Second-Order Patterns in Human Visual Cortex`` on ``Orientation
... backgrounds when their borders are defined by differences in the contrast, orientation or spatial frequency of their constituent elements rather than simply their average luminance? Larsson et al. (2006) in this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology (p. 862– 881) provide novel evidence that the percep ...
... backgrounds when their borders are defined by differences in the contrast, orientation or spatial frequency of their constituent elements rather than simply their average luminance? Larsson et al. (2006) in this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology (p. 862– 881) provide novel evidence that the percep ...
Textures of Natural Images in the Human Brain. Focus on
... backgrounds when their borders are defined by differences in the contrast, orientation or spatial frequency of their constituent elements rather than simply their average luminance? Larsson et al. (2006) in this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology (p. 862– 881) provide novel evidence that the percep ...
... backgrounds when their borders are defined by differences in the contrast, orientation or spatial frequency of their constituent elements rather than simply their average luminance? Larsson et al. (2006) in this issue of Journal of Neurophysiology (p. 862– 881) provide novel evidence that the percep ...
CNS
... than nuclei occipital lobe i.origin Row oflobe cells perpendicular the surface of the brain ii. Inferior to thistoto sulcus is the or destination ii. Sulcus: groove frontal and extends the ii. Divides parietal from one side of the organ brain with the other side form synapses on a second common d. L ...
... than nuclei occipital lobe i.origin Row oflobe cells perpendicular the surface of the brain ii. Inferior to thistoto sulcus is the or destination ii. Sulcus: groove frontal and extends the ii. Divides parietal from one side of the organ brain with the other side form synapses on a second common d. L ...
Synopsis: Overview Perception Retina Central projections LGN
... Vision is ubiquitous, but many different types of eyes evolved Visual processing streams originate in the retina Topography: there are maps of visual space in the brain RGCs have center-surround receptive fields ...
... Vision is ubiquitous, but many different types of eyes evolved Visual processing streams originate in the retina Topography: there are maps of visual space in the brain RGCs have center-surround receptive fields ...
Chapter 15 - Nervous System Brain & Cranial Nerves
... processes called tracts. There are three major types of tracts in the cerebral cortex: Commissural fibers – connect the gray matter between the two hemispheres. e.g. corpus callosum Association fibers – connect adjacent gyri in same hemisphere. e.g. visual and auditory association ...
... processes called tracts. There are three major types of tracts in the cerebral cortex: Commissural fibers – connect the gray matter between the two hemispheres. e.g. corpus callosum Association fibers – connect adjacent gyri in same hemisphere. e.g. visual and auditory association ...
The Sensorimotor System
... patient’s ability to respond to stimuli on the side of the body contralateral to a brain lesion (not a simple sensory or motor deficit). Often associated with large lesions of the right posterior parietal lobe. ...
... patient’s ability to respond to stimuli on the side of the body contralateral to a brain lesion (not a simple sensory or motor deficit). Often associated with large lesions of the right posterior parietal lobe. ...
Cranial Nerves - Austin Community College
... processes called tracts. There are three major types of tracts in the cerebral cortex: Commissural fibers – connect the gray matter between the two hemispheres. e.g. corpus callosum Association fibers – connect adjacent gyri in same hemisphere. e.g. visual and auditory association ...
... processes called tracts. There are three major types of tracts in the cerebral cortex: Commissural fibers – connect the gray matter between the two hemispheres. e.g. corpus callosum Association fibers – connect adjacent gyri in same hemisphere. e.g. visual and auditory association ...
The visual cortex - Neuroscience Network Basel
... Cells in V4 respond to simple shapes, cells in the inferior temporal cortex (IT, = TEO + TE) respond to complex forms, faces. Hierarchical organization of visual areas, with higher areas responding to more complex features, at the same time the size of the receptive field of the neurons increases. ...
... Cells in V4 respond to simple shapes, cells in the inferior temporal cortex (IT, = TEO + TE) respond to complex forms, faces. Hierarchical organization of visual areas, with higher areas responding to more complex features, at the same time the size of the receptive field of the neurons increases. ...
