INFINITIVES AND PARTICIPLES (INCLUDUNG GERUNDIVE AND …
... – The –ns, -ntis ending for the present participle is normally added to the base used in the Imperfect tense – The verb esse had no present participle in the classical period but a form ens, entis came into use in the Middle Ages. – The common irregular verb eō (go) has u before the nt: iēns, euntis ...
... – The –ns, -ntis ending for the present participle is normally added to the base used in the Imperfect tense – The verb esse had no present participle in the classical period but a form ens, entis came into use in the Middle Ages. – The common irregular verb eō (go) has u before the nt: iēns, euntis ...
INFINITIVES AND PARTICIPLES (INCLUDUNG GERUNDIVE AND
... – The –ns, -ntis ending for the present participle is normally added to the base used in the Imperfect tense – The verb esse had no present participle in the classical period but a form ens, entis came into use in the Middle Ages. – The common irregular verb eō (go) has u before the nt: iēns, euntis ...
... – The –ns, -ntis ending for the present participle is normally added to the base used in the Imperfect tense – The verb esse had no present participle in the classical period but a form ens, entis came into use in the Middle Ages. – The common irregular verb eō (go) has u before the nt: iēns, euntis ...
PECULIARITIES OF USING ACTIVE, PASSIVE AND MIDDLE VOICES
... point that a grammatical meaning of this category is found to be very close to a lexical meaning of the verb by its content (meaning). Difficulty of voice categories is also bound with the point that voice differences often intersect with such notions as transitivity and intransitivity. In the syste ...
... point that a grammatical meaning of this category is found to be very close to a lexical meaning of the verb by its content (meaning). Difficulty of voice categories is also bound with the point that voice differences often intersect with such notions as transitivity and intransitivity. In the syste ...
Campus Academic Resource Program
... “…a verbal that is used as an adjective, modifying a noun or pronoun,” (for a definition of verbal, see the glossary section at the end of this handout). Additionally, a participial phrase can be used as to describe or modify a noun or pronoun (more information on participial phrases is available in ...
... “…a verbal that is used as an adjective, modifying a noun or pronoun,” (for a definition of verbal, see the glossary section at the end of this handout). Additionally, a participial phrase can be used as to describe or modify a noun or pronoun (more information on participial phrases is available in ...
Pronunciation of the Regular Past Tense Endings
... Forms 2 and 3 of regular verbs look and sound the same. Forms 2 and 3 of regular verbs are easy for learners once they have learned some rules of spelling and pronunciation. What should you call these forms? The traditional names are sometimes confusing. For example, Form 5 (ing) is traditional ...
... Forms 2 and 3 of regular verbs look and sound the same. Forms 2 and 3 of regular verbs are easy for learners once they have learned some rules of spelling and pronunciation. What should you call these forms? The traditional names are sometimes confusing. For example, Form 5 (ing) is traditional ...
Lk 10_30 - Amador Bible Studies
... plural aorist active participle of the verb EKDUW, which means “to strip; to take someone’s clothes off of them.” The aorist tense is a constative/historical aorist, which views the action in its entirety as a fact. The active voice indicates that the robbers produced the action. The participle is a ...
... plural aorist active participle of the verb EKDUW, which means “to strip; to take someone’s clothes off of them.” The aorist tense is a constative/historical aorist, which views the action in its entirety as a fact. The active voice indicates that the robbers produced the action. The participle is a ...
WORDS FREQUENTLY CONFUSED A / AN
... My cat sits by me when I watch T.V. She is sitting near the window. I sat by Rick. You have sat in the same seat all term. ...
... My cat sits by me when I watch T.V. She is sitting near the window. I sat by Rick. You have sat in the same seat all term. ...
Prolegomena to ATAM acquisition. Theoretical premises and corpus
... ‘imperfective’. Yet, in each context the language user may assign this ‘tense’ the relevant aspectual interpretation. Indeed, all the relevant semantic dimensions (actionality, temporal reference, aspect and mood) are necessarily detectable in each predicative utterance, although some oppositions ma ...
... ‘imperfective’. Yet, in each context the language user may assign this ‘tense’ the relevant aspectual interpretation. Indeed, all the relevant semantic dimensions (actionality, temporal reference, aspect and mood) are necessarily detectable in each predicative utterance, although some oppositions ma ...
