Homing in on Black H..
... after they ran out of hydrogen and other fuel. Once the stars sputtered out, the scientists posited, the remaining gas would collapse under its own gravity into an infinitely dense point. Telescope observations backed up the theory in the 1960s and 1970s. Astronomers discovered quasars—extremely bri ...
... after they ran out of hydrogen and other fuel. Once the stars sputtered out, the scientists posited, the remaining gas would collapse under its own gravity into an infinitely dense point. Telescope observations backed up the theory in the 1960s and 1970s. Astronomers discovered quasars—extremely bri ...
Long Ago and Far Away
... galaxy’s actual distance to the distance you worked out in Part II#3, estimate the angular size of this galaxy if it were observed at a distance corresponding to 5 billion years after the Big Bang. (The small angle formula breaks down for large cosmological distances, but just assume it works approx ...
... galaxy’s actual distance to the distance you worked out in Part II#3, estimate the angular size of this galaxy if it were observed at a distance corresponding to 5 billion years after the Big Bang. (The small angle formula breaks down for large cosmological distances, but just assume it works approx ...
21. Galaxy Evolution Agenda The Monty Hall Problem/Paradox 21.1
... • What do we think is the source of power for active galactic nuclei? • We suspect that active galactic nuclei are powered by supermassive black holes that can exceed one billion solar masses. Observations of the rapid variability of active galactic nuclei tells us that their energy output comes fro ...
... • What do we think is the source of power for active galactic nuclei? • We suspect that active galactic nuclei are powered by supermassive black holes that can exceed one billion solar masses. Observations of the rapid variability of active galactic nuclei tells us that their energy output comes fro ...
Galaxies - science9atsouthcarletonhs
... Galaxy Clusters • Most galaxies are not alone in the vast expanse of space, but are connected to one or more other galaxies by gravity • These collections of galaxies are known as galaxy clusters and they too appear to be organized into larger “superclusters” ...
... Galaxy Clusters • Most galaxies are not alone in the vast expanse of space, but are connected to one or more other galaxies by gravity • These collections of galaxies are known as galaxy clusters and they too appear to be organized into larger “superclusters” ...
PX269 Galaxies - University of Warwick
... SIDEREAL MESSENGER unfolding great and very wonderful sights and displaying to the gaze of everyone, but especially philosophers and astronomers, the things that were observed by GALILEO GALILEI, Florentine patrician and public mathematician of the University of Padua, with the help of a spyglass l ...
... SIDEREAL MESSENGER unfolding great and very wonderful sights and displaying to the gaze of everyone, but especially philosophers and astronomers, the things that were observed by GALILEO GALILEI, Florentine patrician and public mathematician of the University of Padua, with the help of a spyglass l ...
Black Hole - The Crowned Anarchist Literature
... reactions if a mass of hydrogen were to be converted entirely into iron. If the large-scale annihilation of matter and antimatter is excluded from consideration, the release of gravitational binding energy when matter settles onto compact objects is the most powerful mechanism for generating energy ...
... reactions if a mass of hydrogen were to be converted entirely into iron. If the large-scale annihilation of matter and antimatter is excluded from consideration, the release of gravitational binding energy when matter settles onto compact objects is the most powerful mechanism for generating energy ...
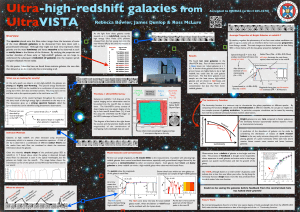
Ultra-high-redshift galaxies from
... At the early epoch we observe at ultra-high-redshift, the galaxies are young and highly star-forming. The spectral energy distribution (the spectra or SED) can be modelled as a combination of many massive young stars with a low dust and metal content. The young stars are hot and blue, and so the spe ...
... At the early epoch we observe at ultra-high-redshift, the galaxies are young and highly star-forming. The spectral energy distribution (the spectra or SED) can be modelled as a combination of many massive young stars with a low dust and metal content. The young stars are hot and blue, and so the spe ...
Irregular galaxies
... to be the result of a density wave radiating from the center of the galaxy • Bars are thought to be a temporary phenomenon in the life of spiral galaxies, the bar structure decaying over time, transforming the galaxy from a barred spiral to a "regular“, or “classical” spiral pattern. ...