Axia College Material Appendix C Brain Response of Behavior Part I
... The response to reach out and catch the ball occurs in this final phase of the scenario as successfully transmitted messages in earlier phases trigger this response. Now the frontal lobe receives the previously processed information and begins to prepare for future movement. The frontal lobe plays a ...
... The response to reach out and catch the ball occurs in this final phase of the scenario as successfully transmitted messages in earlier phases trigger this response. Now the frontal lobe receives the previously processed information and begins to prepare for future movement. The frontal lobe plays a ...
Motor Systems I Cortex
... Posterior Parietal Association Cortex 1 Before a movement can be initiated, need to know: • current position of body parts; and • location of external objects of interest The PPAC receives input from the dorsal streams of the somatosensory, auditory and visual systems and thus plays an important ro ...
... Posterior Parietal Association Cortex 1 Before a movement can be initiated, need to know: • current position of body parts; and • location of external objects of interest The PPAC receives input from the dorsal streams of the somatosensory, auditory and visual systems and thus plays an important ro ...
Two Views of Cortex
... identify an association with any one of the 45 possible pairs of active neurons in a subset of 10 with an efficiency of 50% provided that the neurons were active independently, the pair caused two neurons to be active, the probability of the pair occurring was 0.1, and the average fraction active wa ...
... identify an association with any one of the 45 possible pairs of active neurons in a subset of 10 with an efficiency of 50% provided that the neurons were active independently, the pair caused two neurons to be active, the probability of the pair occurring was 0.1, and the average fraction active wa ...
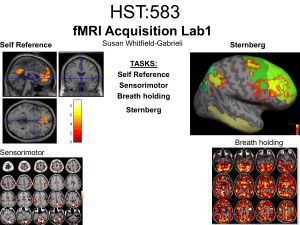
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... UCL, UK). Brodmann Area data is based on information from the online Talairach demon (electronic version of Talairach and Tournoux, 1988). ...
... UCL, UK). Brodmann Area data is based on information from the online Talairach demon (electronic version of Talairach and Tournoux, 1988). ...
12 The Central Nervous System Part A Central Nervous System
... Substantia nigra – functionally linked to basal nuclei Red nucleus – largest nucleus of the reticular formation; red nuclei are relay nuclei for some ...
... Substantia nigra – functionally linked to basal nuclei Red nucleus – largest nucleus of the reticular formation; red nuclei are relay nuclei for some ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
Sparse coding in the primate cortex
... record a set of neurons simultaneously across which sparseness could be measured. Techniques, such as optical recording and multiple electrode recording, may eventually yield data on the density of coding, but there are presently formidable technical difficulties to overcome. We have more informatio ...
... record a set of neurons simultaneously across which sparseness could be measured. Techniques, such as optical recording and multiple electrode recording, may eventually yield data on the density of coding, but there are presently formidable technical difficulties to overcome. We have more informatio ...
Lateral prefrontal cortex
... signal from the prefrontal cortex would arrive to its targets in the posterior cortex at different times. • This synchronization mechanism poses a serious challenge that every human needs to solve during development: • These connections must be fine-tuned to become synchronous. ...
... signal from the prefrontal cortex would arrive to its targets in the posterior cortex at different times. • This synchronization mechanism poses a serious challenge that every human needs to solve during development: • These connections must be fine-tuned to become synchronous. ...
Primer
... understanding how the brain works, this ‘spoticist’ enterprise has been criticized as intellectually sterile by some, since knowing that a function is performed in location A, rather than B or C, tells one nothing about the underlying physiology or neurocomputational structure of the task, which is ...
... understanding how the brain works, this ‘spoticist’ enterprise has been criticized as intellectually sterile by some, since knowing that a function is performed in location A, rather than B or C, tells one nothing about the underlying physiology or neurocomputational structure of the task, which is ...
Cerebral Cortex
... 2. Visual Agnosias (word blindness)- angular gyrus 3. Auditory Agnosias (word deafness)- caudal part of superior temporal gyrus Expressive Aphasias: lesions of Broca’s area; disruption of speech production; poor syntax; word omissions; normal comprehension of language, but speech is labored. ...
