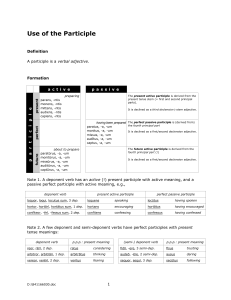
Participles
... oculos iam morte gravatos Pyramus erexit Pyramus opened his eyes, even though they had already been weighed down by death ...
... oculos iam morte gravatos Pyramus erexit Pyramus opened his eyes, even though they had already been weighed down by death ...
湖南省第一师范学院外语系备课用纸
... present habitual action, the infinitive in type II takes the simple form, eg. It is thought that he drives badly. → He is thought to drive badly. If the predicator of the that-clause is the present progressive denoting a present happening, the infinitive in type II takes the progressive form, eg. I ...
... present habitual action, the infinitive in type II takes the simple form, eg. It is thought that he drives badly. → He is thought to drive badly. If the predicator of the that-clause is the present progressive denoting a present happening, the infinitive in type II takes the progressive form, eg. I ...
Verbs as Spatial Deixis Markers in Jingulu1
... melon.species-NU eat-HAB cow-ERG horse-ERG ‘Cows and horses eat this here Kirangkuju melon.’ (versus ‘Cows and horses eat the Kirangkuju melon.’) ...
... melon.species-NU eat-HAB cow-ERG horse-ERG ‘Cows and horses eat this here Kirangkuju melon.’ (versus ‘Cows and horses eat the Kirangkuju melon.’) ...
english grammar
... The O. is a part of the complementation of a verb, a verbal or an adjective within verb, verbal (nonfinite) or adjective phrases. It refers to a person or thing, or a state of affairs which is affected or produced by, or is related to the action or state expressed by the predicate of a sentence. The ...
... The O. is a part of the complementation of a verb, a verbal or an adjective within verb, verbal (nonfinite) or adjective phrases. It refers to a person or thing, or a state of affairs which is affected or produced by, or is related to the action or state expressed by the predicate of a sentence. The ...
Verbals- Gerunds and Participles Gerunds
... Their functions, however, overlap. Gerunds always function as nouns, but infinitives often also serve as nouns. Deciding which to use can be confusing in many situations, especially for people whose first language is not English. Confusion between gerunds and infinitives occurs primarily in cases in ...
... Their functions, however, overlap. Gerunds always function as nouns, but infinitives often also serve as nouns. Deciding which to use can be confusing in many situations, especially for people whose first language is not English. Confusion between gerunds and infinitives occurs primarily in cases in ...
Spanish Pronouns - FunSpanishlearning
... both mean “you” and are used for informal situations. Also, you should have seen “Ud.” This also means you and is an abbreviation of usted. Use Ud. when you are addressing someone in a position of authority over you. Uds. is used in the western hemisphere instead of “vosotros/vosotras”. Uds. is an a ...
... both mean “you” and are used for informal situations. Also, you should have seen “Ud.” This also means you and is an abbreviation of usted. Use Ud. when you are addressing someone in a position of authority over you. Uds. is used in the western hemisphere instead of “vosotros/vosotras”. Uds. is an a ...
THE PASSIVE VOICE
... policy) or passive (The new policy was approved by the executive committee) in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sentence along. In the passive voice, the subject of the sentence is neither a do- ...
... policy) or passive (The new policy was approved by the executive committee) in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sentence along. In the passive voice, the subject of the sentence is neither a do- ...
Subject-verb agreement - Paso Robles High School
... Indefinite pronouns refer to a person or thing whose exact identity is unknown. • Some indefinite pronouns are singular. • Some are plural. • Some may be either singular or plural depending on how they are used. ...
... Indefinite pronouns refer to a person or thing whose exact identity is unknown. • Some indefinite pronouns are singular. • Some are plural. • Some may be either singular or plural depending on how they are used. ...
On the prepositional nature of non
... of them must face a question that has become hotly debated in the recent literature: what is the nature of lexical categories? In GB-based accounts, this issue did not arise, quite simply because the categorial status of an LI was lexically encoded. However, within more recent approaches, this quest ...
