Optics-Optical Instruments_ppt_RevW10
... The Law of Reflection • The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the surface are all in the same plane. • The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
... The Law of Reflection • The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the surface are all in the same plane. • The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
X-Ray and Neutron Reflectivity - Physik der molekularen und
... Generally, the order of magnitude for δ and β is similar to the X-ray case. However, since the scattering length b of the nuclei varies non-monotonously across the periodic table, as opposed to the case of X-rays, the contrast between two given elements is different for Xrays and for neutrons. Thus, ...
... Generally, the order of magnitude for δ and β is similar to the X-ray case. However, since the scattering length b of the nuclei varies non-monotonously across the periodic table, as opposed to the case of X-rays, the contrast between two given elements is different for Xrays and for neutrons. Thus, ...
About UV-Vis Molecular Absorbance Spectroscopy
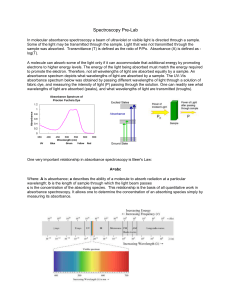
... Spectroscopy Pre-Lab In molecular absorbance spectroscopy a beam of ultraviolet or visible light is directed through a sample. Some of the light may be transmitted through the sample. Light that was not transmitted through the sample was absorbed. Transmittance (T) is defined as the ratio of P/Po. A ...
... Spectroscopy Pre-Lab In molecular absorbance spectroscopy a beam of ultraviolet or visible light is directed through a sample. Some of the light may be transmitted through the sample. Light that was not transmitted through the sample was absorbed. Transmittance (T) is defined as the ratio of P/Po. A ...
Measurement of the Wavelength by Diffraction Gratings
... weak, in this method the wavelength cannot be measured accurately. By increasing the number of slits to a very large number narrow fringes (lines) of higher intensities can be produced (Fig11). Moreover the fringes are formed far apart from one another. For this purpose Fraunhofer made the first gra ...
... weak, in this method the wavelength cannot be measured accurately. By increasing the number of slits to a very large number narrow fringes (lines) of higher intensities can be produced (Fig11). Moreover the fringes are formed far apart from one another. For this purpose Fraunhofer made the first gra ...
Essential Questions and Answers: What is light? Light is a form of
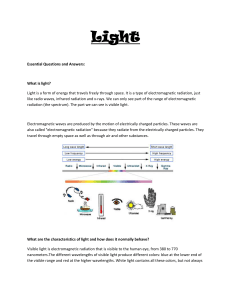
... Electromagnetic waves are produced by the motion of electrically charged particles. These waves are also called "electromagnetic radiation" because they radiate from the electrically charged particles. They travel through empty space as well as through air and other substances. ...
... Electromagnetic waves are produced by the motion of electrically charged particles. These waves are also called "electromagnetic radiation" because they radiate from the electrically charged particles. They travel through empty space as well as through air and other substances. ...
Diffraction-of-light
... We usually think of light as always traveling in straight lines, but when light waves pass near a barrier they tend to bend around that barrier and become spread out. Diffraction of light occurs when a light wave passes by a corner or through an opening or slit that is physically the approximate siz ...
... We usually think of light as always traveling in straight lines, but when light waves pass near a barrier they tend to bend around that barrier and become spread out. Diffraction of light occurs when a light wave passes by a corner or through an opening or slit that is physically the approximate siz ...
Serway_PSE_quick_ch40
... photons passing through a narrow slit have been localized to the width of the slit. Because we have gained information about their position, they must have a larger uncertainty in momentum along the plane of the screen in which the slit is cut. Thus, the photons gain momentum perpendicular to their ...
... photons passing through a narrow slit have been localized to the width of the slit. Because we have gained information about their position, they must have a larger uncertainty in momentum along the plane of the screen in which the slit is cut. Thus, the photons gain momentum perpendicular to their ...
Spatially resolved measurement of femtosecond
... was produced, following Eaton et al. [13] for similar writing parameters. Figure 4(b) shows a well-separated peak that corresponds to an average grating line with a main feature size of 10 μm matching well the optical microscope measurements in Fig. 3. According to Eq. (3), a lateral resolution of ∼ ...
... was produced, following Eaton et al. [13] for similar writing parameters. Figure 4(b) shows a well-separated peak that corresponds to an average grating line with a main feature size of 10 μm matching well the optical microscope measurements in Fig. 3. According to Eq. (3), a lateral resolution of ∼ ...
