EXAM A
... b. A proton (charge +1.6x 1019 C and mass 1.6 x 1027 kg) is released 1 cm from the surface. What will be the speed of the proton when it is 2 cm from the surface? Fig. 22.40 ...
... b. A proton (charge +1.6x 1019 C and mass 1.6 x 1027 kg) is released 1 cm from the surface. What will be the speed of the proton when it is 2 cm from the surface? Fig. 22.40 ...
Ch. 18 sec.8,9 - Physics-YISS
... • They rush to the surface of the copper, because coulomb’s law is affected by distance 1/r^2. • Once static equilibrium is established with all of the excess charge on the surface, no further movement of charge occurs. • Excess positive charge also moves to the surface of a conductor. • At equilib ...
... • They rush to the surface of the copper, because coulomb’s law is affected by distance 1/r^2. • Once static equilibrium is established with all of the excess charge on the surface, no further movement of charge occurs. • Excess positive charge also moves to the surface of a conductor. • At equilib ...
B.Sc. Part - II (Physics) Paper I – Electricity, Magnetism Electrostatics
... in varying Magnetic field , Induction of current in continuous media , Skin effect. Motion of Electron in changing magnetic field , Betatron , Magnetic energy in field , Induced magnetic field (Time varying electric field ) ,Displacement current , Maxwell’s equations, Electromagnetic waves in free s ...
... in varying Magnetic field , Induction of current in continuous media , Skin effect. Motion of Electron in changing magnetic field , Betatron , Magnetic energy in field , Induced magnetic field (Time varying electric field ) ,Displacement current , Maxwell’s equations, Electromagnetic waves in free s ...
Study Guide
... Free charges are the charges that are not a result of polarization. The combination of free and bound charges is the total charge and the enclosed charges will be the sum of both free and bound charges. Free charges might consist of electrons on a conductor or ions embedded in the dielectric materi ...
... Free charges are the charges that are not a result of polarization. The combination of free and bound charges is the total charge and the enclosed charges will be the sum of both free and bound charges. Free charges might consist of electrons on a conductor or ions embedded in the dielectric materi ...
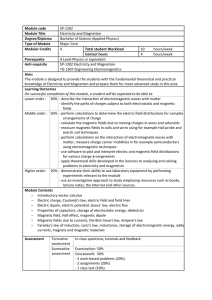
Module code SP-1202 Module Title Electricity and Magnetism
... - use software to plot and interpret electric and magnetic field distributions for various charge arrangements - apply theoretical skills developed in the lectures to analysing and solving problems in electricity and magnetism Higher order: 20% - demonstrate their ability to use laboratory equ ...
... - use software to plot and interpret electric and magnetic field distributions for various charge arrangements - apply theoretical skills developed in the lectures to analysing and solving problems in electricity and magnetism Higher order: 20% - demonstrate their ability to use laboratory equ ...
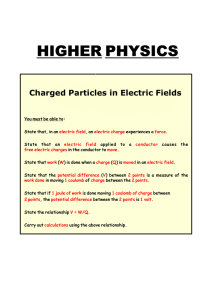
Electric Charge, Coulomb`s Law, Electric Fields, Field Lines, Electric
... Use the diagram at the right to answer the following questions. scale 1cm = 1m a) What is the net force applied on the 7 by the two negative charges? b) What is the net force applied on the 7 C by all charges? c) If the 7 C were free to move, what electric -10C force would have to be applied t ...
... Use the diagram at the right to answer the following questions. scale 1cm = 1m a) What is the net force applied on the 7 by the two negative charges? b) What is the net force applied on the 7 C by all charges? c) If the 7 C were free to move, what electric -10C force would have to be applied t ...
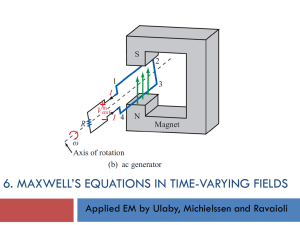
Maxwell`s equation
... space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also in the manner described by this new term. Adding Ampere’s original equation is equivalent to saying that a changing electric field E can produce a magnetic field B . Maxwell’s modifica ...
... space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also in the manner described by this new term. Adding Ampere’s original equation is equivalent to saying that a changing electric field E can produce a magnetic field B . Maxwell’s modifica ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.