... of them must face a question that has become hotly debated in the recent literature: what is the nature of lexical categories? In GB-based accounts, this issue did not arise, quite simply because the categorial status of an LI was lexically encoded. However, within more recent approaches, this quest ...
Verbal Aspect in French Howard B. Garey Language, Vol. 33, No. 2
... must have been, to judge from the testimony of the oldest I E languages, especially Greek, Sanskrit, and OCS. Whatever its origin may have been, it has led to a semantic classification which, once started, has shown itself to be capable of a limitless and most often unsystematic development. Studies ...
... must have been, to judge from the testimony of the oldest I E languages, especially Greek, Sanskrit, and OCS. Whatever its origin may have been, it has led to a semantic classification which, once started, has shown itself to be capable of a limitless and most often unsystematic development. Studies ...
English Grammar Fundamentals for Non
... of these personal pronouns, we use it in different forms: (a) Person. The person refers to whom the subject is about. We have three different persons, and each has a singular form and a plural form. First person refers to a subject that is I, me, my/mine for singular, and we, our, us, for plural. Seco ...
... of these personal pronouns, we use it in different forms: (a) Person. The person refers to whom the subject is about. We have three different persons, and each has a singular form and a plural form. First person refers to a subject that is I, me, my/mine for singular, and we, our, us, for plural. Seco ...
Course Objectives Level 10 Objectives Grammar Reading/Writing
... appropriate for this level and can be integrated with the core objectives Basic Skills Objectives Spells out words (ex. give spelling of name, home country…) Uses basic vocabulary such as days of the week, months of the year and dates (ordinals), as well as vocabulary for performing basic tasks ...
... appropriate for this level and can be integrated with the core objectives Basic Skills Objectives Spells out words (ex. give spelling of name, home country…) Uses basic vocabulary such as days of the week, months of the year and dates (ordinals), as well as vocabulary for performing basic tasks ...
participles - WhippleHill
... having finished her homework are commonly used in English to modify nouns or pronouns, but care must be taken in incorporating such phrases into sentences. Readers will ordinarily associate a participle with the noun, noun phrase, or pronoun adjacent to it, and misplacement may produce comic effects ...
... having finished her homework are commonly used in English to modify nouns or pronouns, but care must be taken in incorporating such phrases into sentences. Readers will ordinarily associate a participle with the noun, noun phrase, or pronoun adjacent to it, and misplacement may produce comic effects ...
Grammar
... 2-We used it when we talk about things happening in a period around now. The action is not finished. Construction : (Am-Is-Are) + Verb + Ing Words : Today -This week -This evening -Look - Listen - Now * Use ... I am doing = Means you have already arranged to do . Past continuous tense : Uses : 1- So ...
... 2-We used it when we talk about things happening in a period around now. The action is not finished. Construction : (Am-Is-Are) + Verb + Ing Words : Today -This week -This evening -Look - Listen - Now * Use ... I am doing = Means you have already arranged to do . Past continuous tense : Uses : 1- So ...
Cognitive processes in grammaticalization
... come up with some interesting new perspectives on the former question.1 Four main findings of this research are listed here: Grammar is not a static, closed or self-contained system, but is highly susceptible to change and highly affected by language use. The loss of grammar is generally acknowledge ...
... come up with some interesting new perspectives on the former question.1 Four main findings of this research are listed here: Grammar is not a static, closed or self-contained system, but is highly susceptible to change and highly affected by language use. The loss of grammar is generally acknowledge ...
Common Usage Problems - Learn English on Skype
... A lot is an informal phrase meaning “a great many,” so you should not use it in formal writing. Alot is a common incorrect spelling. It should never be used; we don’t write alittle, so don’t write alot! Examples: •Allot: My husband allotted a portion of his monthly pay for his sister’s education. •A ...
... A lot is an informal phrase meaning “a great many,” so you should not use it in formal writing. Alot is a common incorrect spelling. It should never be used; we don’t write alittle, so don’t write alot! Examples: •Allot: My husband allotted a portion of his monthly pay for his sister’s education. •A ...