... to be the result of a density wave radiating from the center of the galaxy • Bars are thought to be a temporary phenomenon in the life of spiral galaxies, the bar structure decaying over time, transforming the galaxy from a barred spiral to a "regular“, or “classical” spiral pattern. ...
Galaxies - Stockton University
... Galaxies on the other hand have sizes ranging from 1 to 100 Kpc, but are separated by of order 1 to 10 Mpc from their neighbors, only a factor of 100 to 1000. This means that almost all galaxies have probably had direct interactions, collisions and mergers with others during their lives. For an indi ...
... Galaxies on the other hand have sizes ranging from 1 to 100 Kpc, but are separated by of order 1 to 10 Mpc from their neighbors, only a factor of 100 to 1000. This means that almost all galaxies have probably had direct interactions, collisions and mergers with others during their lives. For an indi ...
The Guide to the Galaxies
... “The term galaxy is derived from the Greek term for our own galaxy, galaxias meaning milky circle ” angle of viewing. Elliptical galaxies commonly do not show much star formation and are dominated by an older generation of stars. Many giant elliptical galaxies form from the collision and merging of ...
... “The term galaxy is derived from the Greek term for our own galaxy, galaxias meaning milky circle ” angle of viewing. Elliptical galaxies commonly do not show much star formation and are dominated by an older generation of stars. Many giant elliptical galaxies form from the collision and merging of ...
Galaxies
... The Milky Way is the small part of the galaxy we can see. To us on Earth it appears as a band of light across the night sky. There are many ancient myths and legends and it is a ...
... The Milky Way is the small part of the galaxy we can see. To us on Earth it appears as a band of light across the night sky. There are many ancient myths and legends and it is a ...
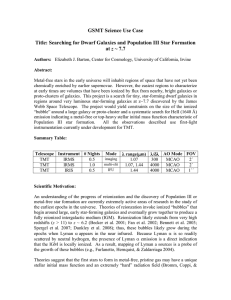
Searching for Dwarf Galaxies and Population III Star
... This multi-step project includes 3 tiers of observations: 1. By 2016, the James Webb Space Telescope will regularly deliver deep infrared images that reveal the most massive star-forming galaxies and proto-clusters of galaxies at z > 7. We will identify the most luminous at z ~ 7.7, where Lyman fa ...
... This multi-step project includes 3 tiers of observations: 1. By 2016, the James Webb Space Telescope will regularly deliver deep infrared images that reveal the most massive star-forming galaxies and proto-clusters of galaxies at z > 7. We will identify the most luminous at z ~ 7.7, where Lyman fa ...
V: 0
... 2. Draw a wave with a low amplitude. 3. Name 2 waves that can easily travel through Earth’s atmosphere ...
... 2. Draw a wave with a low amplitude. 3. Name 2 waves that can easily travel through Earth’s atmosphere ...
telescope as time machine - Galaxy Evolution Explorer
... So how is looking at far away galaxies like looking back in time? At 300,000 kilometers per second (186,000 miles per second), nothing travels faster than light. Even at this speed, though, it still takes time for light to get from one place to another. If you are looking at your girlfriend just acr ...
... So how is looking at far away galaxies like looking back in time? At 300,000 kilometers per second (186,000 miles per second), nothing travels faster than light. Even at this speed, though, it still takes time for light to get from one place to another. If you are looking at your girlfriend just acr ...
Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies
... disk. They come in many sizes, from giant ellipticals of trillions of stars, down to dwarf ellipticals of less than a million stars. Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and show no evidence of ongoing star formation. Many do, however, have large clouds of hot gas, extend ...
... disk. They come in many sizes, from giant ellipticals of trillions of stars, down to dwarf ellipticals of less than a million stars. Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and show no evidence of ongoing star formation. Many do, however, have large clouds of hot gas, extend ...
Hubble - STScI
... measurements of the masses of two distant worlds. Astronomers believe that one of those worlds is the oldest known planet. The planet, whose estimated age is 13 billion years, is more than twice as old as 4.5-billion-year-old Earth. ...
... measurements of the masses of two distant worlds. Astronomers believe that one of those worlds is the oldest known planet. The planet, whose estimated age is 13 billion years, is more than twice as old as 4.5-billion-year-old Earth. ...
