Slides
... We have a large number of predominantly apo form structures being determined by structural genomics and functionally driven structure determination ...
... We have a large number of predominantly apo form structures being determined by structural genomics and functionally driven structure determination ...
Protein PreTest
... 1. Amino acids are: (red) Acids found in meat. (yellow) Building blocks from which proteins are made. (blue) A type of marinade. 2. The most important function of protein is: (red) To provide energy (yellow) The regulation of the body functions (blue) To build and repair 3. Another function of prote ...
... 1. Amino acids are: (red) Acids found in meat. (yellow) Building blocks from which proteins are made. (blue) A type of marinade. 2. The most important function of protein is: (red) To provide energy (yellow) The regulation of the body functions (blue) To build and repair 3. Another function of prote ...
Multiple Choice Questions (2 points each) Which of the following is
... (b.) Both parallel and anti-parallel forms of beta-pleated sheets are found in proteins. They differ in the pattern of hydrogen bonding between the chains and this, in turn, affects the stability of the overall beta-pleated sheets. Describe the differences in the H-bonding (an illustration plus text ...
... (b.) Both parallel and anti-parallel forms of beta-pleated sheets are found in proteins. They differ in the pattern of hydrogen bonding between the chains and this, in turn, affects the stability of the overall beta-pleated sheets. Describe the differences in the H-bonding (an illustration plus text ...
Powerpoint slides - School of Engineering and Applied Science
... Problem: requires crystals; difficult to crystallize proteins by maintaining their native conformation; not all protein can be crystallized; - Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy of proteins in solution (medium to high resolution) Problem: Works only with small and medium size proteins (~5 ...
... Problem: requires crystals; difficult to crystallize proteins by maintaining their native conformation; not all protein can be crystallized; - Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy of proteins in solution (medium to high resolution) Problem: Works only with small and medium size proteins (~5 ...
Discovering Macromolecular Interactions
... buffers because of the addition of ionic detergents like SDS or sodium deoxycholate. While these buffers do not maintain native protein conformation, proteins that are difficult to release with non-denaturing buffers, such as nuclear proteins, can be released with denaturing buffers. Both buffers co ...
... buffers because of the addition of ionic detergents like SDS or sodium deoxycholate. While these buffers do not maintain native protein conformation, proteins that are difficult to release with non-denaturing buffers, such as nuclear proteins, can be released with denaturing buffers. Both buffers co ...
Public data and tool repositories Section 2 Survey of
... Ex: Extracting and aligning human and mouse APP upstream regions ...
... Ex: Extracting and aligning human and mouse APP upstream regions ...
influence of macromolecular crowding on protein stability
... single, well defined conformational state: the native state. Protein folding is thus the physico-chemical process by which a polypeptidic chain undergoes a structural change from an ensemble of coil like structure up to the unique structure encoded in its amino-acid sequence. This process is fascina ...
... single, well defined conformational state: the native state. Protein folding is thus the physico-chemical process by which a polypeptidic chain undergoes a structural change from an ensemble of coil like structure up to the unique structure encoded in its amino-acid sequence. This process is fascina ...
Document
... experience depression, problems with muscular coordination, impaired vision, and personality and behavioral changes such as impaired memory, judgment, and thinking. As the disease progresses, mental impairment becomes severe and involuntary muscle jerks (myoclonus) often occur along with blindness. ...
... experience depression, problems with muscular coordination, impaired vision, and personality and behavioral changes such as impaired memory, judgment, and thinking. As the disease progresses, mental impairment becomes severe and involuntary muscle jerks (myoclonus) often occur along with blindness. ...
Nutrition Unit-Lesson 3 PWRPT
... 2. There are 2 types of carb’s simple & ________. Digestion 3. Fiber helps with _________________. Appetite 4. Empty calorie can ruin your _______________. ...
... 2. There are 2 types of carb’s simple & ________. Digestion 3. Fiber helps with _________________. Appetite 4. Empty calorie can ruin your _______________. ...
Proteome - Nematode bioinformatics. Analysis tools and data
... Protein quantification. Gel-based methods such as differential staining of gels with fluorescent dyes (difference gel electrophoresis). Gel-free methods include various tagging or chemical modification methods, such as isotope-coded affinity tags (ICATs) or combined fractional diagnoal chromatograph ...
