indian association of chemistry teachers
... The elevation in boiling point of a solution containing 13.44g of CuCl2 in 1 kg of water is (Kb = 0.52 K/kg mol–1) (A) 0.05 ...
... The elevation in boiling point of a solution containing 13.44g of CuCl2 in 1 kg of water is (Kb = 0.52 K/kg mol–1) (A) 0.05 ...
Low-Temperature Alkaline pH Hydrolysis of Oxygen-Free
... ocean is similar to that of the early ocean, and neglected the pressure effect on the pH and the solubility. If we consider that this ocean is only composed of 5 wt % NH3, that is, 2.88 mol L-1, then its pH can be determined with the classical weak base formula: ...
... ocean is similar to that of the early ocean, and neglected the pressure effect on the pH and the solubility. If we consider that this ocean is only composed of 5 wt % NH3, that is, 2.88 mol L-1, then its pH can be determined with the classical weak base formula: ...
Abdullah F. Eid
... The crystal structure of HPAs depends on the amount of hydration water. This water can be easily removed on heating, whereby the acid strength is increased due to the dehydration of protons. This is a reversible process accompanied by changing the volume of crystal cell. Unlike the rigid network str ...
... The crystal structure of HPAs depends on the amount of hydration water. This water can be easily removed on heating, whereby the acid strength is increased due to the dehydration of protons. This is a reversible process accompanied by changing the volume of crystal cell. Unlike the rigid network str ...
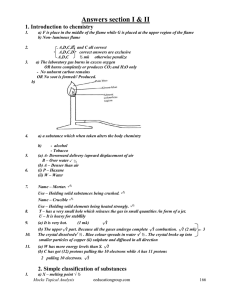
Problem 1-2
... gas C burns with a light blue flame. The elementary analysis of B shows 24.5 % (w/w) of carbon and 28.6 % (w/w) of nitrogen. When annealed with carbon another ionic compound D also results in compound B, too, but without the gas. D reacts with acids to form urea among other substances. The elementar ...
... gas C burns with a light blue flame. The elementary analysis of B shows 24.5 % (w/w) of carbon and 28.6 % (w/w) of nitrogen. When annealed with carbon another ionic compound D also results in compound B, too, but without the gas. D reacts with acids to form urea among other substances. The elementar ...
File
... 37. The hydrides formed by the transfer of electrons from electropositive metals to hydrogen are called __________. (Ionic hydrides, covalent hydrides, Complex hydrides, Interstitial hydrides) 38. NaH is an example of __________. (Ionic hydrides, covalent hydrides, Complex hydrides, Interstitial hyd ...
... 37. The hydrides formed by the transfer of electrons from electropositive metals to hydrogen are called __________. (Ionic hydrides, covalent hydrides, Complex hydrides, Interstitial hydrides) 38. NaH is an example of __________. (Ionic hydrides, covalent hydrides, Complex hydrides, Interstitial hyd ...
www.iitvidya.com salt analysis assignment 1. A compound on
... gives white precipitate which is however soluble in excess of NaOH. An inorganic compound (A), transparent like glass is a strong reducing agent. Its hydrolysis in water gives a white turbidity (B). Aqueous solution of (A) gives white ppt. (C) with NaOH (aq.) which is soluble in excess NaOH. (A) red ...
... gives white precipitate which is however soluble in excess of NaOH. An inorganic compound (A), transparent like glass is a strong reducing agent. Its hydrolysis in water gives a white turbidity (B). Aqueous solution of (A) gives white ppt. (C) with NaOH (aq.) which is soluble in excess NaOH. (A) red ...
György Dombi Gerda Szakonyi Authors
... concentration is determined by the measurement of conductance. This method is used, for example, to check Aqua purificata or Aqua destillata. An electrode is built into the ion-exchange system that continuously monitors the conductance of ion-exchanged water. When the conductance is above a given li ...
... concentration is determined by the measurement of conductance. This method is used, for example, to check Aqua purificata or Aqua destillata. An electrode is built into the ion-exchange system that continuously monitors the conductance of ion-exchanged water. When the conductance is above a given li ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Jamuna Colliery
... into cubic lattice. If the density is 2g/cm3 then find the radius of metal atom (NA = 6.022 x 1023) 5. The density of KBr is 2.75 gm cm -3 . The length of edge of the unit cell is 654 pm. Predict the type of cubic lattice.. NA=6.023 x 1023 ; at mass of K=39: Br. = 80 Ans. Calculate value of z= 4 so ...
