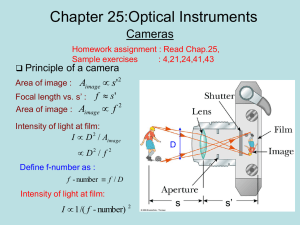
Lab 1
... Click and drag a graph to "Light Intensity." Click and drag the angular position to the x axis and release to create a graph with "Light Intensity" on the y-axis, and "angular position" on the x-axis. Now, you are ready to take data. The best data will be obtained if the light source, polarizers, an ...
... Click and drag a graph to "Light Intensity." Click and drag the angular position to the x axis and release to create a graph with "Light Intensity" on the y-axis, and "angular position" on the x-axis. Now, you are ready to take data. The best data will be obtained if the light source, polarizers, an ...
THE PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
... the opaque slide into the filter holder and use the Zero Adjust to zero the electrometer. The long time constant may make this adjustment a bit tedious, but the adjustment is not too critical since any misadjustment produces only a small added offset voltage. Once the electrometer is warmed up it sh ...
... the opaque slide into the filter holder and use the Zero Adjust to zero the electrometer. The long time constant may make this adjustment a bit tedious, but the adjustment is not too critical since any misadjustment produces only a small added offset voltage. Once the electrometer is warmed up it sh ...
The Polarization of Light
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
Non-invasive ophthalmic imaging of adult zebrafish eye using
... mean retinal thickness and effective refractive index of the crystalline lens. Keywords: Eyes, non-invasive ophthalmic imaging, optical coherence tomography, zebrafish. USE of optical techniques for biomedical imaging is a topic of considerable current interest. This is motivated by the potential of ...
... mean retinal thickness and effective refractive index of the crystalline lens. Keywords: Eyes, non-invasive ophthalmic imaging, optical coherence tomography, zebrafish. USE of optical techniques for biomedical imaging is a topic of considerable current interest. This is motivated by the potential of ...
Background: Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of
... 4. Chemistry: Use optical and specific rotation to identify biopolymers, natural polymers, and synthetic polymer. 5. Important of optical isomers in biological system: a) In human body some compound isomer (enantiomer) is optically active and some is not active or has harm effect; for example, human ...
... 4. Chemistry: Use optical and specific rotation to identify biopolymers, natural polymers, and synthetic polymer. 5. Important of optical isomers in biological system: a) In human body some compound isomer (enantiomer) is optically active and some is not active or has harm effect; for example, human ...
Biology 3235: Resolution and magnification of a light microscopes
... 0.25 will resolve details as small as 1.2 µm when using green light (λ = 500 nm). With a100× objective (NA = 1.3), you could resolve details as small as 0.23 µm using green light. Note that shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue li ...
... 0.25 will resolve details as small as 1.2 µm when using green light (λ = 500 nm). With a100× objective (NA = 1.3), you could resolve details as small as 0.23 µm using green light. Note that shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue li ...
PDF
... in biological sensors 关1–5兴. Abbott et al. proposed a technique based on the anchoring the transition at the nematic surface 关1兴. The LC is aligned in the cell with substrates coated with gold films and surface-bound antigens 共ligands兲. If there is an antibody in the system that binds to the ligands ...
... in biological sensors 关1–5兴. Abbott et al. proposed a technique based on the anchoring the transition at the nematic surface 关1兴. The LC is aligned in the cell with substrates coated with gold films and surface-bound antigens 共ligands兲. If there is an antibody in the system that binds to the ligands ...
Template for Electronic Submission to ACS Journals
... Optical interference filters based in periodic multilayer systems are well known and highly developed passive optical devices.1 Such structures, also known as distributed Bragg reflectors, acquire their optical properties through the periodic modulation of the refractive index, so they are also clas ...
... Optical interference filters based in periodic multilayer systems are well known and highly developed passive optical devices.1 Such structures, also known as distributed Bragg reflectors, acquire their optical properties through the periodic modulation of the refractive index, so they are also clas ...
EEE440 Modern Communication Systems Optical Fibre
... Since the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection the reflected light will again be reflected The light ray will then continue this bouncing path down the length of the fiber optic cable. If the light ray strikes the core-to-cladding interface at an angle less than the critical ...
... Since the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection the reflected light will again be reflected The light ray will then continue this bouncing path down the length of the fiber optic cable. If the light ray strikes the core-to-cladding interface at an angle less than the critical ...
