1. Personal Pronouns Personal pronouns tell which person or thing
... Both during and while refer to a period of time in which something happens. For example: - My phone rang while I was in a meeting. - My phone rang during the meeting. During is used with a noun or noun phrase. For example: - We were busy during the weekend. - During the night the cat woke me up. - T ...
... Both during and while refer to a period of time in which something happens. For example: - My phone rang while I was in a meeting. - My phone rang during the meeting. During is used with a noun or noun phrase. For example: - We were busy during the weekend. - During the night the cat woke me up. - T ...
Breaking into the Hebrew verb system: A learning problem
... 2002, 2008; Mintz, 2003, 2006; Ravid, 2012). Table 1 shows, for example, that the infinitival l- ‘to’ is a stable cue across all binyanim. In the same way, m- and h- denote Present and Past Tense respectively in several binyanim. These boundaries also serve to mark agreement with the grammatical sub ...
... 2002, 2008; Mintz, 2003, 2006; Ravid, 2012). Table 1 shows, for example, that the infinitival l- ‘to’ is a stable cue across all binyanim. In the same way, m- and h- denote Present and Past Tense respectively in several binyanim. These boundaries also serve to mark agreement with the grammatical sub ...
GRS LX 700 Language Acquisition and Linguistic Theory
... Sorace notes that the observed cases of attrition of this sort seem to be the ones involved with discourse and pragmatics, not with fundamental grammatical settings. (The attrited Italian is still a null-subject language, for example—null subjects are still possible and used only in places where nul ...
... Sorace notes that the observed cases of attrition of this sort seem to be the ones involved with discourse and pragmatics, not with fundamental grammatical settings. (The attrited Italian is still a null-subject language, for example—null subjects are still possible and used only in places where nul ...
Module 2: Writing about the past
... Write longer pieces of text using conjunctions, complex sentences and paragraphs Use the present perfect form of verbs Write in complex sentences Reply to job advertisements. ...
... Write longer pieces of text using conjunctions, complex sentences and paragraphs Use the present perfect form of verbs Write in complex sentences Reply to job advertisements. ...
Gerunds - Mrs. Burch
... Their functions, however, overlap. Gerunds always function as nouns, but infinitives often also serve as nouns. Deciding which to use can be confusing in many situations, especially for people whose first language is not English. Confusion between gerunds and infinitives occurs primarily in cases in ...
... Their functions, however, overlap. Gerunds always function as nouns, but infinitives often also serve as nouns. Deciding which to use can be confusing in many situations, especially for people whose first language is not English. Confusion between gerunds and infinitives occurs primarily in cases in ...
Negation patterns in Bengali
... forms and is the negative of the zero verb. The zero verb in Bengali has often been interpreted as the absence or omission of a verb form in the present tense. I disagree with this reading and have discussed it in detail in the chapter on verbs of being in my PhD thesis. The zero verb is the true co ...
... forms and is the negative of the zero verb. The zero verb in Bengali has often been interpreted as the absence or omission of a verb form in the present tense. I disagree with this reading and have discussed it in detail in the chapter on verbs of being in my PhD thesis. The zero verb is the true co ...
Analyzing Texts
... Let’s start with the second row, the past feminine singular. We find ‘lá’ in all three columns. We fin ‘lö’ in all three columns of the third row, the past neuter singular, and we find ‘lí’ in all three columns of the fourth row, the past plural. Note also that /l/ occurs in the forms except the pa ...
... Let’s start with the second row, the past feminine singular. We find ‘lá’ in all three columns. We fin ‘lö’ in all three columns of the third row, the past neuter singular, and we find ‘lí’ in all three columns of the fourth row, the past plural. Note also that /l/ occurs in the forms except the pa ...
La Salud - WLWV Staff Blogs
... Ex: Yo hablo=I talk Ex: Yo hablo con mi madre ahora.=I am talking to my mom now. Ex: Yo hablo con mi padre esta noche.=I am going to talk to my dad tonight. The difference in the meaning comes from 2 things; a) using time words to tell you if the action is happening now or in the future b) using the ...
... Ex: Yo hablo=I talk Ex: Yo hablo con mi madre ahora.=I am talking to my mom now. Ex: Yo hablo con mi padre esta noche.=I am going to talk to my dad tonight. The difference in the meaning comes from 2 things; a) using time words to tell you if the action is happening now or in the future b) using the ...
