Force as a vector Vectors Pressure Gradient force Pressure gradient
... reversed. • 2) The coriolis force gets weaker near the equator, making long-lasting lows and highs very rare in the tropics. • 3) This result means that low-pressure systems have a hard time “filling up”, since air cannot “get into them”, but rather circles the low ...
... reversed. • 2) The coriolis force gets weaker near the equator, making long-lasting lows and highs very rare in the tropics. • 3) This result means that low-pressure systems have a hard time “filling up”, since air cannot “get into them”, but rather circles the low ...
Composition and Structure of Earth`s Interior
... – Contrast plasma ... – All processes governed by • Atomic arrangement (structure) • Atomic dynamics (bonding) ...
... – Contrast plasma ... – All processes governed by • Atomic arrangement (structure) • Atomic dynamics (bonding) ...
MANUFACTURING PROPERTIES of ENGINEERING MATERIALS
... The elastic limit (proportionality limit) is the stress beyond which there is permanent deformation. Below the elastic limit all the deformation is recovered when the load is removed. The 'elastic limit' of a solid requires careful definition. For metals, the elastic limit is defined as the 0.2% off ...
... The elastic limit (proportionality limit) is the stress beyond which there is permanent deformation. Below the elastic limit all the deformation is recovered when the load is removed. The 'elastic limit' of a solid requires careful definition. For metals, the elastic limit is defined as the 0.2% off ...
fully submerged
... It was developed during the late 1950's and early 1960's by Hess and Smith as a simple numerical tool for calculating potential flows about arbitrarily shaped bodies. The technique consists of discretising the boundary of the structure and associated wakes into a number of elements. From each elemen ...
... It was developed during the late 1950's and early 1960's by Hess and Smith as a simple numerical tool for calculating potential flows about arbitrarily shaped bodies. The technique consists of discretising the boundary of the structure and associated wakes into a number of elements. From each elemen ...
Pressure field and buoyancy. Elementary fluid dynamics. Bernoulli
... On any body in a flowing fluid there is a stagnation point. Some of the fluid flows "over" and some "under" the body. The dividing line (the stagnation streamline) terminates at the stagnation point on the body. As indicated by the dye filaments in the water flowing past a streamlined object, the v ...
... On any body in a flowing fluid there is a stagnation point. Some of the fluid flows "over" and some "under" the body. The dividing line (the stagnation streamline) terminates at the stagnation point on the body. As indicated by the dye filaments in the water flowing past a streamlined object, the v ...
Modeling Inelastic Deformation: Viscoelasticity, Plasticity, Fracture
... of inelastic models t h r o u g h the a p p l i c a t i o n of simple forces. T h e user s t a r t s with a circular viscoelastic model fixed at its center. The model simulates t h e r m o p l a s t i c material. T h e user applies a sustained spring force from p o i n t A. T h e spring (under posit ...
... of inelastic models t h r o u g h the a p p l i c a t i o n of simple forces. T h e user s t a r t s with a circular viscoelastic model fixed at its center. The model simulates t h e r m o p l a s t i c material. T h e user applies a sustained spring force from p o i n t A. T h e spring (under posit ...
Kinetics of plasma refilling during hemodialysis sessions after
... (macro) circulation and HtWB is the whole-body hematocrit, i.e. an average of hematocrit values in micro and macro circulations [7]. The methods of assessing blood volume that rely on hematocrit measurements from the macrocirculation (like online optical absorption) could underestimate the final blo ...
... (macro) circulation and HtWB is the whole-body hematocrit, i.e. an average of hematocrit values in micro and macro circulations [7]. The methods of assessing blood volume that rely on hematocrit measurements from the macrocirculation (like online optical absorption) could underestimate the final blo ...
lecture 4 microwave synthesis of materials
... fluorine) or reduce (in the case of nitrogen) various functional materials. ...
... fluorine) or reduce (in the case of nitrogen) various functional materials. ...
Materials Selection and Design
... Selection involves seeking the best match between the property profiles of the materials in the universe and the property profile required by the design ...
... Selection involves seeking the best match between the property profiles of the materials in the universe and the property profile required by the design ...
Topological Dynamics of Fluids
... where m(h) is a dimensionless function of the dimensionless parameter h, this function being determined solely by the topology of the knot K. The function m(h) (described by Moffatt 1990b as the ‘ground-state’ energy of the ‘framed’ knot) may be determined, in principle, by numerical implementation ...
... where m(h) is a dimensionless function of the dimensionless parameter h, this function being determined solely by the topology of the knot K. The function m(h) (described by Moffatt 1990b as the ‘ground-state’ energy of the ‘framed’ knot) may be determined, in principle, by numerical implementation ...
Section_36_Turbulenc..
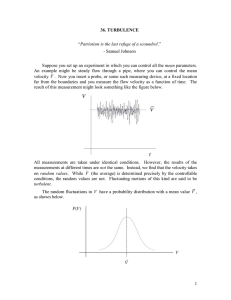
... Suppose you set up an experiment in which you can control all the mean parameters. An example might be steady flow through a pipe, where you can control the mean velocity V . Now you insert a probe, or some such measuring device, at a fixed location far from the boundaries and you measure the flow v ...
... Suppose you set up an experiment in which you can control all the mean parameters. An example might be steady flow through a pipe, where you can control the mean velocity V . Now you insert a probe, or some such measuring device, at a fixed location far from the boundaries and you measure the flow v ...
Topic 2.4.1 and 2.4.2 National income student version
... to _____ the goods and services sold by the firms firms use the factors of production to ________ goods and services households buy the goods with the money they have __________ in working for the firms money passes from firms to households and then back again ...
... to _____ the goods and services sold by the firms firms use the factors of production to ________ goods and services households buy the goods with the money they have __________ in working for the firms money passes from firms to households and then back again ...
simple measurements
... the cylinder? (There is more on this in the section “Activities Using Maple”.) When the marble has reached the bottom of the cylinder you can retrieve it using the tool provided. Go ahead and find the terminal speed v of each marble by releasing it in the fluid and measuring its time of fall between ...
... the cylinder? (There is more on this in the section “Activities Using Maple”.) When the marble has reached the bottom of the cylinder you can retrieve it using the tool provided. Go ahead and find the terminal speed v of each marble by releasing it in the fluid and measuring its time of fall between ...
Week_2
... per unit are perpendicular to it) which is exceeded when the same force is applied to a smaller area. Force is a vector and we can always decompose a vector into its three component. The component perpendicular to the surface is the pressure while the two components parallel to the surface are stres ...
... per unit are perpendicular to it) which is exceeded when the same force is applied to a smaller area. Force is a vector and we can always decompose a vector into its three component. The component perpendicular to the surface is the pressure while the two components parallel to the surface are stres ...
Introduction to fluid dynamics and simulations in COMSOL
... Materials (solids, liquids and gases) are composed of molecules separated by empty space. But the continuum model as a mathematical concept assumes that material exists as a continuous entity. It means that the matter in the body is continuously distributed and fills the entire region of space it oc ...
... Materials (solids, liquids and gases) are composed of molecules separated by empty space. But the continuum model as a mathematical concept assumes that material exists as a continuous entity. It means that the matter in the body is continuously distributed and fills the entire region of space it oc ...