Cell Power Point
... Be able to: • generate and conduct electrical signals in the body • transmit signals from the brain down the spinal cord to the body ExamplesAll nerves ...
... Be able to: • generate and conduct electrical signals in the body • transmit signals from the brain down the spinal cord to the body ExamplesAll nerves ...
Chapter 2 Cells to Systems
... What is the most basic unit of living things? List five parts of all cells and their jobs. List the two parts that are only in plant cells. What are genes made of? What is the process of passing genes from one generation to the next called? ...
... What is the most basic unit of living things? List five parts of all cells and their jobs. List the two parts that are only in plant cells. What are genes made of? What is the process of passing genes from one generation to the next called? ...
Epithelial Tissues
... Blood forms in red marrow of long bones Function: Transports, helps maintain stable internal environment Found: throughout body in blood vessels and heart chambers ...
... Blood forms in red marrow of long bones Function: Transports, helps maintain stable internal environment Found: throughout body in blood vessels and heart chambers ...
cells - AHS
... Cells come only from other cells (Biogenesis) Before this, spontaneous generation was the accepted idea Hey…Mice are always coming out of the hay! ...
... Cells come only from other cells (Biogenesis) Before this, spontaneous generation was the accepted idea Hey…Mice are always coming out of the hay! ...
Strand A - Life Processes and Living Things
... example, corn) and dicots (for example, beans) Life Cycles and Reproduction The Life Cycle and Reproduction Life cycle: development of an organism from birth to growth, reproduction, death Example: Growth stages of a human: embryo, foetus, newborn, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, ol ...
... example, corn) and dicots (for example, beans) Life Cycles and Reproduction The Life Cycle and Reproduction Life cycle: development of an organism from birth to growth, reproduction, death Example: Growth stages of a human: embryo, foetus, newborn, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, ol ...
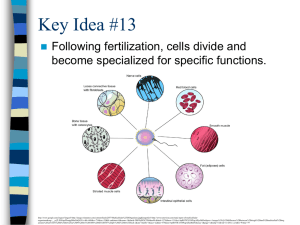
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
... engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
Check In: WHAT ARE CELLS?
... On a separate sheet of paper, draw a picture of an onion skin cell. ...
... On a separate sheet of paper, draw a picture of an onion skin cell. ...
LT #4 I can describe that cells differentiate to form
... differentiate to form specialized cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. ...
... differentiate to form specialized cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. ...
Press Release - MWM
... into pluripotency by the mere modulation of the culture conditions. Recently, Hans Schöler’s research group succeeded in converting adult germline stem cells (GSCs) from mouse testicular cells into pluripotent stem cells by allowing the cells sufficient time and space to develop in their culture med ...
... into pluripotency by the mere modulation of the culture conditions. Recently, Hans Schöler’s research group succeeded in converting adult germline stem cells (GSCs) from mouse testicular cells into pluripotent stem cells by allowing the cells sufficient time and space to develop in their culture med ...
Cells and Basketball
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
I. Introduction
... 25. The allantois is a tube like structure that extends from the yolk sac into the connecting stalk. It gives rise to umbilical blood vessels. 26. The amniochorionic membrane is the fusion of the amnion and chorion. 27. The embryonic stage concludes at the end of the eighth week. 28. Teratogens are ...
... 25. The allantois is a tube like structure that extends from the yolk sac into the connecting stalk. It gives rise to umbilical blood vessels. 26. The amniochorionic membrane is the fusion of the amnion and chorion. 27. The embryonic stage concludes at the end of the eighth week. 28. Teratogens are ...
Chapter 23: Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... 8. The events of implantation are attachment of the blastocyst to endometrium, digestion of a portion of the endometrium, sinking of the blastocyst into a depression in endometrium, and the thickening of the endometrium around the blastocyst. 9. Implantation begins normally about the end of the fir ...
... 8. The events of implantation are attachment of the blastocyst to endometrium, digestion of a portion of the endometrium, sinking of the blastocyst into a depression in endometrium, and the thickening of the endometrium around the blastocyst. 9. Implantation begins normally about the end of the fir ...
The Tiny Living World Around Us
... What your “blood type” means • Antibodies mark pathogens once they are discovered in the body so the immune system can find and destroy them • We are born with or without certain sets of antibodies (A and B) • If you have type O, you have neither A or B antibodies • The plus or minus means you have ...
... What your “blood type” means • Antibodies mark pathogens once they are discovered in the body so the immune system can find and destroy them • We are born with or without certain sets of antibodies (A and B) • If you have type O, you have neither A or B antibodies • The plus or minus means you have ...