NON-FINITE COMPLEMENTS OF PERCEPTION VERBS Mihaela
... Non-finite verbal complements of perception verbs represent an important type of complementation for this class of verbs. The non-finite clause is formed by a noun phrase functioning as a subject and a non-finite verb (an infinitive, an -ing form). In English nonfinite clauses are of three types: th ...
... Non-finite verbal complements of perception verbs represent an important type of complementation for this class of verbs. The non-finite clause is formed by a noun phrase functioning as a subject and a non-finite verb (an infinitive, an -ing form). In English nonfinite clauses are of three types: th ...
Conditionals
... present simple, zero conditionals. These are the most common. They are used for things that generally happen and are always true; such as scientific truths and generalisations: ...
... present simple, zero conditionals. These are the most common. They are used for things that generally happen and are always true; such as scientific truths and generalisations: ...
I. The Gerund - The Latin Library
... The Gerund is a verbal noun, always active in force. The infintive of the verbs supplies the nominative case: Legere est difficile = To read is difficult (reading is difficult) The other cases are formed by adding -nd- to the present stem of the verb (-iend- for 3rd conjugation I-stems and all 4th c ...
... The Gerund is a verbal noun, always active in force. The infintive of the verbs supplies the nominative case: Legere est difficile = To read is difficult (reading is difficult) The other cases are formed by adding -nd- to the present stem of the verb (-iend- for 3rd conjugation I-stems and all 4th c ...
infinitives and infinitive phrases
... a. Like all adjectives, infinitives acting as adjectives modify NOUNS or PRONOUNS! Examples: The candidate to trust with your vote is Tony. Those are the easiest dogs to train. He has a great ability to paint landscapes. Josephine is the one to win the race! ...
... a. Like all adjectives, infinitives acting as adjectives modify NOUNS or PRONOUNS! Examples: The candidate to trust with your vote is Tony. Those are the easiest dogs to train. He has a great ability to paint landscapes. Josephine is the one to win the race! ...
6B – El subjuntivo con verbos de emoción y duda
... Alegrar de – to make happy Complacer – to please Divertir (ie) – to amuse Encantar – to enchant, to delight Fascinar – to fascinate Gustar – to be pleasing, to appeal (like) Importar – to matter, be important Interesar – to interest Molestar – to bother Parecer bien / mal – to seem right / wrong Pre ...
... Alegrar de – to make happy Complacer – to please Divertir (ie) – to amuse Encantar – to enchant, to delight Fascinar – to fascinate Gustar – to be pleasing, to appeal (like) Importar – to matter, be important Interesar – to interest Molestar – to bother Parecer bien / mal – to seem right / wrong Pre ...
Arabic Semantics - Peter Hallman Home
... contexts is called the ‘present under past’, or ‘sequence of tense’ reading in languages where it is available such as English (Prior 1967, Ladusaw 1977, Dowty 1982, Enç 1987, Ogihara 1995, and many others). In Arabic, simultaneity is expressed by the imperfective. For example, the imperfective ver ...
... contexts is called the ‘present under past’, or ‘sequence of tense’ reading in languages where it is available such as English (Prior 1967, Ladusaw 1977, Dowty 1982, Enç 1987, Ogihara 1995, and many others). In Arabic, simultaneity is expressed by the imperfective. For example, the imperfective ver ...
A Description of the French Nucleus VP Using Co-occurrence
... be dealt with lexically or post-lexically (cf. Heap and Roberge, 2001, §3.3.2). We chose to describe our language with a NooJ syntactic grammar. However, this does not mean that we took a strong position on the lexical/post-lexical issue, for two reasons: (i) our grammar is descriptive only, it is n ...
... be dealt with lexically or post-lexically (cf. Heap and Roberge, 2001, §3.3.2). We chose to describe our language with a NooJ syntactic grammar. However, this does not mean that we took a strong position on the lexical/post-lexical issue, for two reasons: (i) our grammar is descriptive only, it is n ...
Split Infinitive
... II) He seems to have seen better days. III) They are reported to have done this. Note : Perfect infinitive is used after past tense of verbs wish, desire, hope intend , command etc. ...
... II) He seems to have seen better days. III) They are reported to have done this. Note : Perfect infinitive is used after past tense of verbs wish, desire, hope intend , command etc. ...