Chapter 25: Indirect Statement Chapter 25 covers the following: the
... real issue here is that the third-conjugation -i present passive infinitive ending is so minimal it’s sometimes hard to recognize that it means “to be (whatever)-ed,” as do all the present passive infinitives. Thus, for example, laudari means “to be praised.” All that should be review for you. Now ...
... real issue here is that the third-conjugation -i present passive infinitive ending is so minimal it’s sometimes hard to recognize that it means “to be (whatever)-ed,” as do all the present passive infinitives. Thus, for example, laudari means “to be praised.” All that should be review for you. Now ...
2º bachillerato: grammar review
... Time clauses referring to the future are formed like the first conditional (present simple in the subordinate clause and future simple in the main clause). What we change are the conjunctions. as long as the moment (that) until before by the time as soon as when Examples: I will phone you when I arr ...
... Time clauses referring to the future are formed like the first conditional (present simple in the subordinate clause and future simple in the main clause). What we change are the conjunctions. as long as the moment (that) until before by the time as soon as when Examples: I will phone you when I arr ...
Module 4 – How to Teach Grammar
... This is an excerpt from a test which checks your students' knowledge of the difference between the present simple and the present continuous: Choose the correct verb form: 1. I take/am taking a bus to school every day. 2. Mary plays/is playing with her friends right now. 3. Michael has/is having two ...
... This is an excerpt from a test which checks your students' knowledge of the difference between the present simple and the present continuous: Choose the correct verb form: 1. I take/am taking a bus to school every day. 2. Mary plays/is playing with her friends right now. 3. Michael has/is having two ...
Document
... A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The linking verbs include: be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, taste Go back to home ...
... A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The linking verbs include: be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, taste Go back to home ...
David Cox – Blog
... Adjectival intensive. aujtov" can also function intensively when it is used adjectivally. In this case aujtov" normally modifies another word and is usually in the predicate position. Translate aujtov" with the reflexive pronoun (himself, herself, itself, themselves, etc.). In this case, aujtov" is ...
... Adjectival intensive. aujtov" can also function intensively when it is used adjectivally. In this case aujtov" normally modifies another word and is usually in the predicate position. Translate aujtov" with the reflexive pronoun (himself, herself, itself, themselves, etc.). In this case, aujtov" is ...
Verbs and their mutations: the genetics of conjugation
... also be a useful and amusing exercise to postulate a Designer of the Italian language. One can deduce, for example, that this mythical Designer was extraordinarily prejudiced against the letter “u” as a marker for verb forms. If only he/she had made systematic use of this perfectly respectable vowel ...
... also be a useful and amusing exercise to postulate a Designer of the Italian language. One can deduce, for example, that this mythical Designer was extraordinarily prejudiced against the letter “u” as a marker for verb forms. If only he/she had made systematic use of this perfectly respectable vowel ...
OMAN COLLEGE of MANAGEMENT and TECHNOLOGY GENERAL
... Nouns and pronouns Common noun Collective noun Number of nouns( conut & uncount nouns) Subject, object &possessive pronouns Verbs and Auxiliary verbs Verb1,2 and 3 Verb to be, have positive and negative in verb1, wh and y/n qns ...
... Nouns and pronouns Common noun Collective noun Number of nouns( conut & uncount nouns) Subject, object &possessive pronouns Verbs and Auxiliary verbs Verb1,2 and 3 Verb to be, have positive and negative in verb1, wh and y/n qns ...
Introduction
... distinguished from a dependent clause which forms only part of another clause or of a phrase. For example: (I clause) He knows everything about it. (D clause) I don't think he knows everything about it. ...
... distinguished from a dependent clause which forms only part of another clause or of a phrase. For example: (I clause) He knows everything about it. (D clause) I don't think he knows everything about it. ...
INFINITIVES AND PARTICIPLES (INCLUDUNG GERUNDIVE AND
... • A verbal noun, identical to the neuter of the gerundive, but used in the active sense. • Equivalent to the English –ing form of the verb when this is used as a noun. In these cases, the –ing form is also called a gerund but when it is used like an adjective it is called a present participle • Can ...
