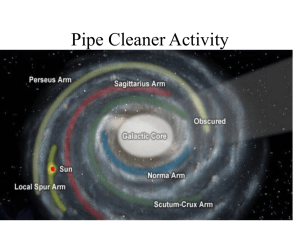
Practice Questions for Final
... B. A spaceship passing near a 10 solar mass black hole is much more likely to be destroyed than a spaceship passing at the same distance from the center of a 10 solar mass mainsequence star. C. If you watch someone else fall into a black hole, you will never see them cross the event horizon. However ...
... B. A spaceship passing near a 10 solar mass black hole is much more likely to be destroyed than a spaceship passing at the same distance from the center of a 10 solar mass mainsequence star. C. If you watch someone else fall into a black hole, you will never see them cross the event horizon. However ...
z - STScI
... forming regions/galaxies that appeared 1 billion years after the Big Bang (to z ~ 5.6) – New stars appear to be forming at roughly a constant rate until very recently (1 < z < 5) – SCUBA may have detected a significant component of dust-hidden star formation at cosmological distances ...
... forming regions/galaxies that appeared 1 billion years after the Big Bang (to z ~ 5.6) – New stars appear to be forming at roughly a constant rate until very recently (1 < z < 5) – SCUBA may have detected a significant component of dust-hidden star formation at cosmological distances ...
Galaxies
... light that has a longer wavelength than it had when it was emitted (a redshift), while observers looking at an approaching source see light that is shifted to shorter wavelength (a blueshift). ...
... light that has a longer wavelength than it had when it was emitted (a redshift), while observers looking at an approaching source see light that is shifted to shorter wavelength (a blueshift). ...
Unit 1
... • Spectra show that interstellar gas clouds are made of mostly hydrogen and helium, just like the Sun • Dust particles do not absorb light the same way that gas atoms do, but using similar methods tells us that the dust is made of silicates ...
... • Spectra show that interstellar gas clouds are made of mostly hydrogen and helium, just like the Sun • Dust particles do not absorb light the same way that gas atoms do, but using similar methods tells us that the dust is made of silicates ...
Unit 1
... • B. they emit a perfect blackbody spectrum • C. no light or any other electromagnetic radiation can escape from inside them • D. their most prominent spectral lines are in the radio ...
... • B. they emit a perfect blackbody spectrum • C. no light or any other electromagnetic radiation can escape from inside them • D. their most prominent spectral lines are in the radio ...
Galaxies - Mike Brotherton
... Measuring the Mass of the Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way By following the orbits of individual stars near the center of the Milky Way, the mass of the central black hole could be determined to be ~ 2.6 million solar masses. ...
... Measuring the Mass of the Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way By following the orbits of individual stars near the center of the Milky Way, the mass of the central black hole could be determined to be ~ 2.6 million solar masses. ...
Section 19.3
... gas, and other objects bound together by gravitational forces. • The sun, along with an estimated 200 billion other stars, belongs to the Milky Way galaxy. ...
... gas, and other objects bound together by gravitational forces. • The sun, along with an estimated 200 billion other stars, belongs to the Milky Way galaxy. ...
color-stellar mass diagram
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
The Milky Way and other Galaxies
... Measuring the Mass of the Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way By following the orbits of individual stars near the center of the Milky Way, the mass of the central black hole could be determined to be ~ 4 million solar masses. ...
... Measuring the Mass of the Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way By following the orbits of individual stars near the center of the Milky Way, the mass of the central black hole could be determined to be ~ 4 million solar masses. ...
Galaxy Formation, Reionization, the First Stars and Quasars
... in lower redshift quasar spectra may change this Possible decrease in the radio-loud fraction at the highest redshifts could indicate a change in the relative accretion modes and spin for the first quasars Most distant QSO (ULAS J112001.48+064124.3), at z = 7.085 has no radio continuum emission — ...