... into cubic lattice. If the density is 2g/cm3 then find the radius of metal atom (NA = 6.022 x 1023) 5. The density of KBr is 2.75 gm cm -3 . The length of edge of the unit cell is 654 pm. Predict the type of cubic lattice.. NA=6.023 x 1023 ; at mass of K=39: Br. = 80 Ans. Calculate value of z= 4 so ...
To do List
... If 3.00 liters of a 6.75 M solution of nitric acid are diluted until the new concentration is only 2.04 M, what will be the final volume of this diluted solution? M1V1 = M2V2 ...
... If 3.00 liters of a 6.75 M solution of nitric acid are diluted until the new concentration is only 2.04 M, what will be the final volume of this diluted solution? M1V1 = M2V2 ...
Topical KCSE Mock-Chemistry Answers(15 Schools)
... Adds excess dilute hydrochloric acid/ sulphuric (vi) acid Filter to obtain copper metal Wash with distilled water To separate samples of CUO and charcoal in test tubes, dilute mineral acid is added with shaking CUO black dissolves to form blue solution ½ Charcoal does not dissolve in dilute mineral ...
... Adds excess dilute hydrochloric acid/ sulphuric (vi) acid Filter to obtain copper metal Wash with distilled water To separate samples of CUO and charcoal in test tubes, dilute mineral acid is added with shaking CUO black dissolves to form blue solution ½ Charcoal does not dissolve in dilute mineral ...
Name:
... 3. 30.0 mL of a solution of a diprotic acid, oxalic acid (C 2H2O4), is titrated with 56 mL of a 0.050 mol/L solution of potassium hydroxide. What was the concentration of the oxalic acid? 4. Sketch a graph that represents a titration of a weak acid with a strong base. 5. Sketch a graph that illustra ...
... 3. 30.0 mL of a solution of a diprotic acid, oxalic acid (C 2H2O4), is titrated with 56 mL of a 0.050 mol/L solution of potassium hydroxide. What was the concentration of the oxalic acid? 4. Sketch a graph that represents a titration of a weak acid with a strong base. 5. Sketch a graph that illustra ...
Acid-Base Biochemistry
... a base; thus, AlCl3, BF3, and SO3 are acids. ► The Lewis theory defines an acid as a species that can accept an electron pair from another atom, and a base as a species that can donate an electron pair to complete the valence shell of another atom ...
... a base; thus, AlCl3, BF3, and SO3 are acids. ► The Lewis theory defines an acid as a species that can accept an electron pair from another atom, and a base as a species that can donate an electron pair to complete the valence shell of another atom ...
IIT-JEE (Advanced) - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Calculation of Limiting Reagent : By calculating the required amount by the equation and comparing it with given amount. [Useful when only two reactant are there] By calculating amount of any one product obtained taking each reactant one by one irrespective of other reactants. The one giving least p ...
... Calculation of Limiting Reagent : By calculating the required amount by the equation and comparing it with given amount. [Useful when only two reactant are there] By calculating amount of any one product obtained taking each reactant one by one irrespective of other reactants. The one giving least p ...
National German Competition and Problems of the IChO
... (Account only for the atom orbitals of the valence electrons.) If iodine is dissolved in different solvents the solutions show different colours. Iodine as an electron-pair acceptor forms Lewis acid-base adducts with the molecules of many solvents. These adducts show charge transfer. You can examine ...
... (Account only for the atom orbitals of the valence electrons.) If iodine is dissolved in different solvents the solutions show different colours. Iodine as an electron-pair acceptor forms Lewis acid-base adducts with the molecules of many solvents. These adducts show charge transfer. You can examine ...
Modern inorganic chemistry
... We now know of the existence of over one hundred elements. A century ago, more than sixty of these were already known, and naturally attempts were made to relate the properties of all these elements in some way. One obvious method was to classify them as metals and non-metals; but this clearly did n ...
... We now know of the existence of over one hundred elements. A century ago, more than sixty of these were already known, and naturally attempts were made to relate the properties of all these elements in some way. One obvious method was to classify them as metals and non-metals; but this clearly did n ...
sch103manual - university of nairobi staff profiles
... any of the three states of matter: Solids, liquid or gas. Water for example, exists in the solid state as ice, liquid state as water and in the gaseous state as steam. The physical properties of a substance often depend on the state of the substance. In this section, we will review the states of mat ...
... any of the three states of matter: Solids, liquid or gas. Water for example, exists in the solid state as ice, liquid state as water and in the gaseous state as steam. The physical properties of a substance often depend on the state of the substance. In this section, we will review the states of mat ...
