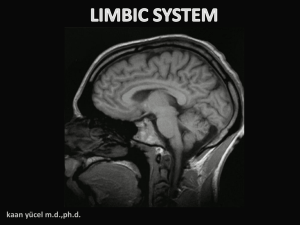
NAlab13_LimbicSystem..
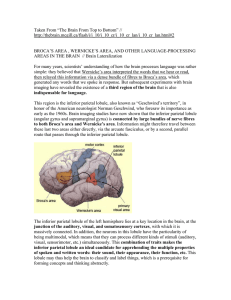
... The orbital gyri are not visible on this slide. What are some functions of the parahippocampal gyrus and temporal pole? The amygdala and rostral hippocampal formation are under the region of the uncus. Space occupying lesions above the cerebellar tentorium may cause the uncus on the side of the lesi ...
... The orbital gyri are not visible on this slide. What are some functions of the parahippocampal gyrus and temporal pole? The amygdala and rostral hippocampal formation are under the region of the uncus. Space occupying lesions above the cerebellar tentorium may cause the uncus on the side of the lesi ...
Hafiz Noordin Term Paper - Engineering Computing Facility
... map, as there is a multitude of input/output relationships. The primary visual cortex, or V1, is the most important cortical region in the occipital lobe of the brain, since almost all signals from the optic nerve will pass through this region. Although there are many other cortical regions (i.e. V2 ...
... map, as there is a multitude of input/output relationships. The primary visual cortex, or V1, is the most important cortical region in the occipital lobe of the brain, since almost all signals from the optic nerve will pass through this region. Although there are many other cortical regions (i.e. V2 ...
The relative advantages of sparse versus distributed encoding for
... extent to which this statement is valid in general is discussed here, by considering some simple formal models of associative memory which include different neurobiological constraints. In nets of linear neurons, trained with either a Hebbian (purely incremental) or a Stanton and Sejnowski learning ...
... extent to which this statement is valid in general is discussed here, by considering some simple formal models of associative memory which include different neurobiological constraints. In nets of linear neurons, trained with either a Hebbian (purely incremental) or a Stanton and Sejnowski learning ...
doc Chapter 13 Notes
... LGN of thalamus primary visual cortex (first level of analysis) extrastriate cortex (analysis of particular attributes of a visual scene like form, color, movement) next level of visual association which is either the ventral (object recognition or “what”) stream or dorsal (perception of loc ...
... LGN of thalamus primary visual cortex (first level of analysis) extrastriate cortex (analysis of particular attributes of a visual scene like form, color, movement) next level of visual association which is either the ventral (object recognition or “what”) stream or dorsal (perception of loc ...
Brain days-Part V-Limbic
... related to motivation and with its connections with the cognitive parts of the brain helps us to “use our mind” a.k.a. accomplish mental processes. ...
... related to motivation and with its connections with the cognitive parts of the brain helps us to “use our mind” a.k.a. accomplish mental processes. ...
Visual Properties of Neurons in a Polysensory Area in Superior
... respond similarly to spots and slits of light, to shadows, to slides and photographs of complex objects, and to three-dimensional objects. Many of these units would even respond to a very small (< 1”) stimulus moving rapidly (>5O”/s) through a small portion of the peripheral visual field. The remain ...
... respond similarly to spots and slits of light, to shadows, to slides and photographs of complex objects, and to three-dimensional objects. Many of these units would even respond to a very small (< 1”) stimulus moving rapidly (>5O”/s) through a small portion of the peripheral visual field. The remain ...
Language Processing in the Brain
... Recent studies have shown that at least two distinct neural systems may be involved in reading. According to this theory, the brain reads mainly by translating written characters into the corresponding phonological elements of spoken language, but also by drawing connections between the complete im ...
... Recent studies have shown that at least two distinct neural systems may be involved in reading. According to this theory, the brain reads mainly by translating written characters into the corresponding phonological elements of spoken language, but also by drawing connections between the complete im ...
Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortex
... influence the spinal cord circuitry for generating muscle contractions. The influence of M1 in generating muscle contractions has been studied using primarily two methods: stimulation and recording. We have already discussed the finding by Sherrington and Penfield that M1 required the least amount o ...
... influence the spinal cord circuitry for generating muscle contractions. The influence of M1 in generating muscle contractions has been studied using primarily two methods: stimulation and recording. We have already discussed the finding by Sherrington and Penfield that M1 required the least amount o ...
CH 14 brain cranial nerves A and P 2017
... - this is the least understood area of brain research parietal lesions = unaware of objects even your own limbs or body temporal lesions =unable to recognize names of objects, or faces frontal lesions = personality disorders, socially inappropriate ...