... in lower redshift quasar spectra may change this Possible decrease in the radio-loud fraction at the highest redshifts could indicate a change in the relative accretion modes and spin for the first quasars Most distant QSO (ULAS J112001.48+064124.3), at z = 7.085 has no radio continuum emission — ...
Galaxies[1] - salendinenookphysics
... When we look into the night sky we can see many stars with our naked eye, we see stars in our galaxy, the Milky Way. Scientists believe the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. It is thought there are hundreds of billions of galaxies. ...
... When we look into the night sky we can see many stars with our naked eye, we see stars in our galaxy, the Milky Way. Scientists believe the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. It is thought there are hundreds of billions of galaxies. ...
Kinematics of the galaxies
... Tspin accounts for the electrons that are in the upper state (i.e. those that do not absorb) Higher Tspin more electrons in the upper state higher column density From galactic studies, typical Tspin= 100 K ...
... Tspin accounts for the electrons that are in the upper state (i.e. those that do not absorb) Higher Tspin more electrons in the upper state higher column density From galactic studies, typical Tspin= 100 K ...
Test #4
... a) Their spectra strongly resemble the spectra of stars. b) They are ordinary stars located at vast distances from Earth. c) They look like stars on photographs. d) Like the stars visible in our night sky, quasars reside within the boundaries of the Milky Way. 9. What is implied about an active gala ...
... a) Their spectra strongly resemble the spectra of stars. b) They are ordinary stars located at vast distances from Earth. c) They look like stars on photographs. d) Like the stars visible in our night sky, quasars reside within the boundaries of the Milky Way. 9. What is implied about an active gala ...
galaxy.
... would have to be turning faster than the speed of light. • Spiral nebulae were never seen in the Milky Way: the “zone of avoidance.” Therefore, their distribution acknowledged the geometry of our galaxy, and they must be part of our galaxy. • A nova, S Andromeda, was observed in the Andromeda Nebula ...
... would have to be turning faster than the speed of light. • Spiral nebulae were never seen in the Milky Way: the “zone of avoidance.” Therefore, their distribution acknowledged the geometry of our galaxy, and they must be part of our galaxy. • A nova, S Andromeda, was observed in the Andromeda Nebula ...
23.cosmology-student
... • What is the power source for quasars and other active galactic nuclei? – The only model that adequately explains the observations holds that supermassive black holes are the power source ...
... • What is the power source for quasars and other active galactic nuclei? – The only model that adequately explains the observations holds that supermassive black holes are the power source ...
Star Systems and Galaxies
... Smaller than other galaxies Many bright, young stars Lots of gas and dust to form new stars ...
... Smaller than other galaxies Many bright, young stars Lots of gas and dust to form new stars ...
Question 1 The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears
... . The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears brighter through a blue filter than it does through a yellow filter. Suppose that a second star is found that has the same brightness as Regulus through the blue filter but is brighter than Regulus through the yellow filter. From this informati ...
... . The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears brighter through a blue filter than it does through a yellow filter. Suppose that a second star is found that has the same brightness as Regulus through the blue filter but is brighter than Regulus through the yellow filter. From this informati ...
Section 28.2 - CPO Science
... 28.2 The central black hole theory The minimum speed an unpowered projectile must have to escape the planet’s gravity is called the escape velocity. A black hole is an object with such strong gravity that its escape velocity equals or exceeds the speed of light. ...
... 28.2 The central black hole theory The minimum speed an unpowered projectile must have to escape the planet’s gravity is called the escape velocity. A black hole is an object with such strong gravity that its escape velocity equals or exceeds the speed of light. ...
Hubble`s Classification of Galaxies (PDF version)
... Hubble now set out to derive distances to as many of the nebulae (now called ‘galaxies’) as he could. (He did this using Cepheids where possible, but also by other means.) He noted that the nebulae do not all look the same. What sorts of galaxies exist? Can they be classified in some useful way? Wha ...
... Hubble now set out to derive distances to as many of the nebulae (now called ‘galaxies’) as he could. (He did this using Cepheids where possible, but also by other means.) He noted that the nebulae do not all look the same. What sorts of galaxies exist? Can they be classified in some useful way? Wha ...