Passive and Active Voices
... or passive (The new policy was approved by the executive committee) in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sentence along. In the passive voice, the subject of the sentence is neither a do-er or a ...
... or passive (The new policy was approved by the executive committee) in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sentence along. In the passive voice, the subject of the sentence is neither a do-er or a ...
74. Colloquial Expressions and Idioms 75. Word Formation
... Many students had read this novel. = This novel had been read by many students. *Notice that in the passive voice, the past participle of werden is worden and not geworden. Durch can replace von when the agent is an impersonal force (fire, wind, etc.); but it cannot be used if preceded by a limiting ...
... Many students had read this novel. = This novel had been read by many students. *Notice that in the passive voice, the past participle of werden is worden and not geworden. Durch can replace von when the agent is an impersonal force (fire, wind, etc.); but it cannot be used if preceded by a limiting ...
Chapter 36: Indirect Command
... became” or “it happened.” Those last two meanings call for different constructions as we’ll see in a second. So, for instance, in arbitrati sumus ab istis factum esse, meaning “We thought it had been done by them,” ab istis (“by them”) is a passive agent with the perfect infinitive of fio. If, howev ...
... became” or “it happened.” Those last two meanings call for different constructions as we’ll see in a second. So, for instance, in arbitrati sumus ab istis factum esse, meaning “We thought it had been done by them,” ab istis (“by them”) is a passive agent with the perfect infinitive of fio. If, howev ...
Verbals ppt
... • Being the boss made Jeff feel uneasy. • Being (gerund) the boss (subject complement for Jeff, via state of being expressed in gerund) ...
... • Being the boss made Jeff feel uneasy. • Being (gerund) the boss (subject complement for Jeff, via state of being expressed in gerund) ...
Second Grade Narrative Rubric
... beginning of the writing Uses details to describe action, thoughts, and feelings Provides a well-developed ...
... beginning of the writing Uses details to describe action, thoughts, and feelings Provides a well-developed ...
Le Passé Composé
... Le Passé Composé In French the same thing happens: we use an expression of time or another (auxiliary) verb to talk about the PAST. For example: J’ai mangé une pomme. or ...
... Le Passé Composé In French the same thing happens: we use an expression of time or another (auxiliary) verb to talk about the PAST. For example: J’ai mangé une pomme. or ...
Translation of Spanish Multiword Expressions into Basque: linguistic
... While Multiword Expressions (MWEs) are constantly used in both oral and written texts, they do not usually follow the common grammatical and lexical rules of languages. Sometimes, the way they are formed is atypical; at other times, their usage in a sentence is non-standard; and sometimes, their mea ...
... While Multiword Expressions (MWEs) are constantly used in both oral and written texts, they do not usually follow the common grammatical and lexical rules of languages. Sometimes, the way they are formed is atypical; at other times, their usage in a sentence is non-standard; and sometimes, their mea ...
Use of `do` as a full verb
... The three verbs are auxiliary (or ‘helping’) verbs when they combine with other verbs to ‘help’ them complete their grammatical functions or meanings. In English, a lot of important meanings are expressed by changes in the verb, for example: questioning, negation, time, completion, continuation, rep ...
... The three verbs are auxiliary (or ‘helping’) verbs when they combine with other verbs to ‘help’ them complete their grammatical functions or meanings. In English, a lot of important meanings are expressed by changes in the verb, for example: questioning, negation, time, completion, continuation, rep ...
Sorani grammar
... KURDISH BELONGS to the Western Iranian group of the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European family. The two principal branches of modern literary Kurdish are (1) Kurmanji, the language of the vast majority of Kurds in Turkey, Syria, Armenia, and Azerbaijan, the area designated by Kurdish nationalis ...
... KURDISH BELONGS to the Western Iranian group of the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European family. The two principal branches of modern literary Kurdish are (1) Kurmanji, the language of the vast majority of Kurds in Turkey, Syria, Armenia, and Azerbaijan, the area designated by Kurdish nationalis ...