highlights the SER but at this magnification reveals general fluorescence from phloem bund ...
... Figure 1. En bloc imaging of FPs using confocal microscopy. A, Unprocessed, free-hand section of a tobacco petiole expressing pSEO2.HDEL:GFP (shown in green; Knoblauch and Peters, 2010). In this construct, GFP highlights the SER but at this magnification reveals general fluorescence from phloem bund ...
19_InstructorGuideMac
... not mean that they have an understanding of image formation. Thus it is important that, especially at first, examples and problems on the thin-lens equation are first preceded by graphical ray tracing. It is ray tracing that fosters understanding of how and where the image is formed; the thin-lens e ...
... not mean that they have an understanding of image formation. Thus it is important that, especially at first, examples and problems on the thin-lens equation are first preceded by graphical ray tracing. It is ray tracing that fosters understanding of how and where the image is formed; the thin-lens e ...
$doc.title
... nanoscale components is challenging Fluid medium Trapped • Optical tweezers can be used to trap particle and move micro and nanoscale components Laser • Examples of devices that can be assembled using optical tweezers The trapped include wave guides, diodes, transistors • Assembly Cell particle is ...
... nanoscale components is challenging Fluid medium Trapped • Optical tweezers can be used to trap particle and move micro and nanoscale components Laser • Examples of devices that can be assembled using optical tweezers The trapped include wave guides, diodes, transistors • Assembly Cell particle is ...
Aberration-free three-dimensional multiphoton imaging of neuronal
... this microscope can scan the focal spot along any three-dimensional trajectory at high speed. Both the objective lens L2 and the specimen remain stationary during imaging because the scanning process is carried out remotely using elements upstream of the objective. The LSU comprises a pair of orthog ...
... this microscope can scan the focal spot along any three-dimensional trajectory at high speed. Both the objective lens L2 and the specimen remain stationary during imaging because the scanning process is carried out remotely using elements upstream of the objective. The LSU comprises a pair of orthog ...
Practice Problems_sources
... 1. Show that optical intensity I and energy density u are related by the relation I=uv Where v is the group speed of light. (Hint: Consider a cube of volume Az where A is the area perpendicular to the light flow. The optical energy crossing the left facet of the cube over a time t would be present ...
... 1. Show that optical intensity I and energy density u are related by the relation I=uv Where v is the group speed of light. (Hint: Consider a cube of volume Az where A is the area perpendicular to the light flow. The optical energy crossing the left facet of the cube over a time t would be present ...
The Optical Design of Miniaturized Microscope Objective for CARS
... sample side (NA S) and optical resolution is proportional to the first power of numerical aperture (NAS). Therefore, in order to decide on an appropriate NAS, we refer to the research of H. Wang and co-workers [17]. They have used the conventional microscope objective with needle-like bill, namely t ...
... sample side (NA S) and optical resolution is proportional to the first power of numerical aperture (NAS). Therefore, in order to decide on an appropriate NAS, we refer to the research of H. Wang and co-workers [17]. They have used the conventional microscope objective with needle-like bill, namely t ...
Biology Intro Notes
... • Cells are broken into pieces in a special blender • Broken cell bits are added to a liquid and placed in a tube • The tube is placed into a centrifuge which spins the tube • Spinning separates the parts based on their mass and specific parts can be selected and studied ...
... • Cells are broken into pieces in a special blender • Broken cell bits are added to a liquid and placed in a tube • The tube is placed into a centrifuge which spins the tube • Spinning separates the parts based on their mass and specific parts can be selected and studied ...
Supplementary Figures 1-14.
... Light penetration in tissue Figure 1 illustrates the problem of light penetration. When light is applied to the skin topically, its penetration is limited to the epidermis and upper dermis layers (Salomatina et al., 2006). At a typical optical dose (180 J/cm2), bleaching of the dye was observed only ...
... Light penetration in tissue Figure 1 illustrates the problem of light penetration. When light is applied to the skin topically, its penetration is limited to the epidermis and upper dermis layers (Salomatina et al., 2006). At a typical optical dose (180 J/cm2), bleaching of the dye was observed only ...
PHYS4014 - Lasers and Nonlinear Optics
... Laser principles: Light sources and coherence, spontaneous and stimulated emission of radiation and the Einstein A and B coefficients and the relationship between them, absorption and gain coefficients in lasing media, population inversions, optical pumping and the principles of optical cavities. Di ...
