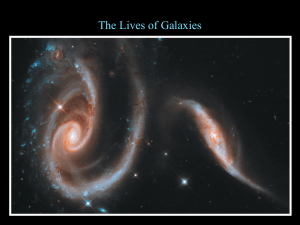
Galaxy interactions - collisions Many stars are thrown out into space
... After a few billion years, when all has settled down, the result is an elliptical galaxy: Stars in random orbits, and little gas and dust left for new star formation. ...
... After a few billion years, when all has settled down, the result is an elliptical galaxy: Stars in random orbits, and little gas and dust left for new star formation. ...
OSP2016Level 3 Map - Oregon Star Party
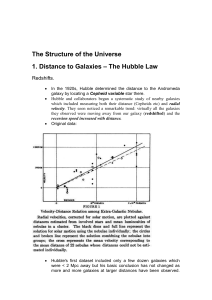
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
24.1 Hubble`s Galaxy Classification
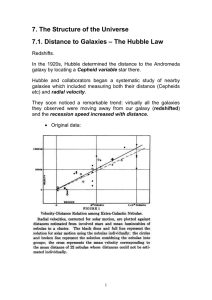
... clusters in the halo of our Galaxy, while Cepheid variables, being so much brighter, allow measurement of galaxies to about 25 Mpc away. The image below shows a Cepheid variable spotted in a galaxy in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. You can see it getting fainter and brighter in the insets. ...
... clusters in the halo of our Galaxy, while Cepheid variables, being so much brighter, allow measurement of galaxies to about 25 Mpc away. The image below shows a Cepheid variable spotted in a galaxy in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. You can see it getting fainter and brighter in the insets. ...
Friday03
... • Fraction of SF galaxies depends on local and large-scale densities (?) • Galaxy-galaxy interactions are the most likely cause of observed segregation ...
... • Fraction of SF galaxies depends on local and large-scale densities (?) • Galaxy-galaxy interactions are the most likely cause of observed segregation ...
Dust and Stellar Emission of Nearby Galaxies in the KINGFISH
... from Herschel. We estimate the stellar and dust emission of these galaxies, in a way that is as empirical and model-independent as possible, and we use these to estimate the ratio of stellar-to-dust emission. The stellar-to-dust ratios can be compared to gas-to-dust ratios determined from SED models ...
... from Herschel. We estimate the stellar and dust emission of these galaxies, in a way that is as empirical and model-independent as possible, and we use these to estimate the ratio of stellar-to-dust emission. The stellar-to-dust ratios can be compared to gas-to-dust ratios determined from SED models ...
X-ray observations of the hot CGM of nearby disk galaxies
... Stacking of absorption line spectra according to intervening galaxy/group redshifts With an effective exposure: ~ 10 Ms, no absorption is detected! • NOVII < 1015 cm-2, or < 1/10 of the column density observed around the Milky Way. • Groups typically contain little gas at T~105.3-106.3 K, unless ...
... Stacking of absorption line spectra according to intervening galaxy/group redshifts With an effective exposure: ~ 10 Ms, no absorption is detected! • NOVII < 1015 cm-2, or < 1/10 of the column density observed around the Milky Way. • Groups typically contain little gas at T~105.3-106.3 K, unless ...
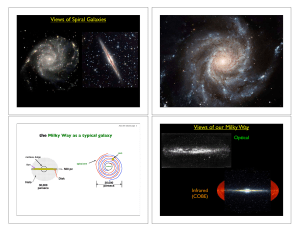
Views of Spiral Galaxies Views of our Milky Way
... • Use differential rotation of galaxy to estimate: • cloud distance using cloud radial velocity ...
... • Use differential rotation of galaxy to estimate: • cloud distance using cloud radial velocity ...
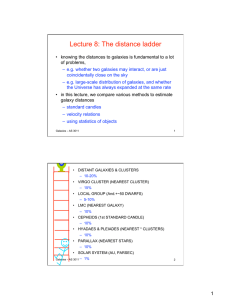
Lecture 8: The distance ladder
... • relate this velocity or period to the luminosity, using local objects (with distances known from other methods) • then we use F = L / 4 π d2 – measure F, know L....work out d • or use the distance modulus: – calculate the absolute magnitude M for the luminosity L, measure m... use m - M = 5 l ...