Resolution questions with solutions
... central maximum around X; correct overall shape (only two secondary maxima need be shown); secondary maxima much less intense than the central maximum; ...
... central maximum around X; correct overall shape (only two secondary maxima need be shown); secondary maxima much less intense than the central maximum; ...
Lect03_Bi177_MicroscopeOptics
... • Velocity in Vacuum (c) = 2.99792458 • 108 m/sec • Frequency remains constant while light travels through different media. Wavelength and speed change. ...
... • Velocity in Vacuum (c) = 2.99792458 • 108 m/sec • Frequency remains constant while light travels through different media. Wavelength and speed change. ...
Photo Contest Winners Member Lens:
... bowl, where they combine to form white light. “This image beautifully demonstrates total internal reflection and three-color mixing, creating a visceral, interactive tutorial for optical fiber technology, modern display technology, Rayleigh scattering, and even integrating sphere technology,” says j ...
... bowl, where they combine to form white light. “This image beautifully demonstrates total internal reflection and three-color mixing, creating a visceral, interactive tutorial for optical fiber technology, modern display technology, Rayleigh scattering, and even integrating sphere technology,” says j ...
introduction - 123seminarsonly.com
... films. Both metals and nonmetals, including plastics, show plasma energy losses. The lost energy may reappear in the form of ultraviolet or visible radiation; no chemical effect is known to have occurred from such losses. ...
... films. Both metals and nonmetals, including plastics, show plasma energy losses. The lost energy may reappear in the form of ultraviolet or visible radiation; no chemical effect is known to have occurred from such losses. ...
Chapter 28 Color
... than mixing light. If you mix red and green paint you get brown. Paints do not reflect a single color of light. They reflect several colors. Color subtraction is on page ...
... than mixing light. If you mix red and green paint you get brown. Paints do not reflect a single color of light. They reflect several colors. Color subtraction is on page ...
Chemistry 201/211 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... 7.061014 Hz is used to examine an object, what is the size of the smallest detail that can be seen? In the 1930’s, scientists built an electron microscope that uses electrons instead of light to probe matter. If the speed of the electrons (m = 9.1110-31 kg) used is 1.45107 m/s, what wavelength do ...
... 7.061014 Hz is used to examine an object, what is the size of the smallest detail that can be seen? In the 1930’s, scientists built an electron microscope that uses electrons instead of light to probe matter. If the speed of the electrons (m = 9.1110-31 kg) used is 1.45107 m/s, what wavelength do ...
this paper (free) - International Journal of Pure and
... set of parameters for investigating the propagation of beam profile of equation (4) are n1 = 1.5, n2 = 1.4, θ = 0.9, X0 = −50, α = 0.87, and the interface is assumed at σ = 0. Here, one can observe that, how the reflection and transmission of the beam are affected by the variation of I (peak intensi ...
... set of parameters for investigating the propagation of beam profile of equation (4) are n1 = 1.5, n2 = 1.4, θ = 0.9, X0 = −50, α = 0.87, and the interface is assumed at σ = 0. Here, one can observe that, how the reflection and transmission of the beam are affected by the variation of I (peak intensi ...
Coating mechanical loss at room and low temperatures
... Conclusions - coatings • Measurements of the loss of a single layer of tantala coating have been made on silicon cantilever substrates • Results at low temperature are consistent with: the mechanical loss of tantala increases as temperature decreases ~1.5x10-4 at 290K → ~4.0x10-4 at 80K ...
... Conclusions - coatings • Measurements of the loss of a single layer of tantala coating have been made on silicon cantilever substrates • Results at low temperature are consistent with: the mechanical loss of tantala increases as temperature decreases ~1.5x10-4 at 290K → ~4.0x10-4 at 80K ...
towards integrated long-wavelength light sources
... sets of applications in a laboratory environment. However by using integrated optics where on-chip lightwave circuits are used to guide and filter light, these systems could be fit on a chip measuring only a few square mm, unlocking the through potential of this wavelength region. Indeed it has been ...
... sets of applications in a laboratory environment. However by using integrated optics where on-chip lightwave circuits are used to guide and filter light, these systems could be fit on a chip measuring only a few square mm, unlocking the through potential of this wavelength region. Indeed it has been ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.