mathcs.slu.edu
... • How is this conversion done? – Originally, there was one big table kept on a computer at Stanford. Whenever a computer needed to know an address, it would ask this computer. – But as the Internet grew, this computer was overloaded with requests and the underlying table was being updated too often. ...
... • How is this conversion done? – Originally, there was one big table kept on a computer at Stanford. Whenever a computer needed to know an address, it would ask this computer. – But as the Internet grew, this computer was overloaded with requests and the underlying table was being updated too often. ...
Part I: Introduction
... Priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined). Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data ...
... Priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined). Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data ...
ppt - CSE Labs User Home Pages
... “…interconnection must preserve intact the internal operation of each network.” “ ..the interface between networks must play a central role in the development of any network interconnection strategy. We give a special name to this interface that performs these functions and call it a GATEWAY.” “.. p ...
... “…interconnection must preserve intact the internal operation of each network.” “ ..the interface between networks must play a central role in the development of any network interconnection strategy. We give a special name to this interface that performs these functions and call it a GATEWAY.” “.. p ...
Lecture 9 & 10
... • Virtual private network (VPN) - a way to use the public telecommunication infrastructure (e.g., Internet) to provide secure access to an organization’s network • Valued-added network (VAN) - a private network, provided by a third party, for exchanging information through a high ...
... • Virtual private network (VPN) - a way to use the public telecommunication infrastructure (e.g., Internet) to provide secure access to an organization’s network • Valued-added network (VAN) - a private network, provided by a third party, for exchanging information through a high ...
Multiple Processor Systems
... – Collection of independent, interconnected processors that communicate and coordinate through message exchanges – A collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single coherent system ...
... – Collection of independent, interconnected processors that communicate and coordinate through message exchanges – A collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single coherent system ...
Networks Sample Exam Solutions
... layer N-1 passes data to layer N, which can read, act upon, & remove this control information before passing the (reduced) data up to layer N+1 • each layer should not need to know which portion of the upper layer’s data is control information, or its meaning Distributed Scripts: peer entities (at s ...
... layer N-1 passes data to layer N, which can read, act upon, & remove this control information before passing the (reduced) data up to layer N+1 • each layer should not need to know which portion of the upper layer’s data is control information, or its meaning Distributed Scripts: peer entities (at s ...
Computer Networks - Texas State Department of Computer Science
... exchange of goods, information and services. (eg. ATMs, electronic tickets,etc.) Entertainment Digital cable TV, multi-player distributed gaming, on-demand movies More?? ...
... exchange of goods, information and services. (eg. ATMs, electronic tickets,etc.) Entertainment Digital cable TV, multi-player distributed gaming, on-demand movies More?? ...
AN OVERVIEW OF INTERNET TECHNOLOGIES & THEIR …
... • Nodes - The terminals that connect to the backbone (PCs, phones, faxes) • Protocols - The logical connections of the network & the rules governing structure • Applications - The business objectives of network usage ...
... • Nodes - The terminals that connect to the backbone (PCs, phones, faxes) • Protocols - The logical connections of the network & the rules governing structure • Applications - The business objectives of network usage ...
PC Maintenance: Preparing for A+ Certification
... Dynamic: Address assigned to the PC by a DHCP server Automatic Private IP Address (APIPA): Address assigned by default if DHCP server is not available ...
... Dynamic: Address assigned to the PC by a DHCP server Automatic Private IP Address (APIPA): Address assigned by default if DHCP server is not available ...
18th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks
... Fiber-wireless networks that rely on the collaborative use of both fiber-based and wireless communication technologies are currently turning into a highly important research area in view of the forthcoming era of 5G mobile networks. The FiWi communication paradigm aims to equip future networks with ...
... Fiber-wireless networks that rely on the collaborative use of both fiber-based and wireless communication technologies are currently turning into a highly important research area in view of the forthcoming era of 5G mobile networks. The FiWi communication paradigm aims to equip future networks with ...
Blue Gene/L system architecture
... – Three high-band width, low-latency networks for data transmission and synchronization. • 3-D torus network for point-to-point communication • Collective network for global operations • Barrier network ...
... – Three high-band width, low-latency networks for data transmission and synchronization. • 3-D torus network for point-to-point communication • Collective network for global operations • Barrier network ...