... • relate this velocity or period to the luminosity, using local objects (with distances known from other methods) • then we use F = L / 4 π d2 – measure F, know L....work out d • or use the distance modulus: – calculate the absolute magnitude M for the luminosity L, measure m... use m - M = 5 l ...
Observational Data
... star formation rate (>100Mo/yr), irregular and possibly merging-like morphologies, large masses, and strong redshift clustering, suggesting that they are massive early-type galaxies in the act of major assembly episodes. ...
... star formation rate (>100Mo/yr), irregular and possibly merging-like morphologies, large masses, and strong redshift clustering, suggesting that they are massive early-type galaxies in the act of major assembly episodes. ...
16 Hubble s Law and Dark Matter
... d) a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. e) there are many separate sources of energy in the core. ...
... d) a chain reaction of supernovas occurs. e) there are many separate sources of energy in the core. ...
Staring Back to Cosmic Dawn - UC-HiPACC
... The Case of the Chaotic Blue Galaxies Ever since Hubble’s first spectacular images of distant galaxies, an enduring puzzle has been why early starforming galaxies look much more irregular and jumbled than nearby blue galaxies. Nearby blue galaxies are relatively smooth. The most beautiful ones are e ...
... The Case of the Chaotic Blue Galaxies Ever since Hubble’s first spectacular images of distant galaxies, an enduring puzzle has been why early starforming galaxies look much more irregular and jumbled than nearby blue galaxies. Nearby blue galaxies are relatively smooth. The most beautiful ones are e ...
Galaxies
... Distant Red Ellipticals • Observations of some distant red elliptical galaxies support the idea that most of their stars formed very early in the history of the universe ...
... Distant Red Ellipticals • Observations of some distant red elliptical galaxies support the idea that most of their stars formed very early in the history of the universe ...
PH607lec08
... The formula z = v / c implies that you can't have redshifts greater than one because that would give you a velocity greater than the speed of light, something not permitted by the laws of physics. ...
... The formula z = v / c implies that you can't have redshifts greater than one because that would give you a velocity greater than the speed of light, something not permitted by the laws of physics. ...
Accretion Disks
... liberated in the boundary layer between disk and star • Accretion disk around a black hole – Inner edge often set by the “innermost stable circular orbit” (ISCO) – GR effects make circular orbits within the ISCO unstable… matter rapidly spirals in – Risco=6GM/c2 for a non-rotating black hole ...
... liberated in the boundary layer between disk and star • Accretion disk around a black hole – Inner edge often set by the “innermost stable circular orbit” (ISCO) – GR effects make circular orbits within the ISCO unstable… matter rapidly spirals in – Risco=6GM/c2 for a non-rotating black hole ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... 7.2 Clusters of Galaxies Clusters are systems a few Mpc across, typically containing at least 50-100 luminous galaxies within the central 1 Mpc Clusters are gravitationally bound Clusters are filled with hot X-ray gas Only ~20% of galaxies live in clusters, most live in groups or in the “fi ...
... 7.2 Clusters of Galaxies Clusters are systems a few Mpc across, typically containing at least 50-100 luminous galaxies within the central 1 Mpc Clusters are gravitationally bound Clusters are filled with hot X-ray gas Only ~20% of galaxies live in clusters, most live in groups or in the “fi ...
Galaxy Powerpoint Notes
... III. Irregular and dwarf galaxies : III. Irregular and dwarf galaxies Irregular galaxies do not have a regular shape, hence the name ‘irregular’. They are very uncommon within our universe though they are believed to once be spiral or elliptical galaxies that were altered by a gravitational pull. Ir ...
... III. Irregular and dwarf galaxies : III. Irregular and dwarf galaxies Irregular galaxies do not have a regular shape, hence the name ‘irregular’. They are very uncommon within our universe though they are believed to once be spiral or elliptical galaxies that were altered by a gravitational pull. Ir ...
슬라이드 1
... Fig. (1) – The bar fraction is higher in redder, brighter galaxies. When color is fixed, it seems barred galaxies have higher star formation activity relative to non-barred galaxies. And the bar fraction also depend on central velocity dispersion (σ ). Fig. (2) – All contours are nearly parallel to ...
... Fig. (1) – The bar fraction is higher in redder, brighter galaxies. When color is fixed, it seems barred galaxies have higher star formation activity relative to non-barred galaxies. And the bar fraction also depend on central velocity dispersion (σ ). Fig. (2) – All contours are nearly parallel to ...
