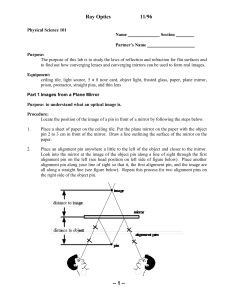
FA15Lec16 Optical Trap
... bead (blue) that is decorated with motor proteins in a focused laser beam (yellow). The optical trap exerts a force on the bead that can be approximated by Hooke’s Law (F = kcx), where kc is the spring constant of the laser trap and x is the displacement of the bead. The red curve illustrates “walki ...
... bead (blue) that is decorated with motor proteins in a focused laser beam (yellow). The optical trap exerts a force on the bead that can be approximated by Hooke’s Law (F = kcx), where kc is the spring constant of the laser trap and x is the displacement of the bead. The red curve illustrates “walki ...
PT symmetry in optics
... changes when gain and loss are involved in the coupled system (Fig. 1). If gain is below threshold, the relative phase difference between the two fields increases with increasing gain from their initial values at 0 and π, and finally, at threshold they coalesce at θ = π/2. Remarkably, light propagat ...
... changes when gain and loss are involved in the coupled system (Fig. 1). If gain is below threshold, the relative phase difference between the two fields increases with increasing gain from their initial values at 0 and π, and finally, at threshold they coalesce at θ = π/2. Remarkably, light propagat ...
Full Text PDF
... of their thermo-optical characteristics. In comparison with other liquids they have a smaller value of dp/dt and consequently a smaller value of dn/dt as shown from Eq. (16). It is known that the water has a maximum density at about 4°C which leads to dp/dt = 0. Therefore, if the temperature of the ...
... of their thermo-optical characteristics. In comparison with other liquids they have a smaller value of dp/dt and consequently a smaller value of dn/dt as shown from Eq. (16). It is known that the water has a maximum density at about 4°C which leads to dp/dt = 0. Therefore, if the temperature of the ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... the wavelength of light such that there was a sharp cut-off and no current flow for long wavelengths. Einstein successful explained the photoelectric effect within the context of the new physics of the time, quantum physics. In his scientific paper, he showed that light was made of packets of energy ...
... the wavelength of light such that there was a sharp cut-off and no current flow for long wavelengths. Einstein successful explained the photoelectric effect within the context of the new physics of the time, quantum physics. In his scientific paper, he showed that light was made of packets of energy ...
2. Measurement of refractive index of liquids using fiber optic
... The paper describes a technique to determine the refractive index of liquids using reflective type fiber optic displacement sensor. The sensor consists of two multimode step index fibers and a mirror. The output light intensity from the receiving fiber is measured as a function of displacement of th ...
... The paper describes a technique to determine the refractive index of liquids using reflective type fiber optic displacement sensor. The sensor consists of two multimode step index fibers and a mirror. The output light intensity from the receiving fiber is measured as a function of displacement of th ...
Introduction to Optical Engineering and Design ENSC 376
... optics, and less on the physics behind the behaviour. It starts with a basic explanation of the concepts of light, as electromagnetic radiation. Then it looks how light is generated, at both the atomic and black body level. Next optical interaction with materials is discussed beginning with reflecti ...
... optics, and less on the physics behind the behaviour. It starts with a basic explanation of the concepts of light, as electromagnetic radiation. Then it looks how light is generated, at both the atomic and black body level. Next optical interaction with materials is discussed beginning with reflecti ...
Review of paper entitled “Athermalization of optical instruments from
... materials that can absorb large amounts of heat with small resulting temperature rise, and conduct this heat away rapidly. Glasses: Most glasses have values in the range of 5 to 25x10-6 which will result in a large wavefront error for a relative small dT. For example, a 10mm thick BK7 element with ...
... materials that can absorb large amounts of heat with small resulting temperature rise, and conduct this heat away rapidly. Glasses: Most glasses have values in the range of 5 to 25x10-6 which will result in a large wavefront error for a relative small dT. For example, a 10mm thick BK7 element with ...
H. F. Ghaemi - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... We identify the transmission minima as the result of Wood’s anomaly,11 which was observed in diffraction gratings and occurs when a diffracted order becomes tangent to the plane of the grating. When the order disappears, the light intensity is redistributed among the remaining orders; it has been su ...
... We identify the transmission minima as the result of Wood’s anomaly,11 which was observed in diffraction gratings and occurs when a diffracted order becomes tangent to the plane of the grating. When the order disappears, the light intensity is redistributed among the remaining orders; it has been su ...
