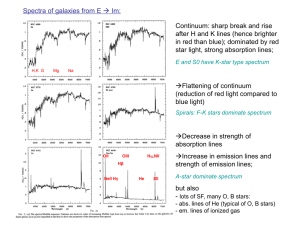
1201 Discussion Notes
... although we didn’t call them by name, and how they indicated that most of the mass in our galaxy is in the halo. Remember, if most of the mass is in the halo, the orbital periods of the stars closer to the edge of the disk would have to be about the same as the stars near the bulge (i.e. their veloc ...
... although we didn’t call them by name, and how they indicated that most of the mass in our galaxy is in the halo. Remember, if most of the mass is in the halo, the orbital periods of the stars closer to the edge of the disk would have to be about the same as the stars near the bulge (i.e. their veloc ...
Lecture #2
... (near-IR, in this case) but there’s no guarantee that the morphological type will be the same in the visible (here Hubble sequence is defined) and the other wavelengths. On the contrary, there are sometimes bars and rings which are revealed only in the UV, IR, or radio wavelengths. ...
... (near-IR, in this case) but there’s no guarantee that the morphological type will be the same in the visible (here Hubble sequence is defined) and the other wavelengths. On the contrary, there are sometimes bars and rings which are revealed only in the UV, IR, or radio wavelengths. ...
Sample Exam 3
... the Milky Way to estimate the structure of the star system in which we live. From this evidence they concluded that A) the Sun was near the middle of a disk-like system of millions of stars. B) stars existed out to such large distances that the Universe must be infinite. C) the Sun was on the outer ...
... the Milky Way to estimate the structure of the star system in which we live. From this evidence they concluded that A) the Sun was near the middle of a disk-like system of millions of stars. B) stars existed out to such large distances that the Universe must be infinite. C) the Sun was on the outer ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... telescopes, spiral galaxies looked a lot like blurry, perhaps gaseous objects. Hence the idea that they’re much smaller parts of the Milky Way. ...
... telescopes, spiral galaxies looked a lot like blurry, perhaps gaseous objects. Hence the idea that they’re much smaller parts of the Milky Way. ...
5X_Measuring_galaxy_redshifts
... One technique is to locate the image in the focal plane in register with that of a metal plate, prepared with drilled holes. Fibres are plugged into the holes. The 2dF/6dF systems (British-Australian) have the fibres connected to magnetic buttons (with miniature prisms). A robot sets up the field be ...
... One technique is to locate the image in the focal plane in register with that of a metal plate, prepared with drilled holes. Fibres are plugged into the holes. The 2dF/6dF systems (British-Australian) have the fibres connected to magnetic buttons (with miniature prisms). A robot sets up the field be ...
A Universe of Galaxies
... “stars” that were very bright at radio wavelengths (normal stars do not produce much radio emission). They were named quasi-stellar radio sources (quasars): ...
... “stars” that were very bright at radio wavelengths (normal stars do not produce much radio emission). They were named quasi-stellar radio sources (quasars): ...
lecture2_3
... •Study their motions, measure their speeds •Fundamental to understand the evolution of the sources and how their interact with each other (e.g. merging, collisions) •Measure their redshift, determine their distance from us •Fundamental to chart the large-scale structure of the Universe and to study ...
... •Study their motions, measure their speeds •Fundamental to understand the evolution of the sources and how their interact with each other (e.g. merging, collisions) •Measure their redshift, determine their distance from us •Fundamental to chart the large-scale structure of the Universe and to study ...
Ground-based Astronomy: Past, Present, and Future
... We can use curved 2-d surfaces to model curved 3-d space The surfaces stand for the flat equatorial plane around a condensed object like a dense star or a black hole. Walking uphill (outwards) is analogous to moving radially outward from the dense object. Note that you walk a long way on the surfac ...
... We can use curved 2-d surfaces to model curved 3-d space The surfaces stand for the flat equatorial plane around a condensed object like a dense star or a black hole. Walking uphill (outwards) is analogous to moving radially outward from the dense object. Note that you walk a long way on the surfac ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... • So…. What’s the maximum size that the light emitting region could possibly be? Think in terms of physics we’ve learned. ...
... • So…. What’s the maximum size that the light emitting region could possibly be? Think in terms of physics we’ve learned. ...
The Milky Way - Zumbroclassroom
... light years across, and _______ light years deep- it is quite large! It contains approximately _______ stars. Amazingly, there are many other galaxies besides the Milky Way. The name “Milky Way” comes from ___________, who called the white streak across the heavens a ______ of _______. _________ was ...
... light years across, and _______ light years deep- it is quite large! It contains approximately _______ stars. Amazingly, there are many other galaxies besides the Milky Way. The name “Milky Way” comes from ___________, who called the white streak across the heavens a ______ of _______. _________ was ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... galaxies are outlying members. Here galaxies are so numerous that they seem to outnumber the visible stars. Estimates of the total number are between 1,200 and 2,000 and the average distance is 53 million light years (a light year is about 10 trillion kilometres). As with virtually all clusters of g ...
... galaxies are outlying members. Here galaxies are so numerous that they seem to outnumber the visible stars. Estimates of the total number are between 1,200 and 2,000 and the average distance is 53 million light years (a light year is about 10 trillion kilometres). As with virtually all clusters of g ...
ASTRONOMY 0089: EXAM 3 Class Meets M,W,F, 1:00 PM April 19
... Now answer all 46 questions. Students should choose the best answer of those given. There is only one correct answer for each question. Read all questions carefully before answering. INSTRUCTIONS: ...
... Now answer all 46 questions. Students should choose the best answer of those given. There is only one correct answer for each question. Read all questions carefully before answering. INSTRUCTIONS: ...
