- ORIGINS Space Telescope
... comprises less than one-hundredth of one percent of the baryonic mass of the Universe, yet approximately one-half of all energy radiated by stars and accreting black holes over its history has been reprocessed by dust to long wavelengths. Dust shrouds the most intense regions of black hole accretion ...
... comprises less than one-hundredth of one percent of the baryonic mass of the Universe, yet approximately one-half of all energy radiated by stars and accreting black holes over its history has been reprocessed by dust to long wavelengths. Dust shrouds the most intense regions of black hole accretion ...
Galaxies have different sizes and shapes.
... centers. The mass of a supermassive black hole can be millions or even billions of times greater than that of the Sun. At the center of the Milky Way, for example, is a black hole with a mass about three million times that of the Sun. Like all black holes, a supermassive black hole is invisible. Ast ...
... centers. The mass of a supermassive black hole can be millions or even billions of times greater than that of the Sun. At the center of the Milky Way, for example, is a black hole with a mass about three million times that of the Sun. Like all black holes, a supermassive black hole is invisible. Ast ...
Galaxy Classification
... Elliptical galaxies are affectionately called “E” galaxies. They can be extremely large and massive. This galaxy is 2 million light years across. The size of the Milky Way in comparison! ...
... Elliptical galaxies are affectionately called “E” galaxies. They can be extremely large and massive. This galaxy is 2 million light years across. The size of the Milky Way in comparison! ...
Galaxies
... • In space, nebulas are giant clouds of gas and dust. • Some types of nebulas glow by themselves, while others absorb light and hide stars. • Some nebulas are regions where new stars form (like the Eagle nebula to the left). • Spiral galaxies generally contain nebulas, but elliptical galaxies do not ...
... • In space, nebulas are giant clouds of gas and dust. • Some types of nebulas glow by themselves, while others absorb light and hide stars. • Some nebulas are regions where new stars form (like the Eagle nebula to the left). • Spiral galaxies generally contain nebulas, but elliptical galaxies do not ...
galaxies, galaxies, galaxies!
... Elliptical galaxies are affectionately called “E” galaxies. They can be extremely large and massive. This galaxy is 2 million light years across. The size of the Milky Way in comparison! ...
... Elliptical galaxies are affectionately called “E” galaxies. They can be extremely large and massive. This galaxy is 2 million light years across. The size of the Milky Way in comparison! ...
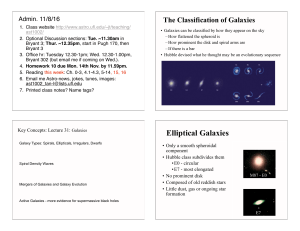
Elliptical Galaxies
... • Release gravitational energy as matter falls in • Rotating matter organizes into a disk • Hot inner parts of disk emit brightly in x-ray-optical ...
... • Release gravitational energy as matter falls in • Rotating matter organizes into a disk • Hot inner parts of disk emit brightly in x-ray-optical ...
ALMA_BoJun605_Gruppioni
... "edge-on" galaxy NGC 891, where the dust correlates well with the CO emission up to a radius of 25 thousand light-years from the center of the galaxy. ...
... "edge-on" galaxy NGC 891, where the dust correlates well with the CO emission up to a radius of 25 thousand light-years from the center of the galaxy. ...
nasafinal - University of Oregon
... initial research money granted by the OSGC, we were able to successfully acquire observing time during cycle 4 of the GALEX emission. However, various technical issues associated with the data pipeline processing of our images, delayed the release of that data by approximately one year. Indeed, it w ...
... initial research money granted by the OSGC, we were able to successfully acquire observing time during cycle 4 of the GALEX emission. However, various technical issues associated with the data pipeline processing of our images, delayed the release of that data by approximately one year. Indeed, it w ...
Exercise 8
... How accurate were you? Is the criterion or criteria you used a good way to find galaxy distances? ...
... How accurate were you? Is the criterion or criteria you used a good way to find galaxy distances? ...
main characteristics of the emission from elliptical galaxies
... primarly due to a halo of extremely hot gas in which ellipticals seem to be embedded. After a brief classi cation, the two main processes linked to these phenomena will be described, together with the informations we can collect thanks to them. Eventually, we will take a quick look at the other regi ...
... primarly due to a halo of extremely hot gas in which ellipticals seem to be embedded. After a brief classi cation, the two main processes linked to these phenomena will be described, together with the informations we can collect thanks to them. Eventually, we will take a quick look at the other regi ...
Document
... Accretion disk of hot gas Jets High velocity clouds Thick torus of gas, dust & stars Low velocity clouds ...
... Accretion disk of hot gas Jets High velocity clouds Thick torus of gas, dust & stars Low velocity clouds ...
Lecture 8 - University of Sydney
... Accretion disk of hot gas Jets High velocity clouds Thick torus of gas, dust & stars Low velocity clouds ...
... Accretion disk of hot gas Jets High velocity clouds Thick torus of gas, dust & stars Low velocity clouds ...
The Transient Radio Sky Astrophysical and Artificial
... A Molecular Einstein Ring: VLA 45 GHz observations of CO2-1 emission from the gravitationally lensed QSO 2322+1944 at z=4.12 (Carilli et al. 2003) Keck Rband ...
