Refraction and Reflection Lab
... to catch any reflection off the first card with the second. Can you see any evidence that the light lines from the first card are being reflected on the second? ...
... to catch any reflection off the first card with the second. Can you see any evidence that the light lines from the first card are being reflected on the second? ...
Two Quick Light Experiments
... arrangement resulting in the least intensity above (it should be zero intensity – darkness) with the first polarizer’s zero angle at six o’clock. This scenario is known as “crossed polarizers.” 6. Add a third polarizer between them. Determine what angles of the third polarizer yield the highest and ...
... arrangement resulting in the least intensity above (it should be zero intensity – darkness) with the first polarizer’s zero angle at six o’clock. This scenario is known as “crossed polarizers.” 6. Add a third polarizer between them. Determine what angles of the third polarizer yield the highest and ...
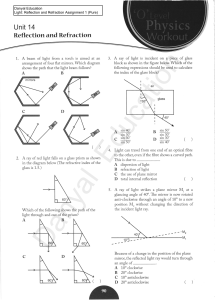
LEVEL –A QESTIONS-OPTICS 1. Draw a ray diagram to show the
... 5. The length of a wave in water diminishes µ times, µ being the refractive index of water. Does this mean that a diver cannot see surrounding objects in their natural colours? (2m) 6. The covered print is not visible from any of the four sides of a glass cube placed on a book. Explain what happens ...
... 5. The length of a wave in water diminishes µ times, µ being the refractive index of water. Does this mean that a diver cannot see surrounding objects in their natural colours? (2m) 6. The covered print is not visible from any of the four sides of a glass cube placed on a book. Explain what happens ...
Phy123 Exam2 review
... You should be able to predict image location and characteristics from a verbal description of the situation, from ray diagrams and from equations. You should also be able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mir ...
... You should be able to predict image location and characteristics from a verbal description of the situation, from ray diagrams and from equations. You should also be able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mir ...
Mimicking the colourful wing scale structure of the
... incidence the artificial replica appears green, while it, d, reflects blue at grazing incidence, showing some iridescence (scale bars 5 mm). e, Under a light microscope, the concavity edges appear turquoise, while the centres and interstitial regions are yellow (left); between crossed polarisers onl ...
... incidence the artificial replica appears green, while it, d, reflects blue at grazing incidence, showing some iridescence (scale bars 5 mm). e, Under a light microscope, the concavity edges appear turquoise, while the centres and interstitial regions are yellow (left); between crossed polarisers onl ...
Optics - Tensors for Tots
... separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted twice, when it enters the prism and when it leaves. Refraction is the change i ...
... separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted twice, when it enters the prism and when it leaves. Refraction is the change i ...
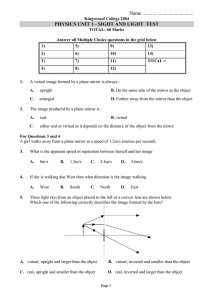
Wave Light Test
... 7. A simple optical fibre consists of a cylindrical tube of transparent material of refractive index 1.50 surrounded by air. A light ray is retained within the fibre by total internal reflection. The light ray travels down the tube striking the wall at an angle, . ...
... 7. A simple optical fibre consists of a cylindrical tube of transparent material of refractive index 1.50 surrounded by air. A light ray is retained within the fibre by total internal reflection. The light ray travels down the tube striking the wall at an angle, . ...
Plane Mirrors
... A source (light bulb, the sun, etc) Another object (that is not creating the light ray, but rather reflects light that strikes it) ...
... A source (light bulb, the sun, etc) Another object (that is not creating the light ray, but rather reflects light that strikes it) ...
Lenses - Cloudfront.net
... monochromatic light on two plates of glass on top of each other The light that has to hit the second surface, has longer to go to hit your eye, so you see the interference between the surfaces Scientists use this in the testing of high precision lenses ...
... monochromatic light on two plates of glass on top of each other The light that has to hit the second surface, has longer to go to hit your eye, so you see the interference between the surfaces Scientists use this in the testing of high precision lenses ...
Efficiency enhancement in a light
... In a standard planar light emitting diode 共LED兲, the efficiency is limited to several percents by a low light extraction efficiency ex due to the total internal reflection 共TIR兲 at semiconductor/air boundaries. To avoid this problem, processes of epitaxial wafers into particular shapes have been d ...
