Lecture 13
... An object immersed in a fluid feels an upward buoyant force that equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Archimedes’s Principle – The fluid pressure increases with depth and exerts forces that are the same whether the submerged object is there or not. – Buoyant forces do not depend o ...
... An object immersed in a fluid feels an upward buoyant force that equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Archimedes’s Principle – The fluid pressure increases with depth and exerts forces that are the same whether the submerged object is there or not. – Buoyant forces do not depend o ...
Introduction to Dental Materials
... They are widely used in dentistry. Polymers versus plastics??? Plastic is any material cabable to be shaped . Ductile metals considered as plastic ...
... They are widely used in dentistry. Polymers versus plastics??? Plastic is any material cabable to be shaped . Ductile metals considered as plastic ...
Influence Ti2O and Ag to exchange of density water and hydrazine 1
... was started by cleaning the substrate through the standard Radio Corporation of America (RCA) method (NH4OH:H2O2:H2O solution with volume ration of 1:1:5) and then rinsed in deionized water.TiO2 layer was deposited on glass substrate using an atmospheric pressure chemical vapor depositing (CVD) syst ...
... was started by cleaning the substrate through the standard Radio Corporation of America (RCA) method (NH4OH:H2O2:H2O solution with volume ration of 1:1:5) and then rinsed in deionized water.TiO2 layer was deposited on glass substrate using an atmospheric pressure chemical vapor depositing (CVD) syst ...
pdf
... » Performance additives, as described below 3 Drymix mortar performance additives With respect to performance additives it is crucial that they are added only in small amounts while having great effects. Performance additives are used for targeted improvement of mortar properties. Their action is ba ...
... » Performance additives, as described below 3 Drymix mortar performance additives With respect to performance additives it is crucial that they are added only in small amounts while having great effects. Performance additives are used for targeted improvement of mortar properties. Their action is ba ...
AP_Physics_B_-_Hydrostatics
... - liquid -Takes the shape of its container, yet has a definite volume. - gas - Takes the shape and volume of its container. ...
... - liquid -Takes the shape of its container, yet has a definite volume. - gas - Takes the shape and volume of its container. ...
Chapter 6. Fluid Mechanics
... It is important to note that motion of the particles that cause the pressure is random in orientation and pressure is therefore isotropic. That is, pressure at one point is the same in all directions. Also, since the pressure at a point is directly proportional to the force effected at that point, i ...
... It is important to note that motion of the particles that cause the pressure is random in orientation and pressure is therefore isotropic. That is, pressure at one point is the same in all directions. Also, since the pressure at a point is directly proportional to the force effected at that point, i ...
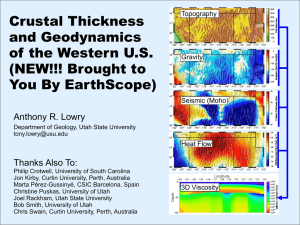
Crustal Thickness of the Western U.S. (NEW!!! Brought
... • Crustal Thickness estimation from EarthScope Transportable ...
... • Crustal Thickness estimation from EarthScope Transportable ...
FLUID MECHANICS PART II(1)
... Using eqution (9) one can calculate the equilibrium velocity of the liquid coming out from a hole in the bottom of the vessel filled upto a height say h . Let us assume that the density of the liquid to be a constant. Let the cross section of the vessel is large and the opening, i.e., the hole is sm ...
... Using eqution (9) one can calculate the equilibrium velocity of the liquid coming out from a hole in the bottom of the vessel filled upto a height say h . Let us assume that the density of the liquid to be a constant. Let the cross section of the vessel is large and the opening, i.e., the hole is sm ...
“ CRANN has a strong affiliation with DePuy, working on cutting
... The interaction between an orthopaedic implant at a cell/tissue interface is a surface phenomenon. Surface properties and material selection play major roles in determining both the biological response to the implant and the material response to the physiological condition. Therefore, it is vital th ...
... The interaction between an orthopaedic implant at a cell/tissue interface is a surface phenomenon. Surface properties and material selection play major roles in determining both the biological response to the implant and the material response to the physiological condition. Therefore, it is vital th ...
Aerodynamics Notes 2
... characteristic of fluid known as kinematic viscosity. Reynolds numbers are used to measure the viscous (Having a thick, sticky consistency between solid and liquid) qualities of a fluid. The symbol Re is used for this number and can be expressed as the equation: Re = V x s ...
