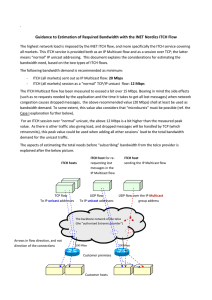
Guidance to Estimation of Required Bandwidth with the INET
... (Megabits per second). This does not necessarily mean that the telco commits to this load as expressed in Mbps. It may be so that the Mbps value is said to be committed if the load is more or less well distributed over the period of time (i.e. over the period being one second), but not if so-called ...
... (Megabits per second). This does not necessarily mean that the telco commits to this load as expressed in Mbps. It may be so that the Mbps value is said to be committed if the load is more or less well distributed over the period of time (i.e. over the period being one second), but not if so-called ...
Simultaneous Chromatography and Electrophoresis: Apparatus Design and Development
... solvent flow. These variables included plate bowing, pressure gaps around the O-ring and electrode channels, and the manually tightened bolt/C-clamp pressure system. In summary, simplifying the apparatus to maximize the uniformity and magnitude of pressure is critical to the pressurized SCE design. ...
... solvent flow. These variables included plate bowing, pressure gaps around the O-ring and electrode channels, and the manually tightened bolt/C-clamp pressure system. In summary, simplifying the apparatus to maximize the uniformity and magnitude of pressure is critical to the pressurized SCE design. ...
Key Points on Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics • Pressure is force per
... Buoyant Forces and Archimedes’ Principle Key Point: The force on an object is an upward force produced by the liquid. A buoyant force is an upward force exerted on an object by the surrounding fluid. Buoyant forces are what keep ships and boats afloat. They also are the reason it’s easier to lift s ...
... Buoyant Forces and Archimedes’ Principle Key Point: The force on an object is an upward force produced by the liquid. A buoyant force is an upward force exerted on an object by the surrounding fluid. Buoyant forces are what keep ships and boats afloat. They also are the reason it’s easier to lift s ...
17-3 Neur Neurosurgical Implants - Sterile, single
... This standard covers requirements for the testing and specification of implantable shunts as related to resistance to flow, direction of flow, materials, radiopacity, mechanical properties, finish, sterility, and labeling of shunt assemblies. The shunt system consists of three basic elements: an in ...
... This standard covers requirements for the testing and specification of implantable shunts as related to resistance to flow, direction of flow, materials, radiopacity, mechanical properties, finish, sterility, and labeling of shunt assemblies. The shunt system consists of three basic elements: an in ...
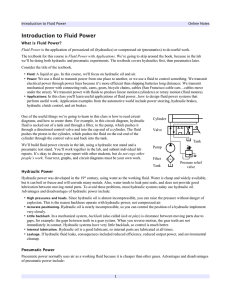
Introduction to Fluid Power
... measure kinematic viscosity of oil in centistokes (1 St = 100 cSt). In the textbook, the author uses “S” for stoke, which is incorrect. The unit of absolute viscosity is therefore ...
... measure kinematic viscosity of oil in centistokes (1 St = 100 cSt). In the textbook, the author uses “S” for stoke, which is incorrect. The unit of absolute viscosity is therefore ...
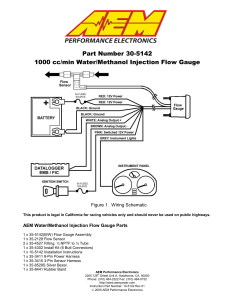
Instructions - AEM Electronics
... Performance products will be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of twelve (12) months from date of the original purchase. Products that fail within this 12-month warranty period will be repaired or replaced at AEM’s option, when determined by AEM that the product failed due t ...
... Performance products will be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of twelve (12) months from date of the original purchase. Products that fail within this 12-month warranty period will be repaired or replaced at AEM’s option, when determined by AEM that the product failed due t ...
chapter14
... Each particle of the fluid follows a smooth path. The paths of the different particles never cross each other. Every given fluid particle arriving at a given point has the same velocity. Turbulent flow An irregular flow characterized by small whirlpool-like regions. Turbulent flow occurs w ...
... Each particle of the fluid follows a smooth path. The paths of the different particles never cross each other. Every given fluid particle arriving at a given point has the same velocity. Turbulent flow An irregular flow characterized by small whirlpool-like regions. Turbulent flow occurs w ...
Changes.
... introduces atomistic and quantum simulation methods and their applications to modeling study nanomaterials (nanoparticles, nanowires, and thin films). The course has three main parts: basic theory of materials (thermodynamics, statistical mechanics, and solid state physics), computational methods to ...
... introduces atomistic and quantum simulation methods and their applications to modeling study nanomaterials (nanoparticles, nanowires, and thin films). The course has three main parts: basic theory of materials (thermodynamics, statistical mechanics, and solid state physics), computational methods to ...