... Protein quantification. Gel-based methods such as differential staining of gels with fluorescent dyes (difference gel electrophoresis). Gel-free methods include various tagging or chemical modification methods, such as isotope-coded affinity tags (ICATs) or combined fractional diagnoal chromatograph ...
The Protein Interaction Prediction Engine (PIPE)
... Character based amino acid representation was converted into binary encodings. Removed need for character-to-index lookup in PAM120. ...
... Character based amino acid representation was converted into binary encodings. Removed need for character-to-index lookup in PAM120. ...
A quantitative analysis to unveil specific binding proteins for
... From: A quantitative analysis to unveil specific binding proteins for bioactive compounds Protein Eng Des Sel. 2012;26(4):249-254. doi:10.1093/protein/gzs103 Protein Eng Des Sel | © The Author 2012. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.p ...
... From: A quantitative analysis to unveil specific binding proteins for bioactive compounds Protein Eng Des Sel. 2012;26(4):249-254. doi:10.1093/protein/gzs103 Protein Eng Des Sel | © The Author 2012. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.p ...
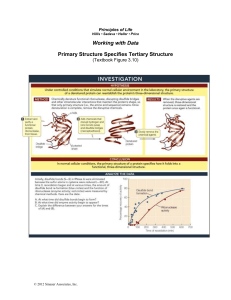
Principles of Life
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
DNA Sequences Analysis
... “BLAST is a set of algorithms that attempt to find a short fragment of a query sequence that aligns perfectly with a fragment of a subject sequence found in a database.” • That initial alignment must be greater than a neighborhood score threshold (T) , the fragment is then used as a seed to extend t ...
... “BLAST is a set of algorithms that attempt to find a short fragment of a query sequence that aligns perfectly with a fragment of a subject sequence found in a database.” • That initial alignment must be greater than a neighborhood score threshold (T) , the fragment is then used as a seed to extend t ...
Recombinant Human Interferon Omaga-1 (rh IFNW1)
... Description: Human recombinant IFNW1 produced in E.coli is a single, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 172 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 19.9kDa. The Interferon-Omega 1 is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. Source: Escherichia coli Physical Appearance: Ster ...
... Description: Human recombinant IFNW1 produced in E.coli is a single, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 172 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 19.9kDa. The Interferon-Omega 1 is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. Source: Escherichia coli Physical Appearance: Ster ...
6. protein folding
... • Folding means arriving at the right combinations of angles for every amino acid residue in the sequence. • Proteins fold on a defined pathway (or a small number of alternative pathways); they don't randomly search all possible conformations until they arrive at the most stable (lowest free energy ...
... • Folding means arriving at the right combinations of angles for every amino acid residue in the sequence. • Proteins fold on a defined pathway (or a small number of alternative pathways); they don't randomly search all possible conformations until they arrive at the most stable (lowest free energy ...
Document
... These coiled coils have a heptad repeat abcdefg with nonpolar residues at position a and d and an electrostatic interaction between residues e and g. ...
... These coiled coils have a heptad repeat abcdefg with nonpolar residues at position a and d and an electrostatic interaction between residues e and g. ...
Molecules, Genes, and Diseases Session 2 Protein Structure and
... referred to as the tertiary structure. This involves folding up of the secondary structures so that amino acids far apart in the primary sequence may interact. • Larger proteins (~200 amino acids or greater) tend to have distinct domains. These are regions of the polypeptide that have distinct struc ...
... referred to as the tertiary structure. This involves folding up of the secondary structures so that amino acids far apart in the primary sequence may interact. • Larger proteins (~200 amino acids or greater) tend to have distinct domains. These are regions of the polypeptide that have distinct struc ...
Supplemental Figures and Tables
... (A) Homo-dimerization yeast two hybrid assays. The same proteins were used as bait (fused to GAL4 DNA binding domain) and prey (fused to GAL4 activation domain). (B) GUS expression in leaf abaxial (lower) epidermal cells of tobacco transiently transformed with pZPR3-uidA and 35S-REV* or pZPR3-uidA a ...
... (A) Homo-dimerization yeast two hybrid assays. The same proteins were used as bait (fused to GAL4 DNA binding domain) and prey (fused to GAL4 activation domain). (B) GUS expression in leaf abaxial (lower) epidermal cells of tobacco transiently transformed with pZPR3-uidA and 35S-REV* or pZPR3-uidA a ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.