The Predictability of the Albanian Infinitive in Geg dialect compared
... In the grammar book designed by Justin Rrota almost fifty years ago, we also notice that instead of the analytical infinitive type me ba there are also other usages substituted by the subjective mood të baj. Scholars think that Fishta’s literary writings and other northern author’s writings, as well ...
... In the grammar book designed by Justin Rrota almost fifty years ago, we also notice that instead of the analytical infinitive type me ba there are also other usages substituted by the subjective mood të baj. Scholars think that Fishta’s literary writings and other northern author’s writings, as well ...
Expressing and Inquiring Expressing and Inquiring volition
... I’d like the food as my starter. I’d like my boyfriend to pick me up. I want my boyfriend to pick me up. I wish I were you. ...
... I’d like the food as my starter. I’d like my boyfriend to pick me up. I want my boyfriend to pick me up. I wish I were you. ...
Summarising Legal Texts - Association for Computational Linguistics
... parliament.uk/judicial_work/judicial_work.cfm ...
... parliament.uk/judicial_work/judicial_work.cfm ...
DISTRIBUTION OF INFINITIVE MARKERS IN ChAUCER`S
... complementation of verbs, Callaway concluded that verbs complemented by accusative objects are more likely to be followed by bare infinitives, and that verbs complemented by objects in the dative or genitive case are more likely to occur with toinfinitives. Verbs that can be followed by either form ...
... complementation of verbs, Callaway concluded that verbs complemented by accusative objects are more likely to be followed by bare infinitives, and that verbs complemented by objects in the dative or genitive case are more likely to occur with toinfinitives. Verbs that can be followed by either form ...
The Computer Project
... Example 1: The driver stopped examining the engine. (=not to examine anymore) Example 2: The driver stopped to examine the engine. (=stopped the car so as to examine) ...
... Example 1: The driver stopped examining the engine. (=not to examine anymore) Example 2: The driver stopped to examine the engine. (=stopped the car so as to examine) ...
Writing Hints
... tuition with money from the G.I. Bill. Graduating Cum Laude with degrees in Business and Social Science, he continued to play trumpet in clubs all over Southern California. Upon marrying Janice Jones, he took a job at California Federal Savings and Loan and was promoted to Senior Vice-President. He ...
... tuition with money from the G.I. Bill. Graduating Cum Laude with degrees in Business and Social Science, he continued to play trumpet in clubs all over Southern California. Upon marrying Janice Jones, he took a job at California Federal Savings and Loan and was promoted to Senior Vice-President. He ...
english handbook
... have been doing something. If I am complaining, for example, I would use this tense: e.g. I have been waiting in the rain for you, and all you do is shrug your shoulders! or: e.g. I have been working on Mr. Horsfield’s essay all morning and still cannot achieve the level of perfection I am aiming fo ...
... have been doing something. If I am complaining, for example, I would use this tense: e.g. I have been waiting in the rain for you, and all you do is shrug your shoulders! or: e.g. I have been working on Mr. Horsfield’s essay all morning and still cannot achieve the level of perfection I am aiming fo ...
Chapter 23: Participles Chapter 23 covers the following: the
... English. Simply put, the Romans used their participles a lot more than we do, both as adjectives and substantives which is to be expected when an adjective’s form naturally indicates number and gender. So dicens (the present active participle of dico) can mean not only “the one speaking” but “the sp ...
... English. Simply put, the Romans used their participles a lot more than we do, both as adjectives and substantives which is to be expected when an adjective’s form naturally indicates number and gender. So dicens (the present active participle of dico) can mean not only “the one speaking” but “the sp ...
Tamil Verb Pattern
... There could be three interrogative forms for each verb form (other than the imperative and optative) and they are not included because they are formed by simple addition at the end of the verb form [ˆ\¥uı⁄ı ‘did he do (it)?’, ˆ\¥uı˜⁄ı ‘did he do (it), I wonder’, ˆ\¥uı˜⁄ ‘he did (it), didn’t he?’]. B ...