... In a standard planar light emitting diode 共LED兲, the efficiency is limited to several percents by a low light extraction efficiency ex due to the total internal reflection 共TIR兲 at semiconductor/air boundaries. To avoid this problem, processes of epitaxial wafers into particular shapes have been d ...
Assignment 1A
... The figure below shows a ray of light crossing the boundary from medium 1 to medium 2. ...
... The figure below shows a ray of light crossing the boundary from medium 1 to medium 2. ...
World Journal Of Engineering ENHANCEMENT OF OPTICAL
... by using an oblique deposition of iron oxide on the top of Ag nanoparticles, and observed the enhanced optical birefringence at around the wavelength of LSPR. Birefringence is induced via the anisotropic dielectric shell and is enhanced by the LSPR of Ag nanoparticles. We believe that the combinatio ...
... by using an oblique deposition of iron oxide on the top of Ag nanoparticles, and observed the enhanced optical birefringence at around the wavelength of LSPR. Birefringence is induced via the anisotropic dielectric shell and is enhanced by the LSPR of Ag nanoparticles. We believe that the combinatio ...
At what intensity is the laser set?
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
Waves – Light and Sound Quiz 4
... light waves are ______________ waves which can be reflected, ______________ and ________ the angle of incidence equals the angle of ______________ refractive index n=______________ ______________ ______________ is used in transmitting information along optical fibres when the angle of incidence is g ...
... light waves are ______________ waves which can be reflected, ______________ and ________ the angle of incidence equals the angle of ______________ refractive index n=______________ ______________ ______________ is used in transmitting information along optical fibres when the angle of incidence is g ...
Figure 3.1: Schematic of experimental setup
... Principle a) Brewster’s Angle When unpolarized light travels from a transparent medium with a refractive index ni to another one with a higher refraction index nt, part of the light is refracted into the second medium while the other part of the light is reflected back into the first medium, as show ...
... Principle a) Brewster’s Angle When unpolarized light travels from a transparent medium with a refractive index ni to another one with a higher refraction index nt, part of the light is refracted into the second medium while the other part of the light is reflected back into the first medium, as show ...
focusing of light by corneal lenses in a reflecting superposition eye
... Pfiicroscope, a decrease in refractive index from the centre of the lens (n = 1 -442) to the edge ( n = 1-417) can be measured. It is this gradient, creating a lens cylinder, that focuses the light (Iga, 1980). Interference fringes, demonstrating the existence of a refractive-index gradient, can be ...
... Pfiicroscope, a decrease in refractive index from the centre of the lens (n = 1 -442) to the edge ( n = 1-417) can be measured. It is this gradient, creating a lens cylinder, that focuses the light (Iga, 1980). Interference fringes, demonstrating the existence of a refractive-index gradient, can be ...
Snell`s Law
... The rays (directions of propagation) are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The above assumption is valid only when the size of the barrier (or the size of the media) is much larger than the wavelength of light ...
... The rays (directions of propagation) are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The above assumption is valid only when the size of the barrier (or the size of the media) is much larger than the wavelength of light ...
INTERFERENCE
... Both of these involve splitting the light from a single source into two beams. Division of amplitude This involves splitting a single light beam into two beams, a reflected beam and a transmitted beam, at a surface between two media of different refractive index. ...
... Both of these involve splitting the light from a single source into two beams. Division of amplitude This involves splitting a single light beam into two beams, a reflected beam and a transmitted beam, at a surface between two media of different refractive index. ...
Full-field refractive index measurement with simultaneous phase
... Therefore, according to Eqs. (12) and (13), when the phase difference is accurately measured, the refractive index of the tested specimen n2 can be obtained using Eq. (7). 3. Experimental setup and results To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, various mixtures of the tested specimen ...
... Therefore, according to Eqs. (12) and (13), when the phase difference is accurately measured, the refractive index of the tested specimen n2 can be obtained using Eq. (7). 3. Experimental setup and results To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method, various mixtures of the tested specimen ...
Class07
... • Material: index of refraction depends on wavelength (prism) • Waveguide: some of wave travels through cladding with different index of refraction (primarily single-mode) – leads to wavelength-dependent effects ...
... • Material: index of refraction depends on wavelength (prism) • Waveguide: some of wave travels through cladding with different index of refraction (primarily single-mode) – leads to wavelength-dependent effects ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.