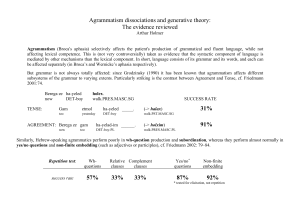
Arthur Holmer
... dissociations depend on the fact that Tense values are inherently underspecified (Tense Underspecification Hypothesis: TUH). A reason for this underspecification would be that Tense establishes a relation between event time and the speech act itself, while agreement only establishes a relation withi ...
... dissociations depend on the fact that Tense values are inherently underspecified (Tense Underspecification Hypothesis: TUH). A reason for this underspecification would be that Tense establishes a relation between event time and the speech act itself, while agreement only establishes a relation withi ...
A corpus study of some rare English verbs
... Span as a past tense of SPIN ‘turn on the spot’ is extremely rare: only one example in the BNC, with another one where span is a form of SPIN ‘make thread’. In general terms both the past tense and past participle of both these verbs is spun. There is a also a verb SPAN, which inflects regularly. Th ...
... Span as a past tense of SPIN ‘turn on the spot’ is extremely rare: only one example in the BNC, with another one where span is a form of SPIN ‘make thread’. In general terms both the past tense and past participle of both these verbs is spun. There is a also a verb SPAN, which inflects regularly. Th ...
A Reference Grammar of Dutch: with Exercises and Key
... direct object The direct recipient of the action described by the verb, e.g. E. I read the book, I saw my friend, D. hij schreef een brief (contrast indirect object). finite verb The part of the verb which may change its form to show person, number and tense. It usually occurs with a subject, e.g. E ...
... direct object The direct recipient of the action described by the verb, e.g. E. I read the book, I saw my friend, D. hij schreef een brief (contrast indirect object). finite verb The part of the verb which may change its form to show person, number and tense. It usually occurs with a subject, e.g. E ...
SABER/CONOCER and PEDIR/PREGUNTAR Pattern: Saber and
... Pattern: Pedir and Preguntar can both mean “to ask,” but they have fundamental differences. The Basics Saber is generally used to express knowledge of facts. Conocer is generally used to express familiarity or acquaintance. Pedir is generally used to make a request. Preguntar is generally used to as ...
... Pattern: Pedir and Preguntar can both mean “to ask,” but they have fundamental differences. The Basics Saber is generally used to express knowledge of facts. Conocer is generally used to express familiarity or acquaintance. Pedir is generally used to make a request. Preguntar is generally used to as ...
spanish and french
... Romance group also included Italian, Portuguese and Romanian. All of these languages developed from dialects of the Latin language which was spread through the region by the Romans (hence the name `Romance’). As English has borrowed many words from Latin, a lot of the vocabulary in Romance languages ...
... Romance group also included Italian, Portuguese and Romanian. All of these languages developed from dialects of the Latin language which was spread through the region by the Romans (hence the name `Romance’). As English has borrowed many words from Latin, a lot of the vocabulary in Romance languages ...
spanish and french
... Romance group also included Italian, Portuguese and Romanian. All of these languages developed from dialects of the Latin language which was spread through the region by the Romans (hence the name `Romance’). As English has borrowed many words from Latin, a lot of the vocabulary in Romance languages ...
... Romance group also included Italian, Portuguese and Romanian. All of these languages developed from dialects of the Latin language which was spread through the region by the Romans (hence the name `Romance’). As English has borrowed many words from Latin, a lot of the vocabulary in Romance languages ...
Chapter 18: The Present Passive System Chapter 18 covers the
... Chapter 18 covers the following: the nature of the passive voice, the formation and translation of the Latin present passive system, the ablative of personal agent, and at the end of the lesson, we’ll review the vocabulary which you should memorize in this chapter. There are three important rules to ...
... Chapter 18 covers the following: the nature of the passive voice, the formation and translation of the Latin present passive system, the ablative of personal agent, and at the end of the lesson, we’ll review the vocabulary which you should memorize in this chapter. There are three important rules to ...
Complete French Grammar
... most basic form of the verb before anything is done to it. In English, infinitives are the to form of the verb, e.g. to play. The infinitive in French can be used in a sentence but it will nearly always be with another verb, e.g. je vais jouer = I am going to play. It is also used to express the –in ...
... most basic form of the verb before anything is done to it. In English, infinitives are the to form of the verb, e.g. to play. The infinitive in French can be used in a sentence but it will nearly always be with another verb, e.g. je vais jouer = I am going to play. It is also used to express the –in ...