Refraction, Lenses, Aberrations
... • Atmospheric refraction is a phenomenon that moves images of objects, seen through the air, due to a gradual change of the air density and temperature. • Thin lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments to enhance our vision. • Aberrations are distortions of images, predicte ...
... • Atmospheric refraction is a phenomenon that moves images of objects, seen through the air, due to a gradual change of the air density and temperature. • Thin lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments to enhance our vision. • Aberrations are distortions of images, predicte ...
Physics Tute Sheet-6 - College of Engineering Roorkee
... Ans. 8.66x10-5cm & its odd multiple. 6. Calculate the thickness of a doubly refracting crystal plate which is required to convert a clockwise circularly polarized light to anticlockwise circularly polarized light. Given μe = 1.5388 and μo= 1.5212 for the wavelength 600nm. Ans. 1.7x10-3cm & its multi ...
... Ans. 8.66x10-5cm & its odd multiple. 6. Calculate the thickness of a doubly refracting crystal plate which is required to convert a clockwise circularly polarized light to anticlockwise circularly polarized light. Given μe = 1.5388 and μo= 1.5212 for the wavelength 600nm. Ans. 1.7x10-3cm & its multi ...
Microscopy Basics
... Bright field microscopy is based on absorption of light in the sample. Most biological objects, however, absorb only weakly in the visible spectrum. This lead to: • Development of specific staining (nowadays almost entirely replaced by fluorescent labeling) • Development of UV microscopy (Köhler) fa ...
... Bright field microscopy is based on absorption of light in the sample. Most biological objects, however, absorb only weakly in the visible spectrum. This lead to: • Development of specific staining (nowadays almost entirely replaced by fluorescent labeling) • Development of UV microscopy (Köhler) fa ...
Diffraction grating has periodic structure that splits and diffracts light
... Ordinary pressed CD and DVD media are every-day examples of diffraction gratings and can be used to demonstrate the effect by reflecting sunlight off them onto a white wall. (see ). This is a side effect of their manufacture, as one surface of a CD has many small pits in the plastic, arranged in a s ...
... Ordinary pressed CD and DVD media are every-day examples of diffraction gratings and can be used to demonstrate the effect by reflecting sunlight off them onto a white wall. (see ). This is a side effect of their manufacture, as one surface of a CD has many small pits in the plastic, arranged in a s ...
Light and Optics Unit Test
... 38. When light hits an uneven or rough reflecting surface the reflecting rays are: a. absorbed b. scattered c. bent d. diverted 39. Kimberley placed a loonie into a pail of water and noticed that when it was in the water it appeared smaller than it really was. She then reached into the pail to pick ...
... 38. When light hits an uneven or rough reflecting surface the reflecting rays are: a. absorbed b. scattered c. bent d. diverted 39. Kimberley placed a loonie into a pail of water and noticed that when it was in the water it appeared smaller than it really was. She then reached into the pail to pick ...
Refractive Index Measurement within a Photonic Crystal Fibre Based on Short Wavelength Diffraction
... transmission band. A major factor that will influence the ultimate fibre employed is the ability to inscribe gratings [6,7]. Solid fibre Bragg grating based refractive index sensors have also been proposed in the past [8-11]. Solid-core photonic crystal fibres are often described by an analogous eff ...
... transmission band. A major factor that will influence the ultimate fibre employed is the ability to inscribe gratings [6,7]. Solid fibre Bragg grating based refractive index sensors have also been proposed in the past [8-11]. Solid-core photonic crystal fibres are often described by an analogous eff ...
dec 2016_nature of light unit test review sheet answer key
... 2. What is the relationship between the size of a shadow on a screen and the distance of the screen from the object that produces the shadow? - When an object is closer to a screen, the shadow size decreases. - When an object is further away from a screen, the shadow size increases. 3. What is the r ...
... 2. What is the relationship between the size of a shadow on a screen and the distance of the screen from the object that produces the shadow? - When an object is closer to a screen, the shadow size decreases. - When an object is further away from a screen, the shadow size increases. 3. What is the r ...
Reflectivity measurements of a quantum well
... quantum information processing or control and for nonlinear optics. Almost all photonic devices are based on the spontaneous emission rate control. Addition of the nitrogen to the InGaAs alloy redshifts the emission energy of the QW (via the change of the bandgap) into the more interesting in view o ...
