1- A well-structured document usually contains a number of clues
... 2- When use the communication link is point-to-point so there is no requirement for network routing. (T) ...
... 2- When use the communication link is point-to-point so there is no requirement for network routing. (T) ...
physical address.
... – It is the transmission mechanism used by the TCP/IP protocols. – It is unreliable and connectionless protocol (a best-effort delivery service). A best effort: IP provides no error checking or tracking. IP assumes the unreliability of the underlying layers and does its best to get a transmissio ...
... – It is the transmission mechanism used by the TCP/IP protocols. – It is unreliable and connectionless protocol (a best-effort delivery service). A best effort: IP provides no error checking or tracking. IP assumes the unreliability of the underlying layers and does its best to get a transmissio ...
related work
... cable which introduces 6 to 10 dB of attenuation Three nodes, located on the roofs of tall buildings, have 12 dBi Yagi directional antennas with 45degree horizontal and vertical beam widths ...
... cable which introduces 6 to 10 dB of attenuation Three nodes, located on the roofs of tall buildings, have 12 dBi Yagi directional antennas with 45degree horizontal and vertical beam widths ...
Lecture 14
... Routing in Case of Broadcast A case could be made either way. First, look at the functions performed at the network layer to deal with the communications network (hiding the details from the upper layers). The network layer is responsible for routing data through the network, but with a broadcast n ...
... Routing in Case of Broadcast A case could be made either way. First, look at the functions performed at the network layer to deal with the communications network (hiding the details from the upper layers). The network layer is responsible for routing data through the network, but with a broadcast n ...
Document
... • RIP is a distance vector routing protocol that uses hop count as its metric to determine the direction and distance to any link in the internetwork • RIP selects the path with the least number of hops • RIP cannot route a packet beyond 15 hops ...
... • RIP is a distance vector routing protocol that uses hop count as its metric to determine the direction and distance to any link in the internetwork • RIP selects the path with the least number of hops • RIP cannot route a packet beyond 15 hops ...
The Internet
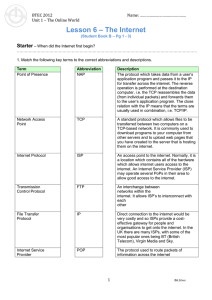
... The protocol which takes data from a user’s application program and passes it to the IP for transfer across the internet. The reverse operation is performed at the destination computer, i.e. the TCP reassembles the data (from individual packets) and forwards them to the user’s application program. T ...
... The protocol which takes data from a user’s application program and passes it to the IP for transfer across the internet. The reverse operation is performed at the destination computer, i.e. the TCP reassembles the data (from individual packets) and forwards them to the user’s application program. T ...
Document
... Step 1: Initiator (I) sends the first I1 packet, which contains own HIT and the HIT of the responder to the responder (R) Step 2: R relies with message R1, which contains the HITs of I and itself as well as a puzzle based challenge for I to solve Step 3: I solves the puzzle and sends in I2 the HITs ...
... Step 1: Initiator (I) sends the first I1 packet, which contains own HIT and the HIT of the responder to the responder (R) Step 2: R relies with message R1, which contains the HITs of I and itself as well as a puzzle based challenge for I to solve Step 3: I solves the puzzle and sends in I2 the HITs ...
Talk slides
... • Prefix Subgraph - The graph induced from a network graph by the set of nodes with a given prefix. ...
... • Prefix Subgraph - The graph induced from a network graph by the set of nodes with a given prefix. ...
1 It is desired to send a sequence of computer screen images over
... frame on an average of once every 100 sec, even if the previous one has not yet been sent (e.g., the stations can buffer outgoing frames). What is the maximum value of N? 7. Consider the delay of pure ALOHA versus slotted ALOHA at low load. Which one is less? Explain your answer. 8. Compare the ways ...
... frame on an average of once every 100 sec, even if the previous one has not yet been sent (e.g., the stations can buffer outgoing frames). What is the maximum value of N? 7. Consider the delay of pure ALOHA versus slotted ALOHA at low load. Which one is less? Explain your answer. 8. Compare the ways ...