Slide 1
... distances to remote galaxies is difficult, but measuring Doppler shifts (velocities) is easier from spectra • Use Hubble’s Law to estimate biggest distances (really LOOKBACK TIME)! ...
... distances to remote galaxies is difficult, but measuring Doppler shifts (velocities) is easier from spectra • Use Hubble’s Law to estimate biggest distances (really LOOKBACK TIME)! ...
The Universe – Powerpoint
... Edwin Hubble was an American Astronomer who helped in creating the theory about extragalactic astronomy. He also provided evidence that many things back then called Nebulae were actually galaxies past the Milky Way. ...
... Edwin Hubble was an American Astronomer who helped in creating the theory about extragalactic astronomy. He also provided evidence that many things back then called Nebulae were actually galaxies past the Milky Way. ...
Rich and Poor Galaxy Clusters
... – Can have clouds of gas near them, or jets racing from their cores – Spectra are heavily redshifted, meaning they are very far away – Energy output is equivalent to one supernova going off every hour! ...
... – Can have clouds of gas near them, or jets racing from their cores – Spectra are heavily redshifted, meaning they are very far away – Energy output is equivalent to one supernova going off every hour! ...
Test 3 Version 3 1. Milky Way halo stars follow: (a) differential
... 2. Which of the following is false: The Milky Way is (a) diffuse band of light across the sky, (b) a spiral galaxy, (c) the galaxy the sun is in, (d) the nearest galaxy outside our own. 3. Which one of the following statements is true? (a) stars in the halo are deficient in heavy elements, (b) stars ...
... 2. Which of the following is false: The Milky Way is (a) diffuse band of light across the sky, (b) a spiral galaxy, (c) the galaxy the sun is in, (d) the nearest galaxy outside our own. 3. Which one of the following statements is true? (a) stars in the halo are deficient in heavy elements, (b) stars ...
Document
... Stellar Birthrate: Ellipticals have older stars than spirals No significant star formation after 1 billion years ...
... Stellar Birthrate: Ellipticals have older stars than spirals No significant star formation after 1 billion years ...
Lecture Notes – Galaxies
... Discovered in the 1940s by Carl Seyfert and appear as normal spirals but with very bright nuclei and emit strong non-thermal spectrum. The visible spectrum contains broad (5 000–10 000 km/s) emission lines indicating clouds of gas moving at very high speeds in the nucleus of the galaxy. 1% of spiral ...
... Discovered in the 1940s by Carl Seyfert and appear as normal spirals but with very bright nuclei and emit strong non-thermal spectrum. The visible spectrum contains broad (5 000–10 000 km/s) emission lines indicating clouds of gas moving at very high speeds in the nucleus of the galaxy. 1% of spiral ...
Quasar

Quasars (/ˈkweɪzɑr/) or quasi-stellar radio sources are the most energetic and distant members of a class of objects called active galactic nuclei (AGN). Quasars are extremely luminous and were first identified as being high redshift sources of electromagnetic energy, including radio waves and visible light, that appeared to be similar to stars, rather than extended sources similar to galaxies. Their spectra contain very broad emission lines, unlike any known from stars, hence the name ""quasi-stellar."" Their luminosity can be 100 times greater than that of the Milky Way. Most quasars were formed approximately 12 billion years ago caused by collisions of galaxies and their central black holes merging to form either a supermassive black hole or a Binary black hole system.Although the true nature of these objects was controversial until the early 1980s, there is now a scientific consensus that a quasar is a compact region in the center of a massive galaxy surrounding a central supermassive black hole. Its size is 10–10,000 times the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole. The energy emitted by a quasar derives from mass falling onto the accretion disc around the black hole.








![Galaxies[1] - salendinenookphysics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008083907_1-b5969f7f2ab35a1d0e21378b751ce81e-300x300.png)