1 L4: Interference L4 INTERFERENCE Objectives Aims When you
... the combined effect of several waves at any place at a particular instant of time is given by the sum (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contribution from one wave is just that which would occur if the other waves were not there. In the c ...
... the combined effect of several waves at any place at a particular instant of time is given by the sum (vector sum if the wave property is a vector) of the wave property for the individual waves. The contribution from one wave is just that which would occur if the other waves were not there. In the c ...
A Tunable Fabry-Perot-Interferometer for 3
... Careful consideration was given in choosing the materials used as the low and high index optical layers in the FPI as well as their deposition processes to insure compatibility with those required for patterning the electrodes and the wafers. Optical layers, without further treatment, would not surv ...
... Careful consideration was given in choosing the materials used as the low and high index optical layers in the FPI as well as their deposition processes to insure compatibility with those required for patterning the electrodes and the wafers. Optical layers, without further treatment, would not surv ...
Activity: Emission spectroscopy and smart sensors
... Direct the output of the laser to the open end of the optical fiber. It is useful to have the fiber and light source well secured so that experiments testing smart sensor designs can be easily carried out. ...
... Direct the output of the laser to the open end of the optical fiber. It is useful to have the fiber and light source well secured so that experiments testing smart sensor designs can be easily carried out. ...
13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]
... Converging Lenses • The Optical Center (O) is point at the exact centre of the lens. • The Principal Focus (F) is the point at the principal axis of a lens where light rays parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction. • The Secondary Principal Focus (F’) is on the same side of the lens ...
... Converging Lenses • The Optical Center (O) is point at the exact centre of the lens. • The Principal Focus (F) is the point at the principal axis of a lens where light rays parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction. • The Secondary Principal Focus (F’) is on the same side of the lens ...
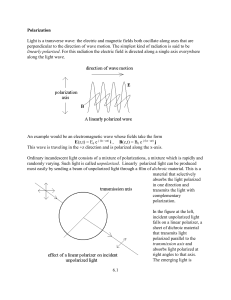
6.1 Polarization Light is a transverse wave: the electric and magnetic
... = /2, the light polarized along one axis will have traveled through an optical path length one quarter of a wavelength longer than light polarized along the perpendicular axis. The emerging light in that case is circularly polarized. A piece of material with this property is called a quarter-wave pl ...
... = /2, the light polarized along one axis will have traveled through an optical path length one quarter of a wavelength longer than light polarized along the perpendicular axis. The emerging light in that case is circularly polarized. A piece of material with this property is called a quarter-wave pl ...
How to turn your microscope into a phase contrast microscope
... Note that, in the absence of any object with shifted phases, the image will always be dark. If there is an object, we will see light, but that does not reveal whether the phase shift is positive or negative. To make the sign visible as well, one needs more professional devices, for instance, a trans ...
... Note that, in the absence of any object with shifted phases, the image will always be dark. If there is an object, we will see light, but that does not reveal whether the phase shift is positive or negative. To make the sign visible as well, one needs more professional devices, for instance, a trans ...
Fabrication and Application of Phase only Holograms for High
... process. Firstly, the hologram design software implicitly presumes that the pixels have a square shape since the optimization algorithm is based on a discrete 2D Fourier transform. As a result square shaped pixels must be also ablated in the ITO coating to match the simulated mask. In the previous w ...
... process. Firstly, the hologram design software implicitly presumes that the pixels have a square shape since the optimization algorithm is based on a discrete 2D Fourier transform. As a result square shaped pixels must be also ablated in the ITO coating to match the simulated mask. In the previous w ...
Lecture - Galileo
... Geometrical Optics:Study of reflection and refraction of light from surfaces ...
... Geometrical Optics:Study of reflection and refraction of light from surfaces ...
Alternative Beam Splitter/Compensator Configurations for Reduction
... (1.8%) ~ 0.04%. This represents a factor of 100 reduction. While any reduction in reflection would be beneficial, an AR coating that would solve the multiple reflection problem (by reducing reflections by a factor of 100 at large angles of incidence) will be difficult to ...
... (1.8%) ~ 0.04%. This represents a factor of 100 reduction. While any reduction in reflection would be beneficial, an AR coating that would solve the multiple reflection problem (by reducing reflections by a factor of 100 at large angles of incidence) will be difficult to ...
Advantages of FTIR spectroscopy
... 400 and about 5 cm-1 wavenumbers. This range covers the vibrational frequencies of both backbone vibrations of large molecules, as well as fundamental vibrations of molecules that include heavy atoms (e.g. inorganic or organometallic compounds). ...
