An Overview of the Ocean
... The overall focus of this unit is to bring about student understanding and appreciation of the complexity of our oceans: the relationship between ocean and atmospheric patterns; how ocean depth relates to ocean content; the diversity of marine organisms and what determines their specific ocean habit ...
... The overall focus of this unit is to bring about student understanding and appreciation of the complexity of our oceans: the relationship between ocean and atmospheric patterns; how ocean depth relates to ocean content; the diversity of marine organisms and what determines their specific ocean habit ...
International Ocean Institute
... We, the class of 2014 of the 10th Training Programme on Regional Ocean Governance for the Baltic, Black, Caspian and Mediterranean Seas of the International Ocean Institute, representing 12 countries from 4 continents, Considering that human behaviour over the past century has led to polluted, overe ...
... We, the class of 2014 of the 10th Training Programme on Regional Ocean Governance for the Baltic, Black, Caspian and Mediterranean Seas of the International Ocean Institute, representing 12 countries from 4 continents, Considering that human behaviour over the past century has led to polluted, overe ...
Sewage Runoff and Thermal Pollution
... consumption can carry viruses and diseases, which if not cooked out properly can result in human illness and the spreading of diseases found in waste and sewage – For example, the spreading of Hepatitis through human waste ...
... consumption can carry viruses and diseases, which if not cooked out properly can result in human illness and the spreading of diseases found in waste and sewage – For example, the spreading of Hepatitis through human waste ...
Gyre in a Bottle - Monterey Bay Aquarium
... Atlantic; South Atlantic; North Pacific; South Pacific and Indian Ocean gyres. Within gyres, waters are relatively constant, remaining stable for long periods instead of circulating around the globe. Gyres have always been areas where large amounts of natural materials, such as driftwood, seeds and ...
... Atlantic; South Atlantic; North Pacific; South Pacific and Indian Ocean gyres. Within gyres, waters are relatively constant, remaining stable for long periods instead of circulating around the globe. Gyres have always been areas where large amounts of natural materials, such as driftwood, seeds and ...
Exceptional influx of oceanic species into the North Sea late 1997
... 1980s/early 1990s and the present, and the appearance of doliolids in the North Sea is not restricted to these time periods. Lucas (1933) noted that when doliolids appeared in the North Sea in 1911 and 1933, the summers were dry and warm with seasurface temperatures well above average. The appearanc ...
... 1980s/early 1990s and the present, and the appearance of doliolids in the North Sea is not restricted to these time periods. Lucas (1933) noted that when doliolids appeared in the North Sea in 1911 and 1933, the summers were dry and warm with seasurface temperatures well above average. The appearanc ...
SPACE-BASED OBSERVATIONS IN THE GLOBAL OCEAN
... diurnal variations and to more representative measurements in the tropical regions frequently obscured by clouds. ...
... diurnal variations and to more representative measurements in the tropical regions frequently obscured by clouds. ...
Programme - The Future Ocean
... is impacted directly by processes operating exactly at this frontline. The characteristics of the microlayer and hence the nature of processes operating there are, themselves, subject to change as a result of the changing forcing. The presentation will focus largely, but not exclusively, on external ...
... is impacted directly by processes operating exactly at this frontline. The characteristics of the microlayer and hence the nature of processes operating there are, themselves, subject to change as a result of the changing forcing. The presentation will focus largely, but not exclusively, on external ...
Biogeographic_Atlas_..
... the organisms. For instance, deep basins on the shelf, which can extend to depths >1000 m, are a very different environment to regions of similar depth on the continental slope. Deep shelf basins often contain thick accumulations of muddy biogenic material produced in the shelf surface waters (Domac ...
... the organisms. For instance, deep basins on the shelf, which can extend to depths >1000 m, are a very different environment to regions of similar depth on the continental slope. Deep shelf basins often contain thick accumulations of muddy biogenic material produced in the shelf surface waters (Domac ...
CHAPTER 7
... - The general structure of the Atlantic Ocean is illustrated in figure 7.5. - In the North Atlantic, the deepest water is called North Atlantic deep water. It has average salinity but high density due to very cold temperatures. This water is formed by the convergence of surface water. Surface water ...
... - The general structure of the Atlantic Ocean is illustrated in figure 7.5. - In the North Atlantic, the deepest water is called North Atlantic deep water. It has average salinity but high density due to very cold temperatures. This water is formed by the convergence of surface water. Surface water ...
Life in the Ocean
... – The photic zone is a dangerous place for marine organisms because predators can easily see them. – Many types of zooplankton avoid this threat by daily vertical migration. • Each day at dusk, they come to the surface zone to feed on phytoplankton. As daylight comes, they return to the relative saf ...
... – The photic zone is a dangerous place for marine organisms because predators can easily see them. – Many types of zooplankton avoid this threat by daily vertical migration. • Each day at dusk, they come to the surface zone to feed on phytoplankton. As daylight comes, they return to the relative saf ...
Stories in IPRC Climate
... and even more pronounced at the surface than indicated by the general circulation model simulations. The origin of the jets is still a mystery. The freely drifting surface buoys also happen to provide a unique opportunity for tracking ocean debris. Carried along by ocean currents, the trajectories o ...
... and even more pronounced at the surface than indicated by the general circulation model simulations. The origin of the jets is still a mystery. The freely drifting surface buoys also happen to provide a unique opportunity for tracking ocean debris. Carried along by ocean currents, the trajectories o ...
Chapter 13 Section 3 Life in the Ocean
... floor of the ocean trenches and any organisms found there. The depth can reach from 6,000 m to 7,000 m below sea level. • The only organisms that have been found in this zone include a type of sponge, a few species of worms, and a type of clam. ...
... floor of the ocean trenches and any organisms found there. The depth can reach from 6,000 m to 7,000 m below sea level. • The only organisms that have been found in this zone include a type of sponge, a few species of worms, and a type of clam. ...
CSIR - National Institute of Oceanography
... defining the nature of seasonality in currents in the North Indian Ocean, particularly along Indian coasts. Observations and models have shown that circulation needs to be looked at holistically across the basin because the winds at a location influence not only the local current, but have an impact ...
... defining the nature of seasonality in currents in the North Indian Ocean, particularly along Indian coasts. Observations and models have shown that circulation needs to be looked at holistically across the basin because the winds at a location influence not only the local current, but have an impact ...
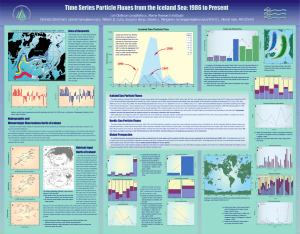
Time Series Particle Fluxes from the Iceland Sea: 1986 to...
... Sediment trap samples from the Parflux Lab, and GB and NS data from B.von ...
... Sediment trap samples from the Parflux Lab, and GB and NS data from B.von ...
Arctic Ocean

The Arctic Ocean (also known as the Northern Ocean), located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea or simply the Arctic Sea, classifying it a mediterranean sea or an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. Alternatively, the Arctic Ocean can be seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.Almost completely surrounded by Eurasia and North America, the Arctic Ocean is partly covered by sea ice throughout the year (and almost completely in winter). The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is the lowest on average of the five major oceans, due to low evaporation, heavy fresh water inflow from rivers and streams, and limited connection and outflow to surrounding oceanic waters with higher salinities. The summer shrinking of the ice has been quoted at 50%. The US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) uses satellite data to provide a daily record of Arctic sea ice cover and the rate of melting compared to an average period and specific past years.