lab 7 Wave Optics
... Your group is involved in a project investigating some properties of viruses. You need to categorize viruses by size, but have found that they are too small to view with any microscope that uses visible light. You know, however, that for a small object illuminated by coherent light, a diffraction pa ...
... Your group is involved in a project investigating some properties of viruses. You need to categorize viruses by size, but have found that they are too small to view with any microscope that uses visible light. You know, however, that for a small object illuminated by coherent light, a diffraction pa ...
1 Fundamental Optics www.cvimellesgriot.com
... A simple graphical method can also be used to determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray ...
... A simple graphical method can also be used to determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray ...
A-141
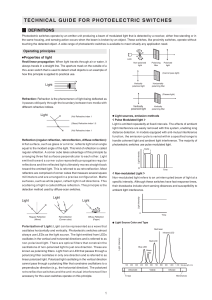
... Non-modulated light refers to an uninterrupted beam of light at a specific intensity. Although these switches have fast response times, their drawbacks include short sensing distances and susceptibility to ambient light interference. Light intensity ...
... Non-modulated light refers to an uninterrupted beam of light at a specific intensity. Although these switches have fast response times, their drawbacks include short sensing distances and susceptibility to ambient light interference. Light intensity ...
Plasmonic Metamaterials
... in electromagnetics that determines how light refracts at the interface between two media. As illustrated in Figure 3A, if light is incident from a positive-index material to a negative-index one, the refracted light lies on the same side as the incident light with respect to the surface normal. Thi ...
... in electromagnetics that determines how light refracts at the interface between two media. As illustrated in Figure 3A, if light is incident from a positive-index material to a negative-index one, the refracted light lies on the same side as the incident light with respect to the surface normal. Thi ...
EVPP 550 Waterscape Ecology and Management
... – Approximated by the Beer-Bouguer Law • In a homogeneous medium a constant proportion of photons and their energy is absorbed (disappears) with each linear unit of medium ...
... – Approximated by the Beer-Bouguer Law • In a homogeneous medium a constant proportion of photons and their energy is absorbed (disappears) with each linear unit of medium ...
Pulsar scintillations from corrugated reconnection sheets in the ISM
... the ambient warm ISM (REFERENCE?); no conventional physical mechanism has been proposed for how such regions may be formed. Radio-wave scattering by non-turbulent large-scale refractive structures has been previously considered by Ro- ...
... the ambient warm ISM (REFERENCE?); no conventional physical mechanism has been proposed for how such regions may be formed. Radio-wave scattering by non-turbulent large-scale refractive structures has been previously considered by Ro- ...
full text pdf
... containing a number of other different discrete wavelengths that are assumed to be already propagating in a fibre. The operation of fibre filters typically involves energy transfer over a coupling length between two distinct fibre cores cou− pled by proximity interaction [11]. To this day, many type ...
... containing a number of other different discrete wavelengths that are assumed to be already propagating in a fibre. The operation of fibre filters typically involves energy transfer over a coupling length between two distinct fibre cores cou− pled by proximity interaction [11]. To this day, many type ...
Hydrogen Balmer Series High Resolution Spectroscopy : the
... to wavelengths predicted by the same equation with the 22 replaced by 12, 32, 42, etc. Subsequent investigations in the far ultraviolet and infrared regions confirmed his predictions with remarkable accuracy. The simplicity of the hydrogen spectrum is due to the fact that it contains only one electr ...
... to wavelengths predicted by the same equation with the 22 replaced by 12, 32, 42, etc. Subsequent investigations in the far ultraviolet and infrared regions confirmed his predictions with remarkable accuracy. The simplicity of the hydrogen spectrum is due to the fact that it contains only one electr ...
High resolution spectral self-interference fluorescence microscopy
... The advantage of light microscopy over electron and scanned probe microscopy is the ability to image the interior of biological specimens. Light would be an ideal carrier of microscopic information if it weren’t for the resolution limit. But because of diffraction, standard light microscopes are not ...