... There could be three interrogative forms for each verb form (other than the imperative and optative) and they are not included because they are formed by simple addition at the end of the verb form [ˆ\¥uı⁄ı ‘did he do (it)?’, ˆ\¥uı˜⁄ı ‘did he do (it), I wonder’, ˆ\¥uı˜⁄ ‘he did (it), didn’t he?’]. B ...
docsymp: graduate students` first linguistics symposium
... In sentences ( 1a) and ( 1b) akar 'want' and fo g 'will' are auxiliaries futni 'to run' and el 'away' are verb carriers. The verb szeret 'like' in sentence (lc) functions as a main verb having no verb carrier. In the present paper I argue that these groups of verbs treat not only their own complemen ...
... In sentences ( 1a) and ( 1b) akar 'want' and fo g 'will' are auxiliaries futni 'to run' and el 'away' are verb carriers. The verb szeret 'like' in sentence (lc) functions as a main verb having no verb carrier. In the present paper I argue that these groups of verbs treat not only their own complemen ...
W04-0102 - Association for Computational Linguistics
... class. Neologisms and foreign loan words all fall into it. The second conjugation has far fewer members (17%), which are for the most part irregular (around 95%). The third conjugation is the smallest class (10%). It is mostly regular (around 10% of its verbs are irregular) and only partially produc ...
... class. Neologisms and foreign loan words all fall into it. The second conjugation has far fewer members (17%), which are for the most part irregular (around 95%). The third conjugation is the smallest class (10%). It is mostly regular (around 10% of its verbs are irregular) and only partially produc ...
Year 8 Literacy Skills Builder
... One day she was walking, and the sky was a wonderful ________ (blue/blew) colour. She stopped to admire the pretty view. The _______ (sun/son) was positively gleaming like a jewel. She didn’t notice the approach of a hunched figure with a cloak, carrying a basket of ___________ (flours/flowers). The ...
... One day she was walking, and the sky was a wonderful ________ (blue/blew) colour. She stopped to admire the pretty view. The _______ (sun/son) was positively gleaming like a jewel. She didn’t notice the approach of a hunched figure with a cloak, carrying a basket of ___________ (flours/flowers). The ...
Do sentences have tense?
... stay in morphology. Predicates express the distinctiveness of lexical and pronominal meanings. They are pointers to the semantics. They are projected from the lexicon to f-structure and to semantic structure (σ-structure). Gender features support grammatical and anaphoric agreement. They are project ...
... stay in morphology. Predicates express the distinctiveness of lexical and pronominal meanings. They are pointers to the semantics. They are projected from the lexicon to f-structure and to semantic structure (σ-structure). Gender features support grammatical and anaphoric agreement. They are project ...
Caput primum - utdiscamusomnes
... Audiō, audīre 4, audivī, auditus: to hear Clamo 1: to shout Cognoscō, cognoscere 3, cognovī, cognotus: to get to know, realize, become aware of Credō, credere 3, credidī, creditus: to believe Dicō, dicere 3, dixī, dictus: to say, speak, tell Nego 1: to deny, refuse Ostendō, ostendere 3, ostendī, ons ...
... Audiō, audīre 4, audivī, auditus: to hear Clamo 1: to shout Cognoscō, cognoscere 3, cognovī, cognotus: to get to know, realize, become aware of Credō, credere 3, credidī, creditus: to believe Dicō, dicere 3, dixī, dictus: to say, speak, tell Nego 1: to deny, refuse Ostendō, ostendere 3, ostendī, ons ...
Subject – Verb Agreement - Johnson County Community College
... the topic of the sentence. It names who or what the sentence is about. The subject is always a noun or pronoun (sometimes with added modifiers) and relates directly to the verb of the sentence. The verb of a sentence indicates an action of body or mind, a state of being, or an occurrence. The verb m ...