... quantum information processing or control and for nonlinear optics. Almost all photonic devices are based on the spontaneous emission rate control. Addition of the nitrogen to the InGaAs alloy redshifts the emission energy of the QW (via the change of the bandgap) into the more interesting in view o ...
Intermittent measurement
... Besides single wavelength monitoring broad-band monitoring is another approach which was investigated since the 1970’s 8. With silicon array detectors 256, 512 or 1024 wavelengths can be monitored at the same time. Today fast CCD array detectors are commercial available. In reference 9 a direct mea ...
... Besides single wavelength monitoring broad-band monitoring is another approach which was investigated since the 1970’s 8. With silicon array detectors 256, 512 or 1024 wavelengths can be monitored at the same time. Today fast CCD array detectors are commercial available. In reference 9 a direct mea ...
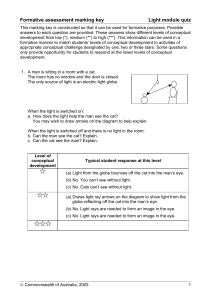
Formative assessment marking key: Light Module Quiz
... This marking key is constructed so that it can be used for formative purposes. Possible answers to each question are provided. These answers show different levels of conceptual development from low (*), medium (**) to high (***). This information can be used in a formative manner to match students’ ...
... This marking key is constructed so that it can be used for formative purposes. Possible answers to each question are provided. These answers show different levels of conceptual development from low (*), medium (**) to high (***). This information can be used in a formative manner to match students’ ...
Operating Principles
... transits independently, light is emitted at random and out of phase. Such light is referred to as incoherent light and is one of the typical characteristics of spontaneous emission. Under thermal equilibrium, the probability of an electron to exist in the lower level, E1, is higher than that in the ...
... transits independently, light is emitted at random and out of phase. Such light is referred to as incoherent light and is one of the typical characteristics of spontaneous emission. Under thermal equilibrium, the probability of an electron to exist in the lower level, E1, is higher than that in the ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Copyright 2006, The Regents of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109 ...
... Copyright 2006, The Regents of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109 ...
Unit 13: EM Radiation and Waves
... The Visible Spectrum and Dispersion Wavelengths of visible light: 400 nm to 750 nm Shorter wavelengths are ultraviolet; longer are infrared The index of refraction of a material varies somewhat with the wavelength of the light. ...
... The Visible Spectrum and Dispersion Wavelengths of visible light: 400 nm to 750 nm Shorter wavelengths are ultraviolet; longer are infrared The index of refraction of a material varies somewhat with the wavelength of the light. ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... •The parallel rays converge at the second focal point F‘. •The first focal point is at the front. All rays originated at This point become parallel to the axis after the lens. ...
... •The parallel rays converge at the second focal point F‘. •The first focal point is at the front. All rays originated at This point become parallel to the axis after the lens. ...
AP Physics B Waves and Optics Sample MC
... (A) It is real and upright. (B) It is real and inverted. (C) It is virtual and upright. (D) It is virtual and inverted. 25. An image is formed by a convex mirror. (A) It is real and upright. (B) It is real and inverted. (C) It is virtual and upright. (D) It is virtual and inverted. ...
... (A) It is real and upright. (B) It is real and inverted. (C) It is virtual and upright. (D) It is virtual and inverted. 25. An image is formed by a convex mirror. (A) It is real and upright. (B) It is real and inverted. (C) It is virtual and upright. (D) It is virtual and inverted. ...
Lab
... goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is ...
... goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is ...
JC2315121515
... dealing with issues such as friction, lubrication, and wear. Surface finish is a desired criterion which influences on performance of mechanical parts as well as productivity. Good surface finish helps in reducing fatigue load, improving corrosion resistance and creep life. It also affects functiona ...
... dealing with issues such as friction, lubrication, and wear. Surface finish is a desired criterion which influences on performance of mechanical parts as well as productivity. Good surface finish helps in reducing fatigue load, improving corrosion resistance and creep life. It also affects functiona ...
Name: ANSWER KEY Period: Date: Nature of Light Unit Test Review
... spectrum, except green, which it reflects back to the observer’s eyes. 5. Why does an object appear white in white light? - The object appears white, because it reflects all of the colors of the visible spectrum. 6. Why does an object appear black in white light? - The object appears black, because ...
... spectrum, except green, which it reflects back to the observer’s eyes. 5. Why does an object appear white in white light? - The object appears white, because it reflects all of the colors of the visible spectrum. 6. Why does an object appear black in white light? - The object appears black, because ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.