PowerPoint - ECSE - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... Chromatic dispersion is a significant issue for 1 Gbps, 100 km fiber lengths In-fiber chirped bragg gratings are used to compensate for chromatic dispersion by adding extra phase for selected wavelength bands Linear polarization refers to the fact that the polarization vector does not ch ...
... Chromatic dispersion is a significant issue for 1 Gbps, 100 km fiber lengths In-fiber chirped bragg gratings are used to compensate for chromatic dispersion by adding extra phase for selected wavelength bands Linear polarization refers to the fact that the polarization vector does not ch ...
science
... If a light wave or infra-red wave is to be transmitted through the air, it is possible that things can get between the transmitter and receiver and reduce the size of the signal or block it altogether. Such problems could be caused by birds, fog, rain or sandstorms (this is known as noise). The beam ...
... If a light wave or infra-red wave is to be transmitted through the air, it is possible that things can get between the transmitter and receiver and reduce the size of the signal or block it altogether. Such problems could be caused by birds, fog, rain or sandstorms (this is known as noise). The beam ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... This course explores the production and nature of light including: the laws of reflection and refraction, theory of image formation, principles of wave optics (including interference, diffraction and polarization), fundamentals of fiber optic theory, principles of lasers and laser safety, and the ba ...
... This course explores the production and nature of light including: the laws of reflection and refraction, theory of image formation, principles of wave optics (including interference, diffraction and polarization), fundamentals of fiber optic theory, principles of lasers and laser safety, and the ba ...
Light -1 - Physics
... pass through, while absorbing the field component perpendicular to this direction. The direction of polarization that a polarizing material allows through is called the transmission axis. It does not matter how the transmission axis is oriented, the average intensity of the transmitted polarized lig ...
... pass through, while absorbing the field component perpendicular to this direction. The direction of polarization that a polarizing material allows through is called the transmission axis. It does not matter how the transmission axis is oriented, the average intensity of the transmitted polarized lig ...
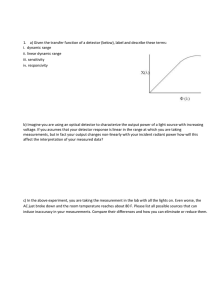
a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and
... technique. In this technique, you project light onto the sample and capture the reflected light from the wound using a photodetector. You purchase a 25mW short wave infrared LED with FWHM of 27nm centered at 1450 nm. This peak wavelength is close to a peak in water absorption spectra. Your next step ...
... technique. In this technique, you project light onto the sample and capture the reflected light from the wound using a photodetector. You purchase a 25mW short wave infrared LED with FWHM of 27nm centered at 1450 nm. This peak wavelength is close to a peak in water absorption spectra. Your next step ...
Direct index of refraction measurement at extreme
... is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which these optical elements are fabricated have finite absorption, there is an additional gain of efficiency du ...
... is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which these optical elements are fabricated have finite absorption, there is an additional gain of efficiency du ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Exercise 6: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
... Exercise 6: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
full Lab Facts summary
... input beam with a lateral offset. • The optic is generally either a solid prism or hollow with coated mirror surfaces. • The common corner cube design is pyramid shaped with light entering the base. • The three faces that make the corner are orthogonal (90 degrees to each other). • There are always ...
... input beam with a lateral offset. • The optic is generally either a solid prism or hollow with coated mirror surfaces. • The common corner cube design is pyramid shaped with light entering the base. • The three faces that make the corner are orthogonal (90 degrees to each other). • There are always ...
Practical Laboratory #2: Emission Spectra 2
... many different frequencies, i.e. different pitches. For example, if we listen to music, we can pick out the drums and voice separately, even though they are happening at the same time. We don’t have that capability with light. Instead, we end up seeing one individual color, which most likely is made ...
... many different frequencies, i.e. different pitches. For example, if we listen to music, we can pick out the drums and voice separately, even though they are happening at the same time. We don’t have that capability with light. Instead, we end up seeing one individual color, which most likely is made ...
Tutor 6
... such as the influence of an ARC on bulk absorption (the first term in parentheses on the right hand side of equation (11)). In the next edition of the Lithography Tutor, the discussion of standing waves will be expanded to include the thin film interference effects which lead to swing ...
... such as the influence of an ARC on bulk absorption (the first term in parentheses on the right hand side of equation (11)). In the next edition of the Lithography Tutor, the discussion of standing waves will be expanded to include the thin film interference effects which lead to swing ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.