... 400 and about 5 cm-1 wavenumbers. This range covers the vibrational frequencies of both backbone vibrations of large molecules, as well as fundamental vibrations of molecules that include heavy atoms (e.g. inorganic or organometallic compounds). ...
Fast Optical Communication Components
... Optical Fiber Numerical Aperture The Numerical Aperture of the fiber is the sine of the maximum angle of an incident beam that can be guided in the core ...
... Optical Fiber Numerical Aperture The Numerical Aperture of the fiber is the sine of the maximum angle of an incident beam that can be guided in the core ...
MEASUREMENTS OF WAVE VELOCITY
... • Sound waves can bounce back and forth between the transmitter and receiver clamps. If the separation between transmitter and receiver is a whole number of half wavelengths, the thereand-back distance for one reflection is twice this, which is an exact whole number of wavelengths, and a standing wa ...
... • Sound waves can bounce back and forth between the transmitter and receiver clamps. If the separation between transmitter and receiver is a whole number of half wavelengths, the thereand-back distance for one reflection is twice this, which is an exact whole number of wavelengths, and a standing wa ...
Title of PAPER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... used with a higher melting point to increase the durability of the mirror. Conclusion To summarise, if conductivity and scattering is ignored, lasers with a wavelength of 500 nm and lower will melt a mirror with silver as its optical coating. Different materials will have different melting points an ...
... used with a higher melting point to increase the durability of the mirror. Conclusion To summarise, if conductivity and scattering is ignored, lasers with a wavelength of 500 nm and lower will melt a mirror with silver as its optical coating. Different materials will have different melting points an ...
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: What`s the Use? Geology 1P Mr
... eye, but this energy exists at a wide range of wavelengths. The micron is the basic unit for measuring the wavelength of electromagnetic waves. The spectrum of waves is divided into sections based on wavelength. The shortest waves are gamma rays, which have wavelengths of 10e-6 microns or less. The ...
... eye, but this energy exists at a wide range of wavelengths. The micron is the basic unit for measuring the wavelength of electromagnetic waves. The spectrum of waves is divided into sections based on wavelength. The shortest waves are gamma rays, which have wavelengths of 10e-6 microns or less. The ...
Reflection
... • Spherical aberration can be avoided by using a parabolic reflector; which are only a little more difficult/expensive to make. • Typically used in Telescopes, Camera lenses Lab equipment, shaving/make-up Mirrors, and this solar fire-lighter for campers! • Mirrors are preferred to lenses in many ...
... • Spherical aberration can be avoided by using a parabolic reflector; which are only a little more difficult/expensive to make. • Typically used in Telescopes, Camera lenses Lab equipment, shaving/make-up Mirrors, and this solar fire-lighter for campers! • Mirrors are preferred to lenses in many ...
Beyond Snel`s law: Refraction of a nano-beam of light.
... optical phenomena. When light wave is transmitted from one optical medium into another at an oblique angle, its direction of propagation changes. If the light is a wide plane wave incident on a relatively large and flat interface of two different isotropic media, the change of wave direction is well ...
... optical phenomena. When light wave is transmitted from one optical medium into another at an oblique angle, its direction of propagation changes. If the light is a wide plane wave incident on a relatively large and flat interface of two different isotropic media, the change of wave direction is well ...
Coatings - CVI Laser Optics
... EXTERNAL REFLECTION AT A DIELECTRIC BOUNDARY Fresnel’s laws of reflection precisely describe amplitude and phase relationships between reflected and incident light at a boundary between two dielectric media. It is convenient to think of the incident radiation as the superposition of two plane-polari ...
... EXTERNAL REFLECTION AT A DIELECTRIC BOUNDARY Fresnel’s laws of reflection precisely describe amplitude and phase relationships between reflected and incident light at a boundary between two dielectric media. It is convenient to think of the incident radiation as the superposition of two plane-polari ...
Comparison of two-color methods based on wavelength and
... The refractive index of air can significantly affect length measurements because the refractive index of air is a function of several air parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and CO2 concentration. For example, when the temperature increases by 1◦ C, the optical length decreases by ap ...
... The refractive index of air can significantly affect length measurements because the refractive index of air is a function of several air parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and CO2 concentration. For example, when the temperature increases by 1◦ C, the optical length decreases by ap ...
of the Physical and Technical Faculty
... SSS topic. Interference in thin films. Michelson Echelon. Interference method for monitoring of surfaces ...
... SSS topic. Interference in thin films. Michelson Echelon. Interference method for monitoring of surfaces ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.


![13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008538239_1-d1798f6d27c8a2d8c0931d41a70fff89-300x300.png)