From: Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 408
... 1. Introduction Although the protein sequence-structure-function paradigm (well known as the “lock-and-key” hypothesis [1]), according to which a protein can achieve its biological function only on folding into a unique, structured state determined by its amino acid sequence, was a dominating view f ...
... 1. Introduction Although the protein sequence-structure-function paradigm (well known as the “lock-and-key” hypothesis [1]), according to which a protein can achieve its biological function only on folding into a unique, structured state determined by its amino acid sequence, was a dominating view f ...
WHAT IS?Protein is an essential nutritional product for the growth
... intake should be a complete protein; the rest can be incomplete and come from many different plant sources. It is important to note that the body does not store much protein, maybe 80-90 gram of complete protein (the daily intake for a pregnant mom), therefore a daily consumption is required. A defi ...
... intake should be a complete protein; the rest can be incomplete and come from many different plant sources. It is important to note that the body does not store much protein, maybe 80-90 gram of complete protein (the daily intake for a pregnant mom), therefore a daily consumption is required. A defi ...
Mechanisms of Translocation of Legionella pneumophila Effectors
... fusions of various L. pneumophila effectors to the rapidly and tightly folding dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) protein. Fusions to DHFR prevented the translocation of nearly all the effectors studied, including a 50 amino acid carboxy-terminal tag of an effector protein, suggesting that tightly folde ...
... fusions of various L. pneumophila effectors to the rapidly and tightly folding dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) protein. Fusions to DHFR prevented the translocation of nearly all the effectors studied, including a 50 amino acid carboxy-terminal tag of an effector protein, suggesting that tightly folde ...
1 BIOINFORMATICS Bioinformatics, based on National Institutes of
... Here is a list to help you think about the various properties a particular database may have. ...
... Here is a list to help you think about the various properties a particular database may have. ...
STING Millennium: a web-based suite of programs
... Protein function determination and identification of possible function modifiers, is in fact the most desirable goal of many genome project efforts. To achieve such goal, bioinformatics counts with some basic activities, such as: 1. sequence homology search and position specific sequence conservatio ...
... Protein function determination and identification of possible function modifiers, is in fact the most desirable goal of many genome project efforts. To achieve such goal, bioinformatics counts with some basic activities, such as: 1. sequence homology search and position specific sequence conservatio ...
TGAC_course_EGPa
... Tyson et al., Nature, 2004 • Acid mine drainage: process in which water, oxygen and chemolithotrophic microorganisms interact with sulfide minerals producing very acidic solutions • Bacterial biofilms floating on acidic water from Richmond Mine (Iron Mountain, California) (pH 0-1 and high concentrat ...
... Tyson et al., Nature, 2004 • Acid mine drainage: process in which water, oxygen and chemolithotrophic microorganisms interact with sulfide minerals producing very acidic solutions • Bacterial biofilms floating on acidic water from Richmond Mine (Iron Mountain, California) (pH 0-1 and high concentrat ...
Novel domains and orthologues of eukaryotic
... search for conserved domains in Xylella fastidiosa Tex (GenInfo code 11278678) using CDD (21) revealed a possible Pfam-FGGY-like RNase H fold domain (amino acids 330±391; E = 1 3 10±3). A PSI-BLAST search using this sequence as the query identi®ed Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 sll0832 as signi®cantly s ...
... search for conserved domains in Xylella fastidiosa Tex (GenInfo code 11278678) using CDD (21) revealed a possible Pfam-FGGY-like RNase H fold domain (amino acids 330±391; E = 1 3 10±3). A PSI-BLAST search using this sequence as the query identi®ed Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 sll0832 as signi®cantly s ...
Projection Structure of a Plant Vacuole Membrane Aquaporin by
... pseudo-2-fold axis of symmetry within each monomer normal to the plane of the crystal. Such a result correlates with the pseudo-2-fold axis of symmetry seen in monomers of AQP1, which is thought to arise from the tandem repeat of amino acids, and hence repeated structure, in the two halves of MIP-fa ...
... pseudo-2-fold axis of symmetry within each monomer normal to the plane of the crystal. Such a result correlates with the pseudo-2-fold axis of symmetry seen in monomers of AQP1, which is thought to arise from the tandem repeat of amino acids, and hence repeated structure, in the two halves of MIP-fa ...
The cDNA-deduced Amino Acid Sequence for
... segment. Interestingly, there are no sulphur-containing amino acids in the deduced sequence, which correlates with their low levels in total trichohyalin and also indicates that no disulphide cross-links, which are typical of hair IF proteins, are present within this region of the tdchohyalin molecu ...
... segment. Interestingly, there are no sulphur-containing amino acids in the deduced sequence, which correlates with their low levels in total trichohyalin and also indicates that no disulphide cross-links, which are typical of hair IF proteins, are present within this region of the tdchohyalin molecu ...
Protein
... Central Fatigue Hypothesis - theory • However studies ingesting TRP have not had any effects upon performance – Evidence in animals but not humans ...
... Central Fatigue Hypothesis - theory • However studies ingesting TRP have not had any effects upon performance – Evidence in animals but not humans ...
File - prepareforchemistry
... chain. These proteins are held together by strong hydrogen and disulphide bonds. ...
... chain. These proteins are held together by strong hydrogen and disulphide bonds. ...