... 2. Visual Agnosias (word blindness)- angular gyrus 3. Auditory Agnosias (word deafness)- caudal part of superior temporal gyrus Expressive Aphasias: lesions of Broca’s area; disruption of speech production; poor syntax; word omissions; normal comprehension of language, but speech is labored. ...
Lect-3-Sensory cortex-Dr.Zahoor2010-10
... Areas 1, 2, and 3, which constitute PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA I, 40 is SECONDARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA II and areas 5 and 7, which constitute the SOMATOSENSORY ASSOCIATION AREA. ...
... Areas 1, 2, and 3, which constitute PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA I, 40 is SECONDARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA II and areas 5 and 7, which constitute the SOMATOSENSORY ASSOCIATION AREA. ...
Pattern recognition and visual word forms
... areas probably include the left angular gyrus [52], left inferior frontal cortex [53], and temporal regions anterior to the VWFA [54]. Finally, ventral visual regions receive top-down attentional influences associated with left and right parietal regions that are likely to affect all processing leve ...
... areas probably include the left angular gyrus [52], left inferior frontal cortex [53], and temporal regions anterior to the VWFA [54]. Finally, ventral visual regions receive top-down attentional influences associated with left and right parietal regions that are likely to affect all processing leve ...
Slide 1
... • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
... • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
Neuron highlight
... house dopamine neurons preferentially respond to novel rather than rare, arousing, or behaviorally relevant stimuli (Bunzeck and Düzel, 2006). From the outside, the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra (SN) are easy to miss. Nestled deep in a bend of the brainstem, these nuclei house t ...
... house dopamine neurons preferentially respond to novel rather than rare, arousing, or behaviorally relevant stimuli (Bunzeck and Düzel, 2006). From the outside, the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra (SN) are easy to miss. Nestled deep in a bend of the brainstem, these nuclei house t ...
Neuroscience 14c – The Limbic System and Drugs of Abuse
... hypothalamus as well as to the cortical areas involved in planning of behaviour and motor responses Thus the limbic system has a role in attaching a behavioural significance and response to a stimulus – especially in respect to emotional content Put simply: hypothalamic mammillary bodies → anterio ...
... hypothalamus as well as to the cortical areas involved in planning of behaviour and motor responses Thus the limbic system has a role in attaching a behavioural significance and response to a stimulus – especially in respect to emotional content Put simply: hypothalamic mammillary bodies → anterio ...
CaseStudyBrain2016
... Directions: Based on the information provided indicate as much as you can about the location of the brain damage experienced by each of the following individuals (Note answers may vary but be sure to explain your proposals). All of the following case studies are based on real patients. Case Study #1 ...
... Directions: Based on the information provided indicate as much as you can about the location of the brain damage experienced by each of the following individuals (Note answers may vary but be sure to explain your proposals). All of the following case studies are based on real patients. Case Study #1 ...
Inferior temporal gyrus

The inferior temporal gyrus is placed below the middle temporal gyrus, and is connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of complex object features, such as global shape. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers.The inferior temporal gyrus is the anterior region of the temporal lobe located underneath the central temporal sulcus. The primary function of the inferior temporal gyrus - otherwise referenced as IT cortex - is associated with visual stimuli processing, namely visual object recognition, and has been suggested by recent experimental results as the final location of the ventral cortical visual system. The IT cortex in humans is also known as the Inferior Temporal Gyrus since it has been located to a specific region of the human temporal lobe. The IT processes visual stimuli of objects in our field of vision, and is involved with memory and memory recall to identify that object; it is involved with the processing and perception created by visual stimuli amplified in the V1, V2, V3, and V4 regions of the occipital lobe. This region processes the color and form of the object in the visual field and is responsible for producing the “what” from this visual stimuli, or in other words identifying the object based on the color and form of the object and comparing that processed information to stored memories of objects to identify that object.The IT cortex’s neurological significance is not just its contribution to the processing of visual stimuli in object recognition but also has been found to be a vital area with regards to simple processing of the visual field, difficulties with perceptual tasks and spatial awareness, and the location of unique single cells that possibly explain the IT cortex’s relation to memory.