... The advantage of light microscopy over electron and scanned probe microscopy is the ability to image the interior of biological specimens. Light would be an ideal carrier of microscopic information if it weren’t for the resolution limit. But because of diffraction, standard light microscopes are not ...
Resolution in Confocal Microscopy
... need to further our investigation into other aspects of microscopy before a decision to favour a particular microscope is used, even when comparing single and two-photon confocal microscopes. There may be some preferences in using light with a longer wavelength due to the biologicals being imaged, t ...
... need to further our investigation into other aspects of microscopy before a decision to favour a particular microscope is used, even when comparing single and two-photon confocal microscopes. There may be some preferences in using light with a longer wavelength due to the biologicals being imaged, t ...
Imaging optical singularities; Understanding the duality of C-points and optical vortices
... superposition of a circularly-polarized optical vortex field with an oppositely-polarized planar field.7, 8 Optical vortices are very sensitive to perturbations, to the point that optical vortices with topological charge greater than one are difficult to preserve and measure.2, 9 The latter is often ...
... superposition of a circularly-polarized optical vortex field with an oppositely-polarized planar field.7, 8 Optical vortices are very sensitive to perturbations, to the point that optical vortices with topological charge greater than one are difficult to preserve and measure.2, 9 The latter is often ...
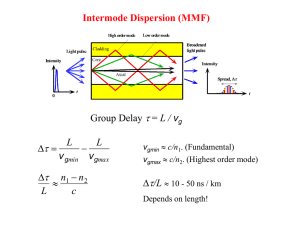
Waveguide Dispersion
... BL = 0.59L/t1/2 = 0.59/(16 ps km-1) = 36.9 Gb s-1 km. The optical and electrical bandwidths for a 10 km distance is fop = 0.75B = 0.75(36.9 Gb s-1 km) / (10 km) = 2.8 GHz. ...
... BL = 0.59L/t1/2 = 0.59/(16 ps km-1) = 36.9 Gb s-1 km. The optical and electrical bandwidths for a 10 km distance is fop = 0.75B = 0.75(36.9 Gb s-1 km) / (10 km) = 2.8 GHz. ...
Surface Water Waves
... impossible feats. These include cloaking devices and perfect optical lenses free from chromatic aberrations. Using metamaterials they would enable light of visible wavelengths to be deflected around an object and continue its path on the far side as though the object were not there. This phenomenon ...
... impossible feats. These include cloaking devices and perfect optical lenses free from chromatic aberrations. Using metamaterials they would enable light of visible wavelengths to be deflected around an object and continue its path on the far side as though the object were not there. This phenomenon ...
UNIT-4 OCN
... index data are likely to be less accurate for graded index fibers than for step index fibers unless the complete refractive index profile is considered. • However, if refractive index data is available on either fiber type from the measurements described the numerical aperture may be determined by c ...
... index data are likely to be less accurate for graded index fibers than for step index fibers unless the complete refractive index profile is considered. • However, if refractive index data is available on either fiber type from the measurements described the numerical aperture may be determined by c ...
Inexpensive optical tweezers for undergraduate laboratories
... The basic operation of optical tweezers can be explained by the momentum transfer associated with redirection of light at a dielectric interface. Since light carries momentum that is proportional to its energy and in the direction of propagation, the reflection and refraction of light at the interfa ...
... The basic operation of optical tweezers can be explained by the momentum transfer associated with redirection of light at a dielectric interface. Since light carries momentum that is proportional to its energy and in the direction of propagation, the reflection and refraction of light at the interfa ...
Document
... At the time the development started, people were expecting X-rays to be generated. However, it turns out that X-rays may not be generated within this century because of the electron beam quality and the X-ray mirror's reflectivity. Recently, the U.S.A.'s National Research Council submitted a report ...
... At the time the development started, people were expecting X-rays to be generated. However, it turns out that X-rays may not be generated within this century because of the electron beam quality and the X-ray mirror's reflectivity. Recently, the U.S.A.'s National Research Council submitted a report ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.