OVAX - Prodinra
... ► Ovalbumin is the major egg white protein (about 50 mg/mL of egg white) of still unknown function ► OVAX and OVAY not yet characterized ► egg white OVAX purification method developed (Estimated concentration : 0,3 mg/mL) ...
... ► Ovalbumin is the major egg white protein (about 50 mg/mL of egg white) of still unknown function ► OVAX and OVAY not yet characterized ► egg white OVAX purification method developed (Estimated concentration : 0,3 mg/mL) ...
BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Going from where to why—interpretable prediction of protein subcellular localization
... State-of-the-art methods show high prediction performance that has significantly improved over the years. Unfortunately, the machine learning models behind high-accuracy predictors are often very complex making it difficult to understand why a particular prediction was made. Moreover, most predictor ...
... State-of-the-art methods show high prediction performance that has significantly improved over the years. Unfortunately, the machine learning models behind high-accuracy predictors are often very complex making it difficult to understand why a particular prediction was made. Moreover, most predictor ...
The Purification and Characterization of the Highly Labeled
... crystallin. Differences in electrophoretic mobility were also observed. The relationship between the HL protein and alpha crystallin and the basis for the observed differences between these proteins is discussed. ...
... crystallin. Differences in electrophoretic mobility were also observed. The relationship between the HL protein and alpha crystallin and the basis for the observed differences between these proteins is discussed. ...
Crystal structure of yeast hexokinase Pl in complex
... A multiple sequence alignment of hexokinases was obtained from the PFAM database,41 in a total of 317 sequences, including that of yeast hexokinase PI. From the alignment, it is possible to compute, in a parameter named DG stat, the discrepancy between amino acid frequencies in a given position and ...
... A multiple sequence alignment of hexokinases was obtained from the PFAM database,41 in a total of 317 sequences, including that of yeast hexokinase PI. From the alignment, it is possible to compute, in a parameter named DG stat, the discrepancy between amino acid frequencies in a given position and ...
Chaperone-assisted protein folding: the path to discovery from a
... binding and unbinding in a mechanism regulated by the GroEL ATPase24. Importantly, Jörg Martin found that GroES can bind the same ring that holds the unfolded substrate protein. Suddenly, the pieces of the puzzle began to fall into place, and we became increasingly confident that GroEL and GroES ess ...
... binding and unbinding in a mechanism regulated by the GroEL ATPase24. Importantly, Jörg Martin found that GroES can bind the same ring that holds the unfolded substrate protein. Suddenly, the pieces of the puzzle began to fall into place, and we became increasingly confident that GroEL and GroES ess ...
Biochemistry – Problem Set 2 Problem Set 2
... Similarly, the Trypsin fragment [Met-Gly-Phe-Leu] overlaps the CNBr fragment [Gly-Phe-Leu-Lys], suggesting the partial sequence: [Met-Gly-Phe-Leu-LysVal-His]. Finally, the Trypsin fragment [Val-His-Met-Cys] overlaps both the Chymotrypsin fragment [Leu-Lys-Val-His] and the CNBr fragment [Cys-Ala], su ...
... Similarly, the Trypsin fragment [Met-Gly-Phe-Leu] overlaps the CNBr fragment [Gly-Phe-Leu-Lys], suggesting the partial sequence: [Met-Gly-Phe-Leu-LysVal-His]. Finally, the Trypsin fragment [Val-His-Met-Cys] overlaps both the Chymotrypsin fragment [Leu-Lys-Val-His] and the CNBr fragment [Cys-Ala], su ...
Best Plant Protein
... for its sweetness. It is a unique species containing the glycosides stevioside and rebaudioside A, which are responsible for the sweet taste of the leaves. 31 Extracted and used as a sweetener for food products, it is 10–15 times sweeter than sucrose and because the human body does not metabolize th ...
