(Figure 4B) in 12 month old Cln5-/- mice. To survey effects on glial
... reactive phenotype that is more pronounced compared to results from a study in younger Cln5-/- mice. These data emphasize the progressive nature of the NCLs. Consistent with a mouse model of JNCL (Cln3 null mutant), Cln5-/- mice display a profound loss of sensory relay thalamic neurons, yet no loss ...
... reactive phenotype that is more pronounced compared to results from a study in younger Cln5-/- mice. These data emphasize the progressive nature of the NCLs. Consistent with a mouse model of JNCL (Cln3 null mutant), Cln5-/- mice display a profound loss of sensory relay thalamic neurons, yet no loss ...
- Stem-cell and Brain Research Institute
... & Driver, 2000). Recent imaging studies performed on humans have shown cortical multisensory integration sites early in visual pathways and especially around the lingual gyrus, where early visual areas are located (Macaluso et al., 2000). This result is also supported by fMRI studies showing multise ...
... & Driver, 2000). Recent imaging studies performed on humans have shown cortical multisensory integration sites early in visual pathways and especially around the lingual gyrus, where early visual areas are located (Macaluso et al., 2000). This result is also supported by fMRI studies showing multise ...
Williams Syndrome Neuronal Size and Neuronal-Packing Density in Primary Visual Cortex
... receptive field size, sensitivity to color and light contrast, and timing properties. The parvo system is ideally suited for form, texture, and color analysis, while magno processes larger sections of space and appears better designed to calculate spatial location and motion. Anatomically, the magno ...
... receptive field size, sensitivity to color and light contrast, and timing properties. The parvo system is ideally suited for form, texture, and color analysis, while magno processes larger sections of space and appears better designed to calculate spatial location and motion. Anatomically, the magno ...
No Slide Title
... A Key to Distinguishing CF from Linguistic Forms Distinguishing the sign from the affordance or the schema Recall: Two Roles for Imitation in the Evolution of Manual-Based Communication 1. Extending imitation from imitation of hand movements by hand movements to pantomime which uses the degrees of ...
... A Key to Distinguishing CF from Linguistic Forms Distinguishing the sign from the affordance or the schema Recall: Two Roles for Imitation in the Evolution of Manual-Based Communication 1. Extending imitation from imitation of hand movements by hand movements to pantomime which uses the degrees of ...
Lateral Geniculate nucleus
... The axons of ganglion cells exit the eyes via the optic nerve, partially cross at the optic chiasm, and form two optic tracts, so that the right and left hemifields reach the left and right ...
... The axons of ganglion cells exit the eyes via the optic nerve, partially cross at the optic chiasm, and form two optic tracts, so that the right and left hemifields reach the left and right ...
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
... level. From a neurobiological point of view, a mechanism for the functional coordination of large neuronal populations is required for several reasons. First, neurons in visual centers typically have spatially restricted receptive fields which - at least at early stages of processing - are small com ...
... level. From a neurobiological point of view, a mechanism for the functional coordination of large neuronal populations is required for several reasons. First, neurons in visual centers typically have spatially restricted receptive fields which - at least at early stages of processing - are small com ...
Local Field Potential in the Visual System
... lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, with most projections arriving in the thalamocortical recipient layer 4 and some also in layer 6. From layer 4, which is often referred to as the granular layer due to the presence of granular cells in this layer, visual signals are sent to the supragranul ...
... lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, with most projections arriving in the thalamocortical recipient layer 4 and some also in layer 6. From layer 4, which is often referred to as the granular layer due to the presence of granular cells in this layer, visual signals are sent to the supragranul ...
ch_12_lecture_outline_a
... • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
... • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
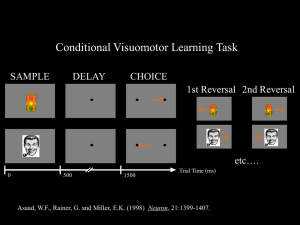
Earl Miller - The Sackler Institutes
... control, is represented in the PFC while irrelevant details are largely discarded. ...