Insights from the HuR-interacting transcriptome: ncRNAs, ubiquitin
... throughout their lifecycle, making important contributions to a coherent set of cellular functions. HuR can increase target mRNA stability and translation efficiency under several stress. Although HuR participate in a number of regulation, but the mechanisms of HuR regulate translation under stress ...
... throughout their lifecycle, making important contributions to a coherent set of cellular functions. HuR can increase target mRNA stability and translation efficiency under several stress. Although HuR participate in a number of regulation, but the mechanisms of HuR regulate translation under stress ...
Secondary structure of proteins - Home
... •Some proteins are entirely α –helix eg α -keratin fibrous protein in hair. •Other proteins have different amount of α -helix e.g. hemoglobin has 80% α -helix •Some proteins have no α -helices eg β–keratin in silk ...
... •Some proteins are entirely α –helix eg α -keratin fibrous protein in hair. •Other proteins have different amount of α -helix e.g. hemoglobin has 80% α -helix •Some proteins have no α -helices eg β–keratin in silk ...
function finders
... and one binds to DNA. -- P53 has several anti-cancer properties: it can activate DNA repair proteins when DNA has been damaged; it can suspend cell division, allowing time for damaged DNA to be repaired; it can initiate cell suicide (apoptosis) if cells are too badly damaged to be repaired. -- Damag ...
... and one binds to DNA. -- P53 has several anti-cancer properties: it can activate DNA repair proteins when DNA has been damaged; it can suspend cell division, allowing time for damaged DNA to be repaired; it can initiate cell suicide (apoptosis) if cells are too badly damaged to be repaired. -- Damag ...
LatFit - Manual - Bioinformatics Group Freiburg
... -fitSideChain If present, a fit of two monomers per amino acid is done. One for backbone and one representing the side chain. The Cα -atom (’CA’) is used to fit the backbone monomer. The atom specified with -pdbAtom is used for the side chain monomer fit. Note: The fit of a Glycine amino acid includ ...
... -fitSideChain If present, a fit of two monomers per amino acid is done. One for backbone and one representing the side chain. The Cα -atom (’CA’) is used to fit the backbone monomer. The atom specified with -pdbAtom is used for the side chain monomer fit. Note: The fit of a Glycine amino acid includ ...
Arabidopsis is a facultative long day plant which flowers earlier in
... the environment on flowering time has important resulting effects on the harvest time for that crop. Being able to understand, and ultimately control flowering time will enable more predictable flowering, better scheduling, and reduced wastage of crops. The model plant Arabidopsis is a facultative l ...
... the environment on flowering time has important resulting effects on the harvest time for that crop. Being able to understand, and ultimately control flowering time will enable more predictable flowering, better scheduling, and reduced wastage of crops. The model plant Arabidopsis is a facultative l ...
Solution structure of the Drosha double-stranded RNA-binding domain Open Access
... upon RNA binding [19]. A model for RNA recognition suggests that the two domains bind to portions of the pri-miRNA that are distant from each other. It is not known whether the dsRBD of Drosha is also important for substrate RNA binding or serves another function, since little to no RNA-binding acti ...
... upon RNA binding [19]. A model for RNA recognition suggests that the two domains bind to portions of the pri-miRNA that are distant from each other. It is not known whether the dsRBD of Drosha is also important for substrate RNA binding or serves another function, since little to no RNA-binding acti ...
BIRKBECK COLLEGE
... Explain how the similarity scores for amino acids in the BLOSUM matrices are used in calculating the best alignment of a pair of protein sequences. {4 Marks}. For each of the below give one reason why you would expect: A much higher score in any given BLOSUM matrix for matching a pair of Trp residue ...
... Explain how the similarity scores for amino acids in the BLOSUM matrices are used in calculating the best alignment of a pair of protein sequences. {4 Marks}. For each of the below give one reason why you would expect: A much higher score in any given BLOSUM matrix for matching a pair of Trp residue ...
A new subfamily of fungal subtilases: structural and functional
... extended 60 bp at the 39 non-coding region. Thus, the whole posl gene sequence was determined. A putative start codon (ATG 166–168) was identified in the 59 gene region, 600 bp upstream from the codon corresponding to the N-terminal of the mature protein. The corresponding cDNA fragment was amplifie ...
... extended 60 bp at the 39 non-coding region. Thus, the whole posl gene sequence was determined. A putative start codon (ATG 166–168) was identified in the 59 gene region, 600 bp upstream from the codon corresponding to the N-terminal of the mature protein. The corresponding cDNA fragment was amplifie ...
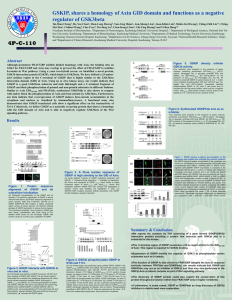
投影片 1
... interaction domain (GID) of Axin. Using an in vitro kinase assay, our results indicate that GSKIP is a good GSK3beta substrate and both full-length and a C-terminal fragment of GSKIP can block phosphorylation of primed and non-primed substrates in different fashions. Similar to Axin GID381-405 and F ...
... interaction domain (GID) of Axin. Using an in vitro kinase assay, our results indicate that GSKIP is a good GSK3beta substrate and both full-length and a C-terminal fragment of GSKIP can block phosphorylation of primed and non-primed substrates in different fashions. Similar to Axin GID381-405 and F ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.