Hubble Deep Field Image
... Needed to be outside of the Milky Way’s disk of dust Could not contain very bright objects or anything that emitted too much infrared, x-ray, or UV In addition, field could never be occulted by the Earth or Moon. ...
... Needed to be outside of the Milky Way’s disk of dust Could not contain very bright objects or anything that emitted too much infrared, x-ray, or UV In addition, field could never be occulted by the Earth or Moon. ...
Published by the Association Pro ISSI No. 37, May 2016
... fact that Neutron Stars may rotate very rapidly with periods of seconds or even fractions thereof. Such a speedy Neutron Star may become a Pulsar emitting radiation observable as short pulses of electromagnetic waves. ...
... fact that Neutron Stars may rotate very rapidly with periods of seconds or even fractions thereof. Such a speedy Neutron Star may become a Pulsar emitting radiation observable as short pulses of electromagnetic waves. ...
Lecture 4
... III High redshift galaxies We now go to the very distant universe (redshift much larger than 1). With the increase of collecting areas of telescopes both in the ground and space these distant objects become accessible but very difficult to identify. Their detection is based on the search of the mai ...
... III High redshift galaxies We now go to the very distant universe (redshift much larger than 1). With the increase of collecting areas of telescopes both in the ground and space these distant objects become accessible but very difficult to identify. Their detection is based on the search of the mai ...
Galaxies
... galaxy is a huge region of space that contains hundreds of billions of stars, planets, glowing nebulae, dust, empty space, and possibly black holes. ...
... galaxy is a huge region of space that contains hundreds of billions of stars, planets, glowing nebulae, dust, empty space, and possibly black holes. ...
Hubble`s Constant - Scientific Research Publishing
... the distances in the Universe are so vast that they cannot be measured directly. The only way to allow observations to enter in the scheme is to suppose that there are some selected uniform types of astronomical systems called Standard Candles, which are systems whose luminosity is the same everywhe ...
... the distances in the Universe are so vast that they cannot be measured directly. The only way to allow observations to enter in the scheme is to suppose that there are some selected uniform types of astronomical systems called Standard Candles, which are systems whose luminosity is the same everywhe ...
Linear optics quantum logic gates in the real world
... HIPASS being a HI All-sky southern survey should find “Dark Galaxies” if they exist Dark Galaxies in HIPASS HI strongly detected but no possible optical counterpart found. We have found 3 candidate Dark Galaxies Will be included in follow-up ATCA high resolution observation Not previously obse ...
... HIPASS being a HI All-sky southern survey should find “Dark Galaxies” if they exist Dark Galaxies in HIPASS HI strongly detected but no possible optical counterpart found. We have found 3 candidate Dark Galaxies Will be included in follow-up ATCA high resolution observation Not previously obse ...
Universe, Galaxies, Solar System
... • Our Solar System was thought to have formed 4.6 billion years ago. • The nebula started to spin and contract; possibly because a nearby star exploded setting this into action. • As it contracted, the density grew immensely. It heated to extreme temperatures and our Sun was born. Soon after, the pl ...
... • Our Solar System was thought to have formed 4.6 billion years ago. • The nebula started to spin and contract; possibly because a nearby star exploded setting this into action. • As it contracted, the density grew immensely. It heated to extreme temperatures and our Sun was born. Soon after, the pl ...
Quasar

Quasars (/ˈkweɪzɑr/) or quasi-stellar radio sources are the most energetic and distant members of a class of objects called active galactic nuclei (AGN). Quasars are extremely luminous and were first identified as being high redshift sources of electromagnetic energy, including radio waves and visible light, that appeared to be similar to stars, rather than extended sources similar to galaxies. Their spectra contain very broad emission lines, unlike any known from stars, hence the name ""quasi-stellar."" Their luminosity can be 100 times greater than that of the Milky Way. Most quasars were formed approximately 12 billion years ago caused by collisions of galaxies and their central black holes merging to form either a supermassive black hole or a Binary black hole system.Although the true nature of these objects was controversial until the early 1980s, there is now a scientific consensus that a quasar is a compact region in the center of a massive galaxy surrounding a central supermassive black hole. Its size is 10–10,000 times the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole. The energy emitted by a quasar derives from mass falling onto the accretion disc around the black hole.