Routing
... Overview • Forwarding vs Routing – forwarding: to select an output port based on destination address and routing table – routing: process by which routing table is built ...
... Overview • Forwarding vs Routing – forwarding: to select an output port based on destination address and routing table – routing: process by which routing table is built ...
OSI Model
... end conversations (called sessions) between applications. This layer requests for a logical connection to be established on an end-user’s request. Any necessary log-on or password validation is also handled by this layer. Session layer is also responsible for terminating the connection. This layer p ...
... end conversations (called sessions) between applications. This layer requests for a logical connection to be established on an end-user’s request. Any necessary log-on or password validation is also handled by this layer. Session layer is also responsible for terminating the connection. This layer p ...
Chapter 11
... Must be unique on the network Must not be chosen at random Must be assigned by a network administrator ...
... Must be unique on the network Must not be chosen at random Must be assigned by a network administrator ...
hw3 - OpenLab
... Today’s internet rely on almost half a century old packet switching system that entails packaging data in specially formatted units called packets that are typically routed from source to destination using network switches and routers. Each packet contains address information that identifies the sen ...
... Today’s internet rely on almost half a century old packet switching system that entails packaging data in specially formatted units called packets that are typically routed from source to destination using network switches and routers. Each packet contains address information that identifies the sen ...
15-441 Socket Programming
... Billions of devices The next billion users “Nothing is permanent but change” ...
... Billions of devices The next billion users “Nothing is permanent but change” ...
CMPT 880: Internet Architectures and Protocols
... resource sharing (statistical multiplexing) • better resource utilization • more users or faster transfer (a single user can use entire bw) • Well suited for bursty traffic (typical in data networks) ...
... resource sharing (statistical multiplexing) • better resource utilization • more users or faster transfer (a single user can use entire bw) • Well suited for bursty traffic (typical in data networks) ...
FCC Regulation of Non-Interconnected VoIP Services and the “Cloud”
... VoIP Services and the “Cloud” ...
... VoIP Services and the “Cloud” ...
ch 11 Data Network Connectivity
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
Data Network Connectivity
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
... Transparent bridging - a bridge begins polling a network to learn about its physical topology as soon as it is installed on the network. ...
Internetting - start [kondor.etf.rs]
... Globally accepted method of identifying computers Each host on a TCP/IP internet is assigned a unique 32-bit address that is used in all communication with that host Must not be confused with physical addresses! Each address is a pair (netid, hostid), where netid identifies a network, and hostid ide ...
... Globally accepted method of identifying computers Each host on a TCP/IP internet is assigned a unique 32-bit address that is used in all communication with that host Must not be confused with physical addresses! Each address is a pair (netid, hostid), where netid identifies a network, and hostid ide ...
Transcript: Network Hardening Techniques Part 1
... Then there is SNMP version 3, that's Simple Network Management Protocol version 3. It's a protocol that is used to manage and configure devices remotely on the network. It's more secure than the prior two versions because it supports encryption. Secure File Transfer Protocol, or SFTP, should always ...
... Then there is SNMP version 3, that's Simple Network Management Protocol version 3. It's a protocol that is used to manage and configure devices remotely on the network. It's more secure than the prior two versions because it supports encryption. Secure File Transfer Protocol, or SFTP, should always ...
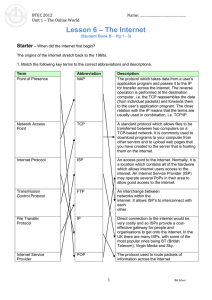
U1L6_The_Internet
... The protocol which takes data from a user’s application program and passes it to the IP for transfer across the internet. The reverse operation is performed at the destination computer, i.e. the TCP reassembles the data (from individual packets) and forwards them to the user’s application program. T ...
... The protocol which takes data from a user’s application program and passes it to the IP for transfer across the internet. The reverse operation is performed at the destination computer, i.e. the TCP reassembles the data (from individual packets) and forwards them to the user’s application program. T ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.





















![Internetting - start [kondor.etf.rs]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008748963_1-a9069059252fd71305a9df1cb24ebaac-300x300.png)