... control, is represented in the PFC while irrelevant details are largely discarded. ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs122.wordpress.com Pathways in
... The limbic system has two main functions: Emotional processing Motivation Another function of the system; short-term memory (also emotional memory) is also important for “survival”. The limbic system works to process our emotions and is related to motivation and with its connections with the cogniti ...
... The limbic system has two main functions: Emotional processing Motivation Another function of the system; short-term memory (also emotional memory) is also important for “survival”. The limbic system works to process our emotions and is related to motivation and with its connections with the cogniti ...
1 Part 1: The Brain - Sinoe Medical Association TM
... which prevents wide changes in intracranial blood flow. When disorders of CSF flow occur, they may therefore impact not only CSF movement, but also the intracranial blood flow, with subsequent neuronal and glial vulnerabilities. The venous system is also important in this equation. Infants and pat ...
... which prevents wide changes in intracranial blood flow. When disorders of CSF flow occur, they may therefore impact not only CSF movement, but also the intracranial blood flow, with subsequent neuronal and glial vulnerabilities. The venous system is also important in this equation. Infants and pat ...
Transcripts/2_4 1
... accessory optic system) can mediate some reflexive behaviors. Sometimes if you do it right, people can do some very simple visually guided tasks like say when they think a light is flashing, but it is in the absence of conscious perception. c. The bottom line is: if you take out the LGN-cortical sys ...
... accessory optic system) can mediate some reflexive behaviors. Sometimes if you do it right, people can do some very simple visually guided tasks like say when they think a light is flashing, but it is in the absence of conscious perception. c. The bottom line is: if you take out the LGN-cortical sys ...
The Cerebrum
... • The cerebral hemipsheres are separated by a deep longitudinal fissure » From the fissure, each hemisphere can be divided into well-defined regions called lobes ...
... • The cerebral hemipsheres are separated by a deep longitudinal fissure » From the fissure, each hemisphere can be divided into well-defined regions called lobes ...
Evidence of Basal Temporo-occipital Cortex
... based on small positional differences, known as retinal disparities. Neurophysiological studies in monkeys showed that there is a widespread distribution of retinal disparity sensitive cells throughout many cortical areas of nonhuman primates. Sensitivity to retinal disparity has been recently found ...
... based on small positional differences, known as retinal disparities. Neurophysiological studies in monkeys showed that there is a widespread distribution of retinal disparity sensitive cells throughout many cortical areas of nonhuman primates. Sensitivity to retinal disparity has been recently found ...
PDF
... of neuronal systems. For example, the inferior temporal cortex processes sensory information about shape and color, but is equally involved in storage of the same types of stimulus features [64]. Although psychology has traditionally divided the mind into separate functions, such as perception, memo ...
... of neuronal systems. For example, the inferior temporal cortex processes sensory information about shape and color, but is equally involved in storage of the same types of stimulus features [64]. Although psychology has traditionally divided the mind into separate functions, such as perception, memo ...
Chapter 2 Functional Neuroanatomy
... occur in the cerebellum and the brain stem. These tumors are found equally in males and females. Although astrocytomas can occur at any age, the most frequent incidence is between five and nine years of age (Hunter et al., 2005). Oligodendroglia cells form and maintain the myelin sheath and, when in ...
... occur in the cerebellum and the brain stem. These tumors are found equally in males and females. Although astrocytomas can occur at any age, the most frequent incidence is between five and nine years of age (Hunter et al., 2005). Oligodendroglia cells form and maintain the myelin sheath and, when in ...
Visual field defect
... Papillitis >> inflammation of the anterior optic nerve causes disc swelling, and sometimes hemorrhages, cells in the vitreous, and deep retinal exudates. After the neuritis resolves, the disc is often pale (optic pallor), most commonly in the temporal aspect. Atrophy is seen over time, especially af ...
... Papillitis >> inflammation of the anterior optic nerve causes disc swelling, and sometimes hemorrhages, cells in the vitreous, and deep retinal exudates. After the neuritis resolves, the disc is often pale (optic pallor), most commonly in the temporal aspect. Atrophy is seen over time, especially af ...
Perceptual Expectation Evokes Category
... temporal cueing or expectation also facilitates visual perception (e.g., Correa et al. 2005; for review, see Nobre et al. 2007). The neural mechanisms of spatial and feature-based visual expectation have been studied extensively. For example, directing attention to a location in anticipation of a ta ...