Cosmic Dawn A Hunting for the First Stars in the Universe
... since their light has traveled for the longest time to reach us. Even the largest telescopes cannot detect individual stars from the early universe, but effective techniques have been developed to measure very trace concentrations of chemicals in the cosmic web. This provides us with a powerful, ind ...
... since their light has traveled for the longest time to reach us. Even the largest telescopes cannot detect individual stars from the early universe, but effective techniques have been developed to measure very trace concentrations of chemicals in the cosmic web. This provides us with a powerful, ind ...
Star Groups and Big Bang Power Point
... The Expanding Universe Using Hubble’s observations, astronomers have been able to determine that the universe is expanding. The expanding universe can be thought of as a raisin cake rising in the oven. If you were able to sit on one raisin, you would see all the other raisins moving away from y ...
... The Expanding Universe Using Hubble’s observations, astronomers have been able to determine that the universe is expanding. The expanding universe can be thought of as a raisin cake rising in the oven. If you were able to sit on one raisin, you would see all the other raisins moving away from y ...
Universe and Galaxy Short Study Guide
... Black holes in the centers of giant galaxies—some more than one billion solar masses—had enough infalling gas to once blaze as quasars. The final mass of a black hole is not primordial, but instead is determined during the galaxy formation process. This shows that there is a close relationship betwe ...
... Black holes in the centers of giant galaxies—some more than one billion solar masses—had enough infalling gas to once blaze as quasars. The final mass of a black hole is not primordial, but instead is determined during the galaxy formation process. This shows that there is a close relationship betwe ...
Introduction to Active Galactic Nuclei
... • Detection of an optical jet in M87 (Curtis 1913) • Same period: Einstein develops GR, Schwarzschild metric (1916), but no connection seen yet • Hubble (1926) - Nebulae are extragalactic (galaxies) • Carl Seyfert (1943) - found several galaxies similar to NGC1068 (henceforth named Seyfert galaxies) ...
... • Detection of an optical jet in M87 (Curtis 1913) • Same period: Einstein develops GR, Schwarzschild metric (1916), but no connection seen yet • Hubble (1926) - Nebulae are extragalactic (galaxies) • Carl Seyfert (1943) - found several galaxies similar to NGC1068 (henceforth named Seyfert galaxies) ...
The Universe - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
The Universe
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
AY1 Homework for Quiz 3: Spring 2017
... 13. What is believed to be the source of energy for QSOs and Active Galactic Nuclei radiation (check all that are true)? ___ material being heated as it is falling into a supermassive black hole ...
... 13. What is believed to be the source of energy for QSOs and Active Galactic Nuclei radiation (check all that are true)? ___ material being heated as it is falling into a supermassive black hole ...
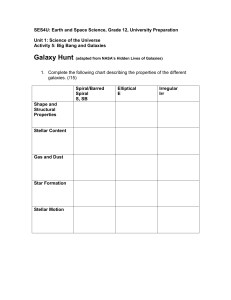
Galaxy Hunt Assignment.
... 2. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. Using the Internet or other resources, research answers to the following questions. ...
... 2. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. Using the Internet or other resources, research answers to the following questions. ...
Measuring the Masses of Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
... the redshift is measured from the observed positions of atomic lines in the spectra of galaxies and quasars for example, the red line of hydrogen (Hα) has a wavelength of 6.563 × 10-5 cm, 6563 Ångstroms, 656.3 nm suppose it were observed at 6603 Ångstroms (1 + z) = 6603 / 6563 = 1.0061 all other li ...
... the redshift is measured from the observed positions of atomic lines in the spectra of galaxies and quasars for example, the red line of hydrogen (Hα) has a wavelength of 6.563 × 10-5 cm, 6563 Ångstroms, 656.3 nm suppose it were observed at 6603 Ångstroms (1 + z) = 6603 / 6563 = 1.0061 all other li ...
Name ______KEY Date Core ______ Study Guide Galaxies and the
... When did the Big Bang happen and what has happened since? The big bang theory is theorized to have happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than ...
... When did the Big Bang happen and what has happened since? The big bang theory is theorized to have happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than ...
Document
... Both sources looked like normal stars – “quasi-stellar objects or QSOs” They appeared bluer than normal stars with strong, broad emission lines. ...
... Both sources looked like normal stars – “quasi-stellar objects or QSOs” They appeared bluer than normal stars with strong, broad emission lines. ...
Astr 40 Final Exam Review ()
... 8. A star is about 5300 light years away from us. If this star underwent a supernova explosion right now, approximately how long would it be until we found out about it? 5300 years. 9. The most important reason for measuring the parallax of a star is to help us find the stars intrinsic brightness (a ...
... 8. A star is about 5300 light years away from us. If this star underwent a supernova explosion right now, approximately how long would it be until we found out about it? 5300 years. 9. The most important reason for measuring the parallax of a star is to help us find the stars intrinsic brightness (a ...
Quasar

Quasars (/ˈkweɪzɑr/) or quasi-stellar radio sources are the most energetic and distant members of a class of objects called active galactic nuclei (AGN). Quasars are extremely luminous and were first identified as being high redshift sources of electromagnetic energy, including radio waves and visible light, that appeared to be similar to stars, rather than extended sources similar to galaxies. Their spectra contain very broad emission lines, unlike any known from stars, hence the name ""quasi-stellar."" Their luminosity can be 100 times greater than that of the Milky Way. Most quasars were formed approximately 12 billion years ago caused by collisions of galaxies and their central black holes merging to form either a supermassive black hole or a Binary black hole system.Although the true nature of these objects was controversial until the early 1980s, there is now a scientific consensus that a quasar is a compact region in the center of a massive galaxy surrounding a central supermassive black hole. Its size is 10–10,000 times the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole. The energy emitted by a quasar derives from mass falling onto the accretion disc around the black hole.