STUDY MATERIAL 2016-17 CHEMISTRY CLASS XII
... Hint- Calculate value of z= 4 so it has fcc lattice 5. CsCl has bcc arrangement and its unit cell edge lenth is 400 pm . calculate the interionic distance of CsCl. Ans. 34604 pm 6. What is the distance between Na+ and Cl- in a NaCl crystal if its density is 2.165 gcm-3 NaCl crystalline in the fcc la ...
... Hint- Calculate value of z= 4 so it has fcc lattice 5. CsCl has bcc arrangement and its unit cell edge lenth is 400 pm . calculate the interionic distance of CsCl. Ans. 34604 pm 6. What is the distance between Na+ and Cl- in a NaCl crystal if its density is 2.165 gcm-3 NaCl crystalline in the fcc la ...
CHAPTER 18
... The rate of the forward reaction decreases accordingly. The concentrations of hydrogen and iodine decrease as they react. As the rates of the opposing reactions become equal, equilibrium is established. The constant color achieved indicates that equilibrium exists among hydrogen, iodine, and hydrog ...
... The rate of the forward reaction decreases accordingly. The concentrations of hydrogen and iodine decrease as they react. As the rates of the opposing reactions become equal, equilibrium is established. The constant color achieved indicates that equilibrium exists among hydrogen, iodine, and hydrog ...
Worked solutions to the problems
... 258 interpretation using a table of group frequencies 259 recognition of hydrogen bonds 260 Raman spectroscopy ...
... 258 interpretation using a table of group frequencies 259 recognition of hydrogen bonds 260 Raman spectroscopy ...
Experimental Chemistry I
... • while stirring bring solution to boiling point, keep adding preheated water until all of the precipitate has dissolved completely; During the course of the dissolving process, MnO2 as a by-product is formed, which must be removed; • warm a funnel and filter by pouring preheated distilled water thr ...
... • while stirring bring solution to boiling point, keep adding preheated water until all of the precipitate has dissolved completely; During the course of the dissolving process, MnO2 as a by-product is formed, which must be removed; • warm a funnel and filter by pouring preheated distilled water thr ...
SQA Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Principles of Chemical
... (Cd2+ ). What weight (in grams to 2 decimal places) of sodium sulphide remains in solution? Q24: The residue from photographic processing equipment is being analysed for its silver ion content by precipitation of silver chloride. The anticipated mass of silver is 0.54 g. How many grams (to 2 decimal ...
... (Cd2+ ). What weight (in grams to 2 decimal places) of sodium sulphide remains in solution? Q24: The residue from photographic processing equipment is being analysed for its silver ion content by precipitation of silver chloride. The anticipated mass of silver is 0.54 g. How many grams (to 2 decimal ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry – Laboratory Techniques
... The primary aim of chemical nomenclature is to provide methodology for assigning descriptors (names and formulae) to chemical species so that they can be identified without ambiguity. The first level of nomenclature, beyond the assignment of totally trivial names, gives some systemic information abo ...
... The primary aim of chemical nomenclature is to provide methodology for assigning descriptors (names and formulae) to chemical species so that they can be identified without ambiguity. The first level of nomenclature, beyond the assignment of totally trivial names, gives some systemic information abo ...
ExamView - 1984 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... If the equilibrium constant for the reaction above is 3.7 × 1015, which of the following correctly describes the standard voltage, E°, and the standard free energy change, ΔG°, for this reaction? A) E° is positive and ΔG° is negative. B) E° is negative and ΔG° is positive. C) E° and ΔG° are both pos ...
... If the equilibrium constant for the reaction above is 3.7 × 1015, which of the following correctly describes the standard voltage, E°, and the standard free energy change, ΔG°, for this reaction? A) E° is positive and ΔG° is negative. B) E° is negative and ΔG° is positive. C) E° and ΔG° are both pos ...
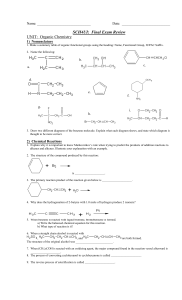
Chapter 4: Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They have -OH groups that can form hydrogen bonds with water. Examples are compounds table sugar, sucrose (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5-OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3-OH). These also are written with “(aq)” when dissolv ...
... Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They have -OH groups that can form hydrogen bonds with water. Examples are compounds table sugar, sucrose (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5-OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3-OH). These also are written with “(aq)” when dissolv ...