... temporal cueing or expectation also facilitates visual perception (e.g., Correa et al. 2005; for review, see Nobre et al. 2007). The neural mechanisms of spatial and feature-based visual expectation have been studied extensively. For example, directing attention to a location in anticipation of a ta ...
Document
... Hypothetical scheme to show the APP-metabolite-induced toxicity through the disruption of ionic balance. APP is processed through the Golgi apparatus and is either (1) metabolized to sAPP, CT and BA fragments and released from the cell or (2) transported to and incorporated into the membrane as full ...
... Hypothetical scheme to show the APP-metabolite-induced toxicity through the disruption of ionic balance. APP is processed through the Golgi apparatus and is either (1) metabolized to sAPP, CT and BA fragments and released from the cell or (2) transported to and incorporated into the membrane as full ...
retina - Bakersfield College
... • The left hemiretina of each eye (right visual field) connects to the right lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN); the right hemiretina (left visual field) connects to the left LGN • Most LGN neurons that project to primary visual cortex (V1, striate cortex) terminate in the lower part of cortical layer ...
... • The left hemiretina of each eye (right visual field) connects to the right lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN); the right hemiretina (left visual field) connects to the left LGN • Most LGN neurons that project to primary visual cortex (V1, striate cortex) terminate in the lower part of cortical layer ...
PFC Part 2
... May mediate learning of arbitrary associations. Many PF neurons coded both an object and a currently-associated directional response. During learning, information about the cue object and the action it instructed gradually merged together in PF activity. This may reflect the role of the PF cortex in ...
... May mediate learning of arbitrary associations. Many PF neurons coded both an object and a currently-associated directional response. During learning, information about the cue object and the action it instructed gradually merged together in PF activity. This may reflect the role of the PF cortex in ...
Jennifer S. Lund
... Carl Kupfer was anxious to apply for program grant funds and we were all roped into contributing research proposals in the area of the primate visual system. I was allotted the visual cortex, and this area has remained my principal research topic for the whole of my career. It is a region of the bra ...
... Carl Kupfer was anxious to apply for program grant funds and we were all roped into contributing research proposals in the area of the primate visual system. I was allotted the visual cortex, and this area has remained my principal research topic for the whole of my career. It is a region of the bra ...
Human Neural Systems for Face Recognition and Social
... 1999; Hoffman and Haxby 2000; Kanwisher et al 1997; Puce et al 1998) (Figure 1). Evoked potential studies using electrodes placed on the cortical surface in patients undergoing brain surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy have shown that sites in these same cortical regions produce facespecific response ...
... 1999; Hoffman and Haxby 2000; Kanwisher et al 1997; Puce et al 1998) (Figure 1). Evoked potential studies using electrodes placed on the cortical surface in patients undergoing brain surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy have shown that sites in these same cortical regions produce facespecific response ...
Inferior temporal gyrus

The inferior temporal gyrus is placed below the middle temporal gyrus, and is connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of complex object features, such as global shape. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers.The inferior temporal gyrus is the anterior region of the temporal lobe located underneath the central temporal sulcus. The primary function of the inferior temporal gyrus - otherwise referenced as IT cortex - is associated with visual stimuli processing, namely visual object recognition, and has been suggested by recent experimental results as the final location of the ventral cortical visual system. The IT cortex in humans is also known as the Inferior Temporal Gyrus since it has been located to a specific region of the human temporal lobe. The IT processes visual stimuli of objects in our field of vision, and is involved with memory and memory recall to identify that object; it is involved with the processing and perception created by visual stimuli amplified in the V1, V2, V3, and V4 regions of the occipital lobe. This region processes the color and form of the object in the visual field and is responsible for producing the “what” from this visual stimuli, or in other words identifying the object based on the color and form of the object and comparing that processed information to stored memories of objects to identify that object.The IT cortex’s neurological significance is not just its contribution to the processing of visual stimuli in object recognition but also has been found to be a vital area with regards to simple processing of the visual field, difficulties with perceptual tasks and spatial awareness, and the location of unique single cells that possibly explain the IT cortex’s relation to memory.