... the topic of the sentence. It names who or what the sentence is about. The subject is always a noun or pronoun (sometimes with added modifiers) and relates directly to the verb of the sentence. The verb of a sentence indicates an action of body or mind, a state of being, or an occurrence. The verb m ...
Name that Verb
... The boy couldn't find his socks. The helping verb is could and the main verb is find. Do not include “not” as part of the verb. ...
... The boy couldn't find his socks. The helping verb is could and the main verb is find. Do not include “not” as part of the verb. ...
Project-ch.7-andes skiing, exotic beachesW
... and describe where you went and what you did. Here, you will use: at least eight different past tense -AR verbs the irregulars "ir and ser" in the past tense at least three times at least five different past tense signal words at least one -gar, one -zar, one -car verb at least three examp ...
... and describe where you went and what you did. Here, you will use: at least eight different past tense -AR verbs the irregulars "ir and ser" in the past tense at least three times at least five different past tense signal words at least one -gar, one -zar, one -car verb at least three examp ...
The optional infinitive stage and child L2 English
... At the first data collection time relevant examples are scarce but give the appearance of an OI stage (look the map). The second data collection time includes numerous root and present participles forms with (I go to the excursion, dog eating, your . . . he . . . look the map) and without nominal or ...
... At the first data collection time relevant examples are scarce but give the appearance of an OI stage (look the map). The second data collection time includes numerous root and present participles forms with (I go to the excursion, dog eating, your . . . he . . . look the map) and without nominal or ...
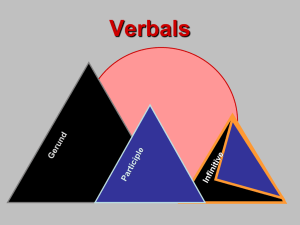
Verbals
... • …is always used as a noun • …is never surrounded by commas (except for appositives) • Caution! -ING verb forms can also be verbs or adjectives (These are NOT gerunds.) • …can be used in each of the 6 noun positions ...
... • …is always used as a noun • …is never surrounded by commas (except for appositives) • Caution! -ING verb forms can also be verbs or adjectives (These are NOT gerunds.) • …can be used in each of the 6 noun positions ...
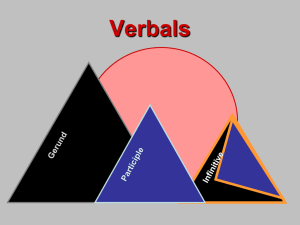
Verbals Powerpoint - Grass Lake Community Schools
... • …is always used as a noun • …is never surrounded by commas (except for appositives) • Caution! -ING verb forms can also be verbs or adjectives (These are NOT gerunds.) • …can be used in each of the 6 noun positions ...
... • …is always used as a noun • …is never surrounded by commas (except for appositives) • Caution! -ING verb forms can also be verbs or adjectives (These are NOT gerunds.) • …can be used in each of the 6 noun positions ...
(Verbs 2)
... because Kelly was not sensing or touching something. In Sentence A, Dawn is again not feeling or sensing anything on her skin, and yet “felt” in this sentence is still an action verb. Again, as we did earlier with the verb “turn,” we are using a metaphorical sense of the verb in saying that Dawn “fe ...
... because Kelly was not sensing or touching something. In Sentence A, Dawn is again not feeling or sensing anything on her skin, and yet “felt” in this sentence is still an action verb. Again, as we did earlier with the verb “turn,” we are using a metaphorical sense of the verb in saying that Dawn “fe ...
do not work. - WordPress.com
... To contradict a negative statement: "You didn't do your homework, did you?" "Oh, but I did finish it." To ask a clarifying question about a previous negative statement: "Ridwell didn't take the tools." "Then who did take the tools?" To indicate a strong concession: "Although the Clintons denied any ...
... To contradict a negative statement: "You didn't do your homework, did you?" "Oh, but I did finish it." To ask a clarifying question about a previous negative statement: "Ridwell didn't take the tools." "Then who did take the tools?" To indicate a strong concession: "Although the Clintons denied any ...