... for its sweetness. It is a unique species containing the glycosides stevioside and rebaudioside A, which are responsible for the sweet taste of the leaves. 31 Extracted and used as a sweetener for food products, it is 10–15 times sweeter than sucrose and because the human body does not metabolize th ...
Going from where to why—interpretable
... State-of-the-art methods show high prediction performance that has significantly improved over the years. Unfortunately, the machine learning models behind high-accuracy predictors are often very complex making it difficult to understand why a particular prediction was made. Moreover, most predictor ...
... State-of-the-art methods show high prediction performance that has significantly improved over the years. Unfortunately, the machine learning models behind high-accuracy predictors are often very complex making it difficult to understand why a particular prediction was made. Moreover, most predictor ...
Data-driven docking for the study of biomolecular complexes
... With the presently available amount of genetic information, a lot of attention focuses on systems biology and in particular on biomolecular interactions. Considering the huge number of such interactions, and their often weak and transient nature, conventional experimental methods such as Xray crysta ...
... With the presently available amount of genetic information, a lot of attention focuses on systems biology and in particular on biomolecular interactions. Considering the huge number of such interactions, and their often weak and transient nature, conventional experimental methods such as Xray crysta ...
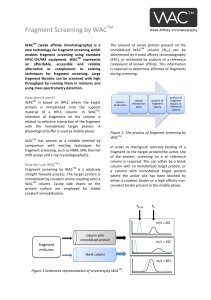
Fragment Screening by WAC - Transientic Interactions
... A WACTM column is usually very stable as the immobilized protein is significantly more stable than when present in solution. Proteins such as thrombin and Hsp90 has proven to maintain 90% ...
... A WACTM column is usually very stable as the immobilized protein is significantly more stable than when present in solution. Proteins such as thrombin and Hsp90 has proven to maintain 90% ...
Lecture 24
... maintenance of protein structure and functionality is difficult. The expressed proteins have a short shelf life, if not stored correctly, which makes protein storage difficult. One of the other challenges of using a prokaryotic system such as E. coli is that posttranslational modifications may not b ...
... maintenance of protein structure and functionality is difficult. The expressed proteins have a short shelf life, if not stored correctly, which makes protein storage difficult. One of the other challenges of using a prokaryotic system such as E. coli is that posttranslational modifications may not b ...
Integrative Assignment
... Other fonts are a mess for displaying sequence data. Reference Sequence: YP_003024038.1 cytochrome b [Homo sapiens] >gi|251831119|ref|YP_003024038.1| cytochrome b [Homo sapiens] ...
... Other fonts are a mess for displaying sequence data. Reference Sequence: YP_003024038.1 cytochrome b [Homo sapiens] >gi|251831119|ref|YP_003024038.1| cytochrome b [Homo sapiens] ...
Downloadable - University of New Hampshire
... designated as a “lid” domain. The plasticity of this lid domain is apparent in several open and closed state structures of different lipase enzymes. However, the functional significance of the lid domain and underlying conformational change remains under debate. Various mechanisms of lipase activati ...
... designated as a “lid” domain. The plasticity of this lid domain is apparent in several open and closed state structures of different lipase enzymes. However, the functional significance of the lid domain and underlying conformational change remains under debate. Various mechanisms of lipase activati ...
Enzymatic Protein Deglycosylation Kit (EDEGLY)
... sugars because of their limited specificities and because they leave one N-acetylglucosamine residue attached to the asparagine.6,7 There is no enzyme comparable to PNGase F for removing intact O-linked sugars. Monosaccharides must be removed by a series of exoglycosidases until only the Gal-β(1→3)- ...
... sugars because of their limited specificities and because they leave one N-acetylglucosamine residue attached to the asparagine.6,7 There is no enzyme comparable to PNGase F for removing intact O-linked sugars. Monosaccharides must be removed by a series of exoglycosidases until only the Gal-β(1→3)- ...
Lecture
... lines = f.read().split("\n") ds1 = DNASequence(lines[0]) ds2 = DNASequence(lines[1]) print "Hamming distance:", ds1.hamm(ds2) ...