What is a cell? - Epiphany Catholic School
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material tha ...
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material tha ...
2017 Year 8 Term3 Programme
... • describing the structure of each organ in a system and relating its function to the overall function of the system • examining the specialised cells and tissues involved in structure and function of particular organs • comparing similar systems in different organisms such as digestive systems in h ...
... • describing the structure of each organ in a system and relating its function to the overall function of the system • examining the specialised cells and tissues involved in structure and function of particular organs • comparing similar systems in different organisms such as digestive systems in h ...
Chapter 1 - SharpSchool
... • If you cut yourself, blood cells will kill bacteria that may enter your body through your cut. The blood cells use energy to do their work! ...
... • If you cut yourself, blood cells will kill bacteria that may enter your body through your cut. The blood cells use energy to do their work! ...
Definitions handout
... Group of cells of the same type doing a particular job. E.g. the blood Group of tissues doing a particular job between them. E.g. the heart Group of organs doing a particular job between them. E.g. the circulatory system Molecules and ions diffuse from regions of higher concentration to regions of l ...
... Group of cells of the same type doing a particular job. E.g. the blood Group of tissues doing a particular job between them. E.g. the heart Group of organs doing a particular job between them. E.g. the circulatory system Molecules and ions diffuse from regions of higher concentration to regions of l ...
Levels of Organization
... The nervous system detects and interprets information from the environment outside the body and from within the body; controls most body functions. The immune system fights ...
... The nervous system detects and interprets information from the environment outside the body and from within the body; controls most body functions. The immune system fights ...
Reproduction and Development Vocabulary
... A type of cleavage in which there is incomplete division of yolk-rich egg, characteristic of avian development. The middle primary germ layer of an early embryo that develops into the notochord, the lining of the coelom, muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys, and most of the circulatory system. A solid ...
... A type of cleavage in which there is incomplete division of yolk-rich egg, characteristic of avian development. The middle primary germ layer of an early embryo that develops into the notochord, the lining of the coelom, muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys, and most of the circulatory system. A solid ...
development
... complete, a single large haploid egg and three smaller cells called polar bodies will be produced. The polar bodies have very little cytoplasm and ...
... complete, a single large haploid egg and three smaller cells called polar bodies will be produced. The polar bodies have very little cytoplasm and ...
Laboratory 4: Cells Structure and Function
... Although the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms, cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their i ...
... Although the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms, cells differ enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their i ...
doc
... and present in the woman’s urine Fetal development… The inner wall of the uterus together with embryonic tissues become the placenta, which transfers oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes between the mother and the developing fetus [Fig. 46.16] Two basic reproductive modes: Asexual reproducti ...
... and present in the woman’s urine Fetal development… The inner wall of the uterus together with embryonic tissues become the placenta, which transfers oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes between the mother and the developing fetus [Fig. 46.16] Two basic reproductive modes: Asexual reproducti ...
Basic Structure PowerPoint
... 3. Chromatin network: located in nucleus; forms chromosomes which contain genes that carry inherited characteristics; DNA (A-T/G-C bases); males XY and females XX 4. Centrosome: located in cytoplasm near nucleus; contains 2 centrioles important in reproduction 5. Mitochondria: located throughout the ...
... 3. Chromatin network: located in nucleus; forms chromosomes which contain genes that carry inherited characteristics; DNA (A-T/G-C bases); males XY and females XX 4. Centrosome: located in cytoplasm near nucleus; contains 2 centrioles important in reproduction 5. Mitochondria: located throughout the ...
File
... 3. Chromatin network: located in nucleus; forms chromosomes which contain genes that carry inherited characteristics; DNA (A-T/G-C bases); males XY and females XX 4. Centrosome: located in cytoplasm near nucleus; contains 2 centrioles important in reproduction 5. Mitochondria: located throughout the ...
... 3. Chromatin network: located in nucleus; forms chromosomes which contain genes that carry inherited characteristics; DNA (A-T/G-C bases); males XY and females XX 4. Centrosome: located in cytoplasm near nucleus; contains 2 centrioles important in reproduction 5. Mitochondria: located throughout the ...
animal tissues and organ systems
... 10. Immune System (Lymph nodes, Vessels, and Lymph) Protects body from infection, injury & cancer. ...
... 10. Immune System (Lymph nodes, Vessels, and Lymph) Protects body from infection, injury & cancer. ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.