Lecture 1 - Introduction to optical Communications and networking
... • all specifications related to electrical properties, radio frequencies, and signals belong in layer 1 ...
... • all specifications related to electrical properties, radio frequencies, and signals belong in layer 1 ...
Optical Fibre Communication
... • all specifications related to electrical properties, radio frequencies, and signals belong in layer 1 ...
... • all specifications related to electrical properties, radio frequencies, and signals belong in layer 1 ...
Document
... of a protocol an agreed-upon series of rules and conventions Communication between machines is peer-to-peer process using protocols at any given layer Each layer adds information to the data – Headers are added to the data at layers 6, 5, 4, 3 and 2. Trailers are usually added at layer 2 Each laye ...
... of a protocol an agreed-upon series of rules and conventions Communication between machines is peer-to-peer process using protocols at any given layer Each layer adds information to the data – Headers are added to the data at layers 6, 5, 4, 3 and 2. Trailers are usually added at layer 2 Each laye ...
Solar System Internet - The Ultimate Collaboration
... Several low-priority images were destroyed upon time-to-live expiration prior to delivery, due to insufficient contact opportunity (unplanned DSN link service outages). ...
... Several low-priority images were destroyed upon time-to-live expiration prior to delivery, due to insufficient contact opportunity (unplanned DSN link service outages). ...
IP address
... ■ Packets with address in the range 10.1.8.0-10.1.11.255 will be routed to network 10.1.8.0/22 based on the first 22 bits ...
... ■ Packets with address in the range 10.1.8.0-10.1.11.255 will be routed to network 10.1.8.0/22 based on the first 22 bits ...
Client-server Systems - University of Manitoba
... Each layer invokes API functions of the layer below it. Messages start from the transmitter network based program and flow down the stack, across the physical network, up the stack at the receiver, and are finally received by the receiver network based program. ...
... Each layer invokes API functions of the layer below it. Messages start from the transmitter network based program and flow down the stack, across the physical network, up the stack at the receiver, and are finally received by the receiver network based program. ...
OSI vs TCP/IP models
... they deal with the user interface, data formatting, and the application access. ...
... they deal with the user interface, data formatting, and the application access. ...
Slide 1
... ambient network, by providing two services: Picture service – enables other devices to get the images captured by the mobile phone, SMS service – allows other devices with IP connectivity to the phone to send SMS messages. ...
... ambient network, by providing two services: Picture service – enables other devices to get the images captured by the mobile phone, SMS service – allows other devices with IP connectivity to the phone to send SMS messages. ...
ppt - Computer Science Division - University of California, Berkeley
... End-to-end arguments address design more than implementation and implementation more than execution-that is, they suggest who should provide the code, not which box it should run on. ...
... End-to-end arguments address design more than implementation and implementation more than execution-that is, they suggest who should provide the code, not which box it should run on. ...
CCNP Routing Semester 5 - YSU Computer Science & Information
... Used in context of VLANS; the mechanism by which a switch can route between VLANS; also refers to routers when the routing decision has been made and the result has been cached – the subsequent lookup involves switching on a Layer 3 decision ...
... Used in context of VLANS; the mechanism by which a switch can route between VLANS; also refers to routers when the routing decision has been made and the result has been cached – the subsequent lookup involves switching on a Layer 3 decision ...
intro-Routing240
... client/server model • client host requests, receives service from server • e.g., WWW client (browser)/ server; email client/server ...
... client/server model • client host requests, receives service from server • e.g., WWW client (browser)/ server; email client/server ...
Networking Concepts An Introduction to
... many shorter point-to-point links. At each of the locations where these links meet, there is hardware designed to switch or route the packets to their various destinations. The difference between switching and routing lies in how devices are addressed on the network. Packet switching occurs when the ...
... many shorter point-to-point links. At each of the locations where these links meet, there is hardware designed to switch or route the packets to their various destinations. The difference between switching and routing lies in how devices are addressed on the network. Packet switching occurs when the ...
Introduction - Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer
... Encapsulation is key to layering IP provides for transfer of packets across diverse ...
... Encapsulation is key to layering IP provides for transfer of packets across diverse ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.