... - this is the least understood area of brain research parietal lesions = unaware of objects even your own limbs or body temporal lesions =unable to recognize names of objects, or faces frontal lesions = personality disorders, socially inappropriate ...
Contributions of temporal-parietal junction to the human
... patients who could discriminate the stimuli. Further behavioral studies of these same temporal-parietal patients have shown reduced orienting to distracting stimuli 17. Other investigators have reported that patients with anterograde memory deficits due to posterior association cortex or limbic path ...
... patients who could discriminate the stimuli. Further behavioral studies of these same temporal-parietal patients have shown reduced orienting to distracting stimuli 17. Other investigators have reported that patients with anterograde memory deficits due to posterior association cortex or limbic path ...
brain anatomy - Sinoe Medical Association
... hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. • The hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers, and also by other smaller commissures, including the ante ...
... hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. • The hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers, and also by other smaller commissures, including the ante ...
The Integrative Role of Posterior Parietal Cortex and related Clinical S
... disturbs related to the deficit in the spatial cognition or on the use of that as an aid to some other superior function (language, spatial orientation, attention orientation, etc.). The accurate correlation between each one of those syndromes and the subjacent anatomic injury is usually not possibl ...
... disturbs related to the deficit in the spatial cognition or on the use of that as an aid to some other superior function (language, spatial orientation, attention orientation, etc.). The accurate correlation between each one of those syndromes and the subjacent anatomic injury is usually not possibl ...
Reverse-Engineering the Human Auditory Pathway
... fast/serial architecture. It is common to regard the cortical columns as basic units of computation [19][21][22][24], and in principle, I see no reason why these columns (or groups of columns) could not be reasonably modeled by a sufficiently capable microprocessor running a suitable program, provid ...
... fast/serial architecture. It is common to regard the cortical columns as basic units of computation [19][21][22][24], and in principle, I see no reason why these columns (or groups of columns) could not be reasonably modeled by a sufficiently capable microprocessor running a suitable program, provid ...
Neurocase - McGill University
... cerebral blood flow were observed across all three languages (French, Spanish and English), when synonym generation was compared with a silent resting baseline. In particular, several regions in the right inferior frontal cortex were activated. These foci are in locations corresponding to those obser ...
... cerebral blood flow were observed across all three languages (French, Spanish and English), when synonym generation was compared with a silent resting baseline. In particular, several regions in the right inferior frontal cortex were activated. These foci are in locations corresponding to those obser ...
Synaptic Responses of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons to Light
... potentials mediated by GABA. This response sequence results from the coactivation of pyramidal and GABAergic non-pyramidal cells, followed by feed-forward and possibly feedback pyramidal cell inhibition, and is partly dependent on differences in the membrane properties of pyramidal and non-pyramidal ...
... potentials mediated by GABA. This response sequence results from the coactivation of pyramidal and GABAergic non-pyramidal cells, followed by feed-forward and possibly feedback pyramidal cell inhibition, and is partly dependent on differences in the membrane properties of pyramidal and non-pyramidal ...
Anatomy Written Exam #2 Cranial Nerves Introduction Embryological
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
Anatomy of the Temporal Lobe
... represents the free edge of the pallium, and the associated white matter, the alveus, fimbria, and fornix. The cortex adjacent to the hippocampus is known as the entorhinal area; it is present along the whole length of the parahippocampal gyrus [21]. The subiculum is a transitional zone between the ...
... represents the free edge of the pallium, and the associated white matter, the alveus, fimbria, and fornix. The cortex adjacent to the hippocampus is known as the entorhinal area; it is present along the whole length of the parahippocampal gyrus [21]. The subiculum is a transitional zone between the ...
Neural correlates of consciousness: A definition of the dorsal and
... specific for movements such as walking [24]. This serves the ventral stream function of recognition that a subject is walking,for example. It may be misleading to consider this a true exchange between the parallel streams given the current disagreement on what areas constitute the dorsal stream [25] ...
... specific for movements such as walking [24]. This serves the ventral stream function of recognition that a subject is walking,for example. It may be misleading to consider this a true exchange between the parallel streams given the current disagreement on what areas constitute the dorsal stream [25] ...
The neural mechanisms of top- down attentional control
... top-down attentional control, whereas subsequent selective modulation of sensory inputs reflects the result of this top-down control on sensory information processing. Studies in neurological patients and physiological studies in humans and animals implicate a network of cortical and subcortical reg ...
... top-down attentional control, whereas subsequent selective modulation of sensory inputs reflects the result of this top-down control on sensory information processing. Studies in neurological patients and physiological studies in humans and animals implicate a network of cortical and subcortical reg ...