Hwihyun Kim
... • By a BPT analysis, AGN contamination was removed from the sample with S/N > 3 (11% removed) • Removed all strong radio sources by the VLA FIRST survey • Volume-limited CMR – Some of UV blue galaxies are not genuine early-types – Late-types and AGN candidates are bluer ...
... • By a BPT analysis, AGN contamination was removed from the sample with S/N > 3 (11% removed) • Removed all strong radio sources by the VLA FIRST survey • Volume-limited CMR – Some of UV blue galaxies are not genuine early-types – Late-types and AGN candidates are bluer ...
The Classification of Galaxies By Daniel Underwood Contents The
... they weren’t gaseous, but actually massive collections of stars. These masses outside the Milky Way were becoming more and more noticed by astronomers, and they had their own characteristics which helped identify them. But it didn’t end there... Even though galaxies these days are widely recognised, ...
... they weren’t gaseous, but actually massive collections of stars. These masses outside the Milky Way were becoming more and more noticed by astronomers, and they had their own characteristics which helped identify them. But it didn’t end there... Even though galaxies these days are widely recognised, ...
The first billion years of galaxy formation and evolution
... All-sky optical/near-IR surveys: hunting for z>4 QSOs All-sky surveys such as the SLOAN have found numerous, extremely luminous z > 4 QSOs by means of drop-out techniques in the optical They represent massive, extremely rare, overdensities in the primordial density distribution. ...
... All-sky optical/near-IR surveys: hunting for z>4 QSOs All-sky surveys such as the SLOAN have found numerous, extremely luminous z > 4 QSOs by means of drop-out techniques in the optical They represent massive, extremely rare, overdensities in the primordial density distribution. ...
Early Star-Forming Galaxies
... their intervening dust. This allowed the astronomers to assemble a more complete picture of star birth than ever before. The team targeted two well-known regions of the sky that had been observed by Hubble and other telescopes. These were the Cosmological Evolution Survey (COSMOS), and the Great Obs ...
... their intervening dust. This allowed the astronomers to assemble a more complete picture of star birth than ever before. The team targeted two well-known regions of the sky that had been observed by Hubble and other telescopes. These were the Cosmological Evolution Survey (COSMOS), and the Great Obs ...
Spiral Galaxies - Astronomy Centre
... universes, which are now referred to as galaxies • The word Universe now refers to the full expanse of space and its contents • While most diffuse nebulae are nearby clouds of gas and dust within the Milky Way, the elliptical and spiral nebulae are galaxies located well beyond the limits of the Milk ...
... universes, which are now referred to as galaxies • The word Universe now refers to the full expanse of space and its contents • While most diffuse nebulae are nearby clouds of gas and dust within the Milky Way, the elliptical and spiral nebulae are galaxies located well beyond the limits of the Milk ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... structure of the Milky Way. 1. The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) extends much further than previously thought. The disk of the Milky Way extends further is a clear possibility and is supported by evidence of the newly discovered Outer Arm extension of the Cygnus Arm. 2. With the discovery of the Sagittariu ...
... structure of the Milky Way. 1. The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) extends much further than previously thought. The disk of the Milky Way extends further is a clear possibility and is supported by evidence of the newly discovered Outer Arm extension of the Cygnus Arm. 2. With the discovery of the Sagittariu ...
Quasar

Quasars (/ˈkweɪzɑr/) or quasi-stellar radio sources are the most energetic and distant members of a class of objects called active galactic nuclei (AGN). Quasars are extremely luminous and were first identified as being high redshift sources of electromagnetic energy, including radio waves and visible light, that appeared to be similar to stars, rather than extended sources similar to galaxies. Their spectra contain very broad emission lines, unlike any known from stars, hence the name ""quasi-stellar."" Their luminosity can be 100 times greater than that of the Milky Way. Most quasars were formed approximately 12 billion years ago caused by collisions of galaxies and their central black holes merging to form either a supermassive black hole or a Binary black hole system.Although the true nature of these objects was controversial until the early 1980s, there is now a scientific consensus that a quasar is a compact region in the center of a massive galaxy surrounding a central supermassive black hole. Its size is 10–10,000 times the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole. The energy emitted by a quasar derives from mass falling onto the accretion disc around the black hole.