... lines = f.read().split("\n") ds1 = DNASequence(lines[0]) ds2 = DNASequence(lines[1]) print "Hamming distance:", ds1.hamm(ds2) ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... frame is a structural gene (data not shown). The open reading frame is preceded by a possible ribosome-binding site (Fig. 2). This gene, which we designated nodO, codes for a protein of 284 amino acids with a predicted molecular size of 30,002 daltons. To test whether the gene identified above codes ...
... frame is a structural gene (data not shown). The open reading frame is preceded by a possible ribosome-binding site (Fig. 2). This gene, which we designated nodO, codes for a protein of 284 amino acids with a predicted molecular size of 30,002 daltons. To test whether the gene identified above codes ...
Folding quality control in the export of proteins by the
... agnostic • The state of the protein (folding) determined which pathway was used ...
... agnostic • The state of the protein (folding) determined which pathway was used ...
Isolation by Calcium-Dependent Translocation to
... from these proteins commonly translocating to all organelles, a protein of 42-kD, migrating as a double band, was associated with the specific granules, but neither with azurophil granules nor secretory vesicles/plasma membranes. Association with the organelles of this protein was detectable at a ca ...
... from these proteins commonly translocating to all organelles, a protein of 42-kD, migrating as a double band, was associated with the specific granules, but neither with azurophil granules nor secretory vesicles/plasma membranes. Association with the organelles of this protein was detectable at a ca ...
Macromolecular Structure Database group
... • Provide a resource that facilitates the automatic selection of potential targets for protein structure determination while minimising human interaction with the software (if required). Input: • Raw amino acid sequence • UniProt accession number • UniProt accession number and a sequence range Outpu ...
... • Provide a resource that facilitates the automatic selection of potential targets for protein structure determination while minimising human interaction with the software (if required). Input: • Raw amino acid sequence • UniProt accession number • UniProt accession number and a sequence range Outpu ...
This JET help is useful to understand files in the folder
... -g pdb-results-file (name1,name2, ...) : list of names separated by commas in parenthesis. Names are those of the results columns in the results files {tr ;freq ;pc ;trace ;clusters ;axs ;surfAxs ;percentSurfAxs ;inter ;atomAxs ;atomSurfAxs}. Columns results selected with these names are written in ...
... -g pdb-results-file (name1,name2, ...) : list of names separated by commas in parenthesis. Names are those of the results columns in the results files {tr ;freq ;pc ;trace ;clusters ;axs ;surfAxs ;percentSurfAxs ;inter ;atomAxs ;atomSurfAxs}. Columns results selected with these names are written in ...
Comparative Analysis of ,Multiple Protein
... Multiple alignment methods are often used without Comparison of primary sequence information is rapidly becoming the major source of data in the elu- knowledge of the assumptions implicit in their operation. cidation of the rnolecuIar mechanismsof replication and We willassess the major academically ...
... Multiple alignment methods are often used without Comparison of primary sequence information is rapidly becoming the major source of data in the elu- knowledge of the assumptions implicit in their operation. cidation of the rnolecuIar mechanismsof replication and We willassess the major academically ...
Protein synthesis
... • 1) Ternary complex formation (IF2.GTP.initiator tRNA) • This complex binds to mRNA to form 30S initiation complex • The intereacting components are(mRNA+30S subunit+fMet tRNAf+GTP+Initiation factors) • The fmet-tRNAf is located to the AUG (initiator)codon • 50S subunit joins to 30S initiation comp ...
... • 1) Ternary complex formation (IF2.GTP.initiator tRNA) • This complex binds to mRNA to form 30S initiation complex • The intereacting components are(mRNA+30S subunit+fMet tRNAf+GTP+Initiation factors) • The fmet-tRNAf is located to the AUG (initiator)codon • 50S subunit joins to 30S initiation comp ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.