... A Molecular Einstein Ring: VLA 45 GHz observations of CO2-1 emission from the gravitationally lensed QSO 2322+1944 at z=4.12 (Carilli et al. 2003) Keck Rband ...
Galaxies - senwiki
... that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers believe that each galaxy contains at least one supermassive black hole at its centre. ...
... that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers believe that each galaxy contains at least one supermassive black hole at its centre. ...
Galaxies Powerpoint
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Main Types of Galaxies
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... approximately 100 new stars per year. LIRGs are effect, the frequency scale of the spectrum was converted into velocity scale. The velocity width of the result of mix or collisions of galaxies. the line is related to the rotational speed of the HI Line : Neutral hydrogen in galaxies emit a line gala ...
... approximately 100 new stars per year. LIRGs are effect, the frequency scale of the spectrum was converted into velocity scale. The velocity width of the result of mix or collisions of galaxies. the line is related to the rotational speed of the HI Line : Neutral hydrogen in galaxies emit a line gala ...
Does size matter (in the SFRs)?
... sented the results on the SFRs of two small spiral galaxies with very similar HI content but with different size. According to Kennicutt (1998) they both should be galaxies are more the same locations of the graph, and have very similar values of the SFRs. On the contrary of course, UGC 5296 is not ...
... sented the results on the SFRs of two small spiral galaxies with very similar HI content but with different size. According to Kennicutt (1998) they both should be galaxies are more the same locations of the graph, and have very similar values of the SFRs. On the contrary of course, UGC 5296 is not ...
Hubble Space Telescope Image
... researchers. They believe it may be an extremely remote object made visible by the cluster's magnifying powers. This is the second time Hubble observed this cluster. ...
... researchers. They believe it may be an extremely remote object made visible by the cluster's magnifying powers. This is the second time Hubble observed this cluster. ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... which Mkn 205 is 14 times farther away at a distance of 1 billion light year. The very distant quasar is nearly as bright as the much closer galaxy. The extraordinary brightness of quasars, which is a blending of the term quasi-stellar radio source, indicates that some incredibly powerful mechanism ...
... which Mkn 205 is 14 times farther away at a distance of 1 billion light year. The very distant quasar is nearly as bright as the much closer galaxy. The extraordinary brightness of quasars, which is a blending of the term quasi-stellar radio source, indicates that some incredibly powerful mechanism ...
- Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
... Then neutron stars and black holes in accreting binaries were discovered to be strong x-ray emitters – 10 orders of magnitude greater! ...
... Then neutron stars and black holes in accreting binaries were discovered to be strong x-ray emitters – 10 orders of magnitude greater! ...
GAIA Composition, Formation and Evolution of our Galaxy
... – clean Hertzsprung-Russell sequences throughout the Galaxy – solar neighbourhood mass function and luminosity function e.g. white dwarfs (~200,000) and brown dwarfs (~50,000) – initial mass and luminosity functions in star forming regions ...
... – clean Hertzsprung-Russell sequences throughout the Galaxy – solar neighbourhood mass function and luminosity function e.g. white dwarfs (~200,000) and brown dwarfs (~50,000) – initial mass and luminosity functions in star forming regions ...
Page 25 - Types of Galaxies
... • These galaxies are neither spiral nor elliptical. • They tend to be smaller objects that are without definite shape and tend to have very hot newer stars mixed in with lots of gas and dust. • These galaxies often have active regions of star formation. Sometimes the irregular shape of these galaxie ...
... • These galaxies are neither spiral nor elliptical. • They tend to be smaller objects that are without definite shape and tend to have very hot newer stars mixed in with lots of gas and dust. • These galaxies often have active regions of star formation. Sometimes the irregular shape of these galaxie ...
Lecture 2: ppt, 5 MB
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
v = H o χ d “Hubble`s Law”
... • Some quasars can double their brightness within a few hours. • Therefore they cannot be larger than a few lighthours across (solar system size) – Why? Think about the time it takes light from the front of the object to get to us compared to the light from the back. ...
... • Some quasars can double their brightness within a few hours. • Therefore they cannot be larger than a few lighthours across (solar system size) – Why? Think about the time it takes light from the front of the object to get to us compared to the light from the back. ...
Quasar

Quasars (/ˈkweɪzɑr/) or quasi-stellar radio sources are the most energetic and distant members of a class of objects called active galactic nuclei (AGN). Quasars are extremely luminous and were first identified as being high redshift sources of electromagnetic energy, including radio waves and visible light, that appeared to be similar to stars, rather than extended sources similar to galaxies. Their spectra contain very broad emission lines, unlike any known from stars, hence the name ""quasi-stellar."" Their luminosity can be 100 times greater than that of the Milky Way. Most quasars were formed approximately 12 billion years ago caused by collisions of galaxies and their central black holes merging to form either a supermassive black hole or a Binary black hole system.Although the true nature of these objects was controversial until the early 1980s, there is now a scientific consensus that a quasar is a compact region in the center of a massive galaxy surrounding a central supermassive black hole. Its size is 10–10,000 times the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole. The energy emitted by a quasar derives from mass falling onto the accretion disc around the black hole.