Motor and cognitive functions of the ventral premotor cortex
... inactivation experiments directly tested this proposal [33•]. Monkeys were trained to reach for and grasp geometric solids of different size, shape and orientation. In separate sessions, F5ab, F5c and the hand field of F1 were reversibly inactivated. The results showed that after inactivation of F5a ...
... inactivation experiments directly tested this proposal [33•]. Monkeys were trained to reach for and grasp geometric solids of different size, shape and orientation. In separate sessions, F5ab, F5c and the hand field of F1 were reversibly inactivated. The results showed that after inactivation of F5a ...
Three Controversial Hypotheses Concerning Computation in the
... we have “three times as many neurons.” According to Sapolsky the genes responsible for this difference govern the number of rounds of cell division during fetal brain development. Clearly Sapolsky is not saying that it is just the quantity of neurons but, rather, he is depending on all that follows ...
... we have “three times as many neurons.” According to Sapolsky the genes responsible for this difference govern the number of rounds of cell division during fetal brain development. Clearly Sapolsky is not saying that it is just the quantity of neurons but, rather, he is depending on all that follows ...
Frontal Lobe
... prone to imitative behaviors. They often show a change in personality, irresponsibility, and lack of concern for the present or future. A similar loss of social guidance of behavior can be observed in primates after they receive lesions to their prefrontal cortex. The social status of animals that r ...
... prone to imitative behaviors. They often show a change in personality, irresponsibility, and lack of concern for the present or future. A similar loss of social guidance of behavior can be observed in primates after they receive lesions to their prefrontal cortex. The social status of animals that r ...
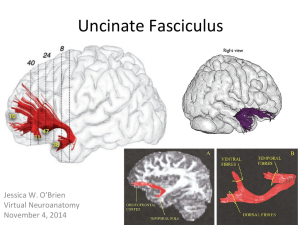
Uncinate Fasciculus
... neurons were linked to sensory features of sOmuli, some to their behavioral significance, and some were condiOonal – E.g., neuron responds only if parOcular sOmulus is present AND that sOmulus signifies rewa ...
... neurons were linked to sensory features of sOmuli, some to their behavioral significance, and some were condiOonal – E.g., neuron responds only if parOcular sOmulus is present AND that sOmulus signifies rewa ...
Feedforward, horizontal, and feedback processing
... V2, and to V3 and the medial temporal area (MT) — feeds into parietal cortex, where spatial information is processed. Pyramidal cells in this pathway have larger dendritic fields and higher spine densities in higher areas than in lower areas, supporting the idea that more complex processing is perfo ...
... V2, and to V3 and the medial temporal area (MT) — feeds into parietal cortex, where spatial information is processed. Pyramidal cells in this pathway have larger dendritic fields and higher spine densities in higher areas than in lower areas, supporting the idea that more complex processing is perfo ...
CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX
... Basics of Neurobiology: Cytoarchitecture of cerebral cortex PROPERTIES OF CORTICAL INTERNEURONS Summary of the the Petilla Interneuron Nomenclature Group Morphological features • Soma: shape; size; orientation; other • Dendrite: arborization polarity; branch metrics; fine structure; postsynaptic el ...
... Basics of Neurobiology: Cytoarchitecture of cerebral cortex PROPERTIES OF CORTICAL INTERNEURONS Summary of the the Petilla Interneuron Nomenclature Group Morphological features • Soma: shape; size; orientation; other • Dendrite: arborization polarity; branch metrics; fine structure; postsynaptic el ...
Inferior temporal gyrus

The inferior temporal gyrus is placed below the middle temporal gyrus, and is connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of complex object features, such as global shape. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers.The inferior temporal gyrus is the anterior region of the temporal lobe located underneath the central temporal sulcus. The primary function of the inferior temporal gyrus - otherwise referenced as IT cortex - is associated with visual stimuli processing, namely visual object recognition, and has been suggested by recent experimental results as the final location of the ventral cortical visual system. The IT cortex in humans is also known as the Inferior Temporal Gyrus since it has been located to a specific region of the human temporal lobe. The IT processes visual stimuli of objects in our field of vision, and is involved with memory and memory recall to identify that object; it is involved with the processing and perception created by visual stimuli amplified in the V1, V2, V3, and V4 regions of the occipital lobe. This region processes the color and form of the object in the visual field and is responsible for producing the “what” from this visual stimuli, or in other words identifying the object based on the color and form of the object and comparing that processed information to stored memories of objects to identify that object.The IT cortex’s neurological significance is not just its contribution to the processing of visual stimuli in object recognition but also has been found to be a vital area with regards to simple processing of the visual field, difficulties with perceptual tasks and spatial awareness, and the location of unique single cells that possibly explain the IT cortex’s relation to memory.