\ A/58
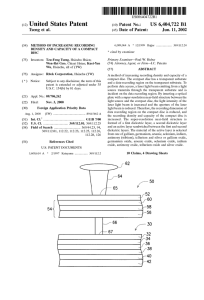
... are used to control the thermal conductivity of the recording layer 16. The upper and loWer dielectric layers 18 and 14 thus include materials such as silicon nitride, silicon oxide, Zinc sul?de-silicon dioxide, titanium oxide or carbide. The compact disc is shone With a laser light beam 26 from a l ...
... are used to control the thermal conductivity of the recording layer 16. The upper and loWer dielectric layers 18 and 14 thus include materials such as silicon nitride, silicon oxide, Zinc sul?de-silicon dioxide, titanium oxide or carbide. The compact disc is shone With a laser light beam 26 from a l ...
secon harmonic generation
... experiments. Two input fields, each possessing a frequency , are combined together to generate an output frequency at a frequency of 2. The two input electric fields are from the same wave. Energy conservation rule dictates, 1+2=+2. The conservation of momentum (or wavevectors) should also b ...
... experiments. Two input fields, each possessing a frequency , are combined together to generate an output frequency at a frequency of 2. The two input electric fields are from the same wave. Energy conservation rule dictates, 1+2=+2. The conservation of momentum (or wavevectors) should also b ...
Supplementary Material for
... divergence angle, θ, of the output wave. In our measurement, a single mode fiber with mode field diameter of 8 µm and numerical aperture of 0.13 is used and b = 2 mm. Since the divergence angle at the output of the sample is less than 0.2°, the resolution achievable in samples of one or two slides i ...
... divergence angle, θ, of the output wave. In our measurement, a single mode fiber with mode field diameter of 8 µm and numerical aperture of 0.13 is used and b = 2 mm. Since the divergence angle at the output of the sample is less than 0.2°, the resolution achievable in samples of one or two slides i ...
Optoniks
... challenge for a broad range of industry for decades that is remained unresolved. In many industries, despite the higher cost, the films are thickened to make sure that the films have the required thickness, which other than cost may result in compromising the performance, increasing the waste of mat ...
... challenge for a broad range of industry for decades that is remained unresolved. In many industries, despite the higher cost, the films are thickened to make sure that the films have the required thickness, which other than cost may result in compromising the performance, increasing the waste of mat ...
CP1: Investigation into the Feasibility of a Three Axis
... combining of electromagnetic waves in order to obtain information from those waves. It uses the principle of superposition: that the amplitudes of electromagnetic waves add vectorially when interfered. The relative phase of the combined waves dictates whether this superposition leads to constructive ...
... combining of electromagnetic waves in order to obtain information from those waves. It uses the principle of superposition: that the amplitudes of electromagnetic waves add vectorially when interfered. The relative phase of the combined waves dictates whether this superposition leads to constructive ...
Arbitrary GRIN component fabrication in optically
... quantified by relating the measured optical path difference at each location to the thickness of the sample under test. ...
... quantified by relating the measured optical path difference at each location to the thickness of the sample under test. ...
1 Introduction to Optics and Photophysics - Wiley-VCH
... vacuum, the speed of light does not depend on its color, the vacuum wavelength λ is short for blue light (∼ 450 nm) and gets longer for green (∼ 520 nm), yellow (∼ 580 nm), red (∼ 630 nm), and infrared (∼ 800 nm), respectively. In addition, note that the same wave theory of light governs all wavelen ...
... vacuum, the speed of light does not depend on its color, the vacuum wavelength λ is short for blue light (∼ 450 nm) and gets longer for green (∼ 520 nm), yellow (∼ 580 nm), red (∼ 630 nm), and infrared (∼ 800 nm), respectively. In addition, note that the same wave theory of light governs all wavelen ...
IQSE Banner News Page
... Spotlight summary: What is bb? As light propagates through the ocean, it experiences an exponential attenuation due to absorption and scattering. The backscattering coefficient bb is that component of the total scattering coefficient at angles greater than 90°. This is important because light that i ...
... Spotlight summary: What is bb? As light propagates through the ocean, it experiences an exponential attenuation due to absorption and scattering. The backscattering coefficient bb is that component of the total scattering coefficient at angles greater than 90°. This is important because light that i ...
Visualization of optical deflection and switching operations by a
... where r33 is the largest electro-optic coefficient accessed by extraordinary s-polarized light, ne is the wavelength dependent value of extraordinary refractive index, and d is the thickness of the device. The induced refractive-index change related to p-polarized light can be derived from Eq. (2) b ...
... where r33 is the largest electro-optic coefficient accessed by extraordinary s-polarized light, ne is the wavelength dependent value of extraordinary refractive index, and d is the thickness of the device. The induced refractive-index change related to p-polarized light can be derived from Eq. (2) b ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.