... • A verbal noun, identical to the neuter of the gerundive, but used in the active sense. • Equivalent to the English –ing form of the verb when this is used as a noun. In these cases, the –ing form is also called a gerund but when it is used like an adjective it is called a present participle • Can ...
The Bare Bones
... A singular verb is used with a singular subject. e.g. A dog chews bones. A cat drinks milk. A plural verb is used with a plural subject. e.g. The dogs chew bones. The cats drink milk. Verbs show tense. It is the verb in a sentence that determines when something occurs. Verbs indicate three dif ...
... A singular verb is used with a singular subject. e.g. A dog chews bones. A cat drinks milk. A plural verb is used with a plural subject. e.g. The dogs chew bones. The cats drink milk. Verbs show tense. It is the verb in a sentence that determines when something occurs. Verbs indicate three dif ...
Grammatical Categories
... was wearing a security guard’s uniform. Back in his apartment, where he was living with his mother, he filled his bedroom with priceless works of art. His mother, Mireille, 53, thought all the paintings were copies. One day while they were having supper, the police arrived, and they took Stephane to ...
... was wearing a security guard’s uniform. Back in his apartment, where he was living with his mother, he filled his bedroom with priceless works of art. His mother, Mireille, 53, thought all the paintings were copies. One day while they were having supper, the police arrived, and they took Stephane to ...
GRS LX 700 Language Acquisition and Linguistic Theory
... are simply utterances with an unpronounced modal. This would for the most part make sense. Mommy (should) not go. Eve (will) sit on (the) floor. ...
... are simply utterances with an unpronounced modal. This would for the most part make sense. Mommy (should) not go. Eve (will) sit on (the) floor. ...
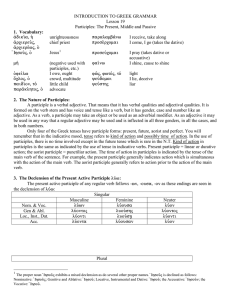
INTRODUCTION TO GREEK GRAMMAR Lesson 19 Participles: The
... Sentence b has an accusative participle because it relates to the accusative noun which is the object of the verb. This participle also shows that the speaking was taking place at the same time as the seeing. It is generally best to translate a participle in the predicate position (when it does not ...
... Sentence b has an accusative participle because it relates to the accusative noun which is the object of the verb. This participle also shows that the speaking was taking place at the same time as the seeing. It is generally best to translate a participle in the predicate position (when it does not ...
УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЙ КОМПЛЕКС
... The problem of potential polysemy in grammar is one of the most important, the one which is very complex and seems to be relevant to a number of aspects. All languages seem to have polysemy on several levels. Like words which are often signs not of one but of several things, a single grammatical for ...
... The problem of potential polysemy in grammar is one of the most important, the one which is very complex and seems to be relevant to a number of aspects. All languages seem to have polysemy on several levels. Like words which are often signs not of one but of several things, a single grammatical for ...
Principal Parts of Verbs
... have (have, has, had). • Examples: She uses her pencil today. (present) She is using her pencil again today. (present participle) She used her pencil. (past) She had used her pencil yesterday. (past participle) ...
... have (have, has, had). • Examples: She uses her pencil today. (present) She is using her pencil again today. (present participle) She used her pencil. (past) She had used her pencil yesterday. (past participle) ...
Gramatica: Unidad 1 Etapa 1
... ENGLISH GRAMMAR CONNECTION: Pronouns are words that take the place of nouns. Subject pronouns indicate who is being described or who does the action in the sentence. We are friends. ...
... ENGLISH GRAMMAR CONNECTION: Pronouns are words that take the place of nouns. Subject pronouns indicate who is being described or who does the action in the sentence. We are friends. ...
Verb Prominence in English and Arabic
... This iterative use of coordination found with verbs and it can also occur with adverbs such as' again ' and the prepositional adverbs 'over, on, up, down, around, etc. 16-I've said it again and again (repeatedly). 17-He kept repeating the name over and over. 18-She talked on and on and on (continuou ...
... This iterative use of coordination found with verbs and it can also occur with adverbs such as' again ' and the prepositional adverbs 'over, on, up, down, around, etc. 16-I've said it again and again (repeatedly). 17-He kept repeating the name over and over. 18-She talked on and on and on (continuou ...