Use of Nanotechnology in Reduction of Friction and Wear
... improvement of nanopolymer composites as lubricants. The polymeric materials have to exhibit good abrasion and wear resistance by mechanical strength, lightness, ease of processing, versatility and low cost, together with acceptable thermal and environmental resistances which are suitable for tribol ...
... improvement of nanopolymer composites as lubricants. The polymeric materials have to exhibit good abrasion and wear resistance by mechanical strength, lightness, ease of processing, versatility and low cost, together with acceptable thermal and environmental resistances which are suitable for tribol ...
Conservation of mass and momentum
... Another important and very large class of fluid flows are the so-called potential flows, defined as flows having a velocity field which is the gradient of a scalar potential, usually denoted by φ: u = ∇φ. ...
... Another important and very large class of fluid flows are the so-called potential flows, defined as flows having a velocity field which is the gradient of a scalar potential, usually denoted by φ: u = ∇φ. ...
chapter15 - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... A water hose 2.50cm in diameter is used by a gardener to fill a 30.0-L bucket. The gardener notes that it takes1.00 min to fill the bucket. A nozzle with an opening of cross-sectional area 0.500cm2 is then attached to the hose. The nozzle is held so that water is projected horizontally from a point ...
... A water hose 2.50cm in diameter is used by a gardener to fill a 30.0-L bucket. The gardener notes that it takes1.00 min to fill the bucket. A nozzle with an opening of cross-sectional area 0.500cm2 is then attached to the hose. The nozzle is held so that water is projected horizontally from a point ...
mechanical_sensors_17august
... All work by measuring the deflection of a solid object by an external pressure. This displacement is then measured, and converted into a pressure reading Membrane sensors can be made very small using micromachining; called microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). ...
... All work by measuring the deflection of a solid object by an external pressure. This displacement is then measured, and converted into a pressure reading Membrane sensors can be made very small using micromachining; called microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). ...
Physics: Principles and Applications
... All work by measuring the deflection of a solid object by an external pressure. This displacement is then measured, and converted into a pressure reading Membrane sensors can be made very small using micromachining; called microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). ...
... All work by measuring the deflection of a solid object by an external pressure. This displacement is then measured, and converted into a pressure reading Membrane sensors can be made very small using micromachining; called microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). ...
Document
... • Still have to enforce mass-conservation constaint: • Standard equation does not take boundary conditions into account – Boundary conditions are things like walls, fluid/air boundaries, rubber duckies, and so on – Have to ‘hack’ the equations…this is hard… ...
... • Still have to enforce mass-conservation constaint: • Standard equation does not take boundary conditions into account – Boundary conditions are things like walls, fluid/air boundaries, rubber duckies, and so on – Have to ‘hack’ the equations…this is hard… ...
Project_fracture_crack.doc
... For solder creep and stress relaxation is significant relative to the initial plastic strains due to yielding, determination of W or p is not straightforward. The total plastic strains increase with time as the strain energy elastically stored in the assembly (component, solder joint, PCB) is c ...
... For solder creep and stress relaxation is significant relative to the initial plastic strains due to yielding, determination of W or p is not straightforward. The total plastic strains increase with time as the strain energy elastically stored in the assembly (component, solder joint, PCB) is c ...
Micro/Nano-Scale Fabrication - Industrial and Systems Engineering
... infinitely rapid, infinitely wide dynamic response. • Zero physical size: Could be installed virtually anywhere, extreme spatial resolution by arrays. • Zero energy. ...
... infinitely rapid, infinitely wide dynamic response. • Zero physical size: Could be installed virtually anywhere, extreme spatial resolution by arrays. • Zero energy. ...
The Weight of Time
... weight will be less (greater) than 10 force of support by the scale. This is N. also what the dial on the scale indiThat acceleration is remarkably cates, and what we call the apparent easy to calculate, using some reasonweight. From impulse considerations able simplifying assumptions. At we can con ...
... weight will be less (greater) than 10 force of support by the scale. This is N. also what the dial on the scale indiThat acceleration is remarkably cates, and what we call the apparent easy to calculate, using some reasonweight. From impulse considerations able simplifying assumptions. At we can con ...
Oxide-ceramic products for high-temperature technology
... ensuing products that can fulfil even the most extreme and complex technical demands. ...
... ensuing products that can fulfil even the most extreme and complex technical demands. ...
Fluids and Fluid Mechanics Fluids in motion – Dynamics Equation of
... fluid moving into point 1. This takes work and the work done to move the fluid into point 1 is given by some applied force and how far into the pipe you need to move the mass of fluid. Thus, W1 = F1Δl1 = P1 A1Δl1 , where P1 is the pressure of the fluid at point 1 and Δl1 is the distance it takes to ...
... fluid moving into point 1. This takes work and the work done to move the fluid into point 1 is given by some applied force and how far into the pipe you need to move the mass of fluid. Thus, W1 = F1Δl1 = P1 A1Δl1 , where P1 is the pressure of the fluid at point 1 and Δl1 is the distance it takes to ...