... characteristic of fluid known as kinematic viscosity. Reynolds numbers are used to measure the viscous (Having a thick, sticky consistency between solid and liquid) qualities of a fluid. The symbol Re is used for this number and can be expressed as the equation: Re = V x s ...
Reaction coefficient of molecular fluorine at wall coated with
... Various measurements show that the duration of the unstable regime is independent of the deposition thickness. Furthermore, the ignition of F2 plasma after the stability interval, i.e. after the 500 s, leads to a drastic increase of the SiF4 signal. The decrease of the SiF4 signal and the correspond ...
... Various measurements show that the duration of the unstable regime is independent of the deposition thickness. Furthermore, the ignition of F2 plasma after the stability interval, i.e. after the 500 s, leads to a drastic increase of the SiF4 signal. The decrease of the SiF4 signal and the correspond ...
No Slide Title
... • Semiconductors are a class of material between conductors and insulators • Materials such as selenium, copper oxide, and gallium arsenide, are all semiconductors • Of the various semiconductor materials available the two most common are silicon and germanium • Many diodes are manufactured from the ...
... • Semiconductors are a class of material between conductors and insulators • Materials such as selenium, copper oxide, and gallium arsenide, are all semiconductors • Of the various semiconductor materials available the two most common are silicon and germanium • Many diodes are manufactured from the ...
SIMULATION OF FLUID FLOW WITH INTERACTING PARTICLES
... Immobilization of particles may be used as a model of porous medium. The presence of particles in the fluid, assuming their high density, changes significantly the character of the flow, compared to the pure liquid so the classical approach based on Navier-Stokes equations is no longer valid. Despit ...
... Immobilization of particles may be used as a model of porous medium. The presence of particles in the fluid, assuming their high density, changes significantly the character of the flow, compared to the pure liquid so the classical approach based on Navier-Stokes equations is no longer valid. Despit ...
normal force measurement on the rheolyst series AR1000-N
... Normal force during loading The magnitude of these forces will be entirely sample dependent and if not monitored or at least accounted for may lead to reproducibility problems in any subsequent data produced. This effect is particularly noticeable in stiff samples such as polymer melts, which have t ...
... Normal force during loading The magnitude of these forces will be entirely sample dependent and if not monitored or at least accounted for may lead to reproducibility problems in any subsequent data produced. This effect is particularly noticeable in stiff samples such as polymer melts, which have t ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... 1) A solid sphere and a hoop of equal radius and mass are both rolled up an incline with the same initial velocity. Which object will travel farthest up the inclined plane? a) the sphere b) the hoop c) they’ll both travel the same distance up the plane d) it depends on the angle of the incline 2) If ...
... 1) A solid sphere and a hoop of equal radius and mass are both rolled up an incline with the same initial velocity. Which object will travel farthest up the inclined plane? a) the sphere b) the hoop c) they’ll both travel the same distance up the plane d) it depends on the angle of the incline 2) If ...
Raskevicius - NSERC
... rocks south of the Cadillac-Larder Lake fault zone. Generally, Au mineralization is associated with quartz-carbonate-biotite stockworks as well as disseminations in the surrounding altered sedimentary rocks. In an effort to fully categorize the largest recognizable footprint attributable to this dep ...
... rocks south of the Cadillac-Larder Lake fault zone. Generally, Au mineralization is associated with quartz-carbonate-biotite stockworks as well as disseminations in the surrounding altered sedimentary rocks. In an effort to fully categorize the largest recognizable footprint attributable to this dep ...
Intermediate IV Practice Problems Practice Problem 1 Practice
... An IV of D5LR is infusing at 150mL/hr. Calculate the manual infusion rate for macrodrip tubing calibrated at 10gtt/mL. flow rate x drop factor x 1hr/60min = gtt/min – answer 150mL/hr What is the flow rate? Remember the flow rate is how much volume should be administered in a specific amount of ...
... An IV of D5LR is infusing at 150mL/hr. Calculate the manual infusion rate for macrodrip tubing calibrated at 10gtt/mL. flow rate x drop factor x 1hr/60min = gtt/min – answer 150mL/hr What is the flow rate? Remember the flow rate is how much volume should be administered in a specific amount of ...