... Laser principles: Light sources and coherence, spontaneous and stimulated emission of radiation and the Einstein A and B coefficients and the relationship between them, absorption and gain coefficients in lasing media, population inversions, optical pumping and the principles of optical cavities. Di ...
DIC and Polarized light microscopy
... 1. Contrast is directional 2. Contrast highlights edges 3. One end brighter, other is dimmer giving a pseudo – 3D image ...
... 1. Contrast is directional 2. Contrast highlights edges 3. One end brighter, other is dimmer giving a pseudo – 3D image ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... five beams of light (such as those from a ray box) hit a concave lens. ...
... five beams of light (such as those from a ray box) hit a concave lens. ...
Document
... Close packing of colloidal nanospheres to form a photonic crystal of close-packed colloidal array. (Left) Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) image of the surface layer. (Right) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) image of a cross-section (Markowicz and Prasad; unpublished). ...
... Close packing of colloidal nanospheres to form a photonic crystal of close-packed colloidal array. (Left) Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) image of the surface layer. (Right) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) image of a cross-section (Markowicz and Prasad; unpublished). ...
Image processing in Spectral Domain Optical Coherence
... A depth profile is formed by the detection of the interference pattern between the reference and sample arm as the reference arm is scanned. ...
... A depth profile is formed by the detection of the interference pattern between the reference and sample arm as the reference arm is scanned. ...
Syllabus
... Introduction to optical waveguides and fibers, propagation characteristics of fibers, characterization methods, LEDs, laser diodes, optical receivers, optical amplifiers, all-optical switching and fiber optic communication systems. The objective is to give students a comprehensive understanding of t ...
... Introduction to optical waveguides and fibers, propagation characteristics of fibers, characterization methods, LEDs, laser diodes, optical receivers, optical amplifiers, all-optical switching and fiber optic communication systems. The objective is to give students a comprehensive understanding of t ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. What are principal points and principal planes? 2. Two lenses of focal lengths 8 cm and 6 cm are placed at a certain distance apart. Calculate the distance between the lenses if they form an achromatic combination. 3. Explain the formation of colours in thin film. 4. Light of wavelength 6000 Å fa ...
... 1. What are principal points and principal planes? 2. Two lenses of focal lengths 8 cm and 6 cm are placed at a certain distance apart. Calculate the distance between the lenses if they form an achromatic combination. 3. Explain the formation of colours in thin film. 4. Light of wavelength 6000 Å fa ...
Wollaston and Nomarski Prisms
... prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of the optical axis must be fabricated to produce a single Wollaston (or Nomarski) prism. The wedg ...
... prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of the optical axis must be fabricated to produce a single Wollaston (or Nomarski) prism. The wedg ...
Microscopy and Microbes
... is principally controlled using the coarse and fine focus knobs. However, intensity of light, controlled by the substage diaphragm (located below the stage), also has a dramatic effect upon the resolution of the image. Parfocal lenses. The objective lenses on our microscopes are parfocal. This means ...
... is principally controlled using the coarse and fine focus knobs. However, intensity of light, controlled by the substage diaphragm (located below the stage), also has a dramatic effect upon the resolution of the image. Parfocal lenses. The objective lenses on our microscopes are parfocal. This means ...
Preview of “ZEISS Microscopy Online ...Aperture and Resolution”
... 700 nanometers. As a reference, it is important to know that 1 millimeter equals 1000 micrometers and 1 micrometer equals 1000 nanometers. Light of green color has a wavelength range centered at 550 nanometers, which corresponds to 0.55 micrometers. If small ob ...
... 700 nanometers. As a reference, it is important to know that 1 millimeter equals 1000 micrometers and 1 micrometer equals 1000 nanometers. Light of green color has a wavelength range centered at 550 nanometers, which corresponds to 0.55 micrometers. If small ob ...
Lecture 1 Introduction, History and Microscopy
... resolution of about 0.2 nm • Two major types of electron microscopes – Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for observing internal cell structure down to the molecular level – Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for 3-D imaging and examining surfaces ...
... resolution of about 0.2 nm • Two major types of electron microscopes – Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for observing internal cell structure down to the molecular level – Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for 3-D imaging and examining surfaces ...
Parts of a Microscope
... Specifically, what is the purpose of a with your naked eye (microscopic); to make microscope? things larger; to see more detail ...
... Specifically, what is the purpose of a with your naked eye (microscopic); to make microscope? things larger; to see more detail ...
Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of adding a spatial pinhole placed at the confocal plane of the lens to eliminate out-of-focus light. It enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures from the obtained images. This technique has gained popularity in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science.