How does the food you eat provide energy to cells in
... orchestra needs a variety of musical instruments - some flutes, some oboes, a piano, drums, and so on. In the same way, a multicellular organism cannot be made up only of identical cells. As Figure 2.13 shows, although multicellular organisms grow from single cells that repeatedly divide, their cell ...
... orchestra needs a variety of musical instruments - some flutes, some oboes, a piano, drums, and so on. In the same way, a multicellular organism cannot be made up only of identical cells. As Figure 2.13 shows, although multicellular organisms grow from single cells that repeatedly divide, their cell ...
Tissue Types - wwhsanatomy
... Cells are large, long and multinucleated Separate cells are hard to see Is held together by MUSCLE FASCIA Moves bones and other structures VOLUNTARILY when stimulated by nerves Has the ability to respond to stimuli has “Irritability” ...
... Cells are large, long and multinucleated Separate cells are hard to see Is held together by MUSCLE FASCIA Moves bones and other structures VOLUNTARILY when stimulated by nerves Has the ability to respond to stimuli has “Irritability” ...
Anatomy – structure
... 2. histology – study of tissue C. Levels of biological organization 1. chemical level 2. cellular level 3. tissue level – mass of similar functioning cells 4.organ – two or more tissues 5. system – several organs 6.organismic – all systems D.life processes 1. - metabolism – sum of all chemical proce ...
... 2. histology – study of tissue C. Levels of biological organization 1. chemical level 2. cellular level 3. tissue level – mass of similar functioning cells 4.organ – two or more tissues 5. system – several organs 6.organismic – all systems D.life processes 1. - metabolism – sum of all chemical proce ...
Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems
... Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
... Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
Cells - WordPress.com
... Your unique DNA sequence can be analysed from a body fluid sample. Forensic scientists can match the DNA taken from a crime scene with suspects DNA profiles to determine who committed the crime. ...
... Your unique DNA sequence can be analysed from a body fluid sample. Forensic scientists can match the DNA taken from a crime scene with suspects DNA profiles to determine who committed the crime. ...
Themes of Life
... body. Luckily, the cells in our body are specialized. Some cells are specialized to move, to react to the environment; still others to produce substance that the organism needs. Each of these specialized cells contributes to homeostasis in the organism. Describe how cells of a multicellular organism ...
... body. Luckily, the cells in our body are specialized. Some cells are specialized to move, to react to the environment; still others to produce substance that the organism needs. Each of these specialized cells contributes to homeostasis in the organism. Describe how cells of a multicellular organism ...
- Smart Science
... A blue whale’s brain is the largest brain known. It has a mass of about 6.0 kg, which is slightly more than four times more massive than a human brain. This might mean blue whales are very intelligent, but we know that the size of an animal’s brain does not necessarily relate to the animal’s intelli ...
... A blue whale’s brain is the largest brain known. It has a mass of about 6.0 kg, which is slightly more than four times more massive than a human brain. This might mean blue whales are very intelligent, but we know that the size of an animal’s brain does not necessarily relate to the animal’s intelli ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
Animal Cells/ Cellular Function
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multicellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
... Students describe the general structure and function of cells. They can explain that all living systems are composed of cells and that organisms may be unicellular or multicellular. They understand that cells are composed of biological macromolecules and that the complex processes of the cell allow ...
Homework Exercise 1 - Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Place the
... other organs which help. The stomach and intestines form the digestive system, the heart and blood vessels form the circulatory system and they work together to circulate blood around the body. (a) What term is given to a living organism that consists of more than one cell? ...
... other organs which help. The stomach and intestines form the digestive system, the heart and blood vessels form the circulatory system and they work together to circulate blood around the body. (a) What term is given to a living organism that consists of more than one cell? ...
File
... Sex Linked Traits: X-linked Genes are carried on the X chromosome. Female: XX (can be a carrier) male: XY has only one X, disoder more likely to be in phenotype ...
... Sex Linked Traits: X-linked Genes are carried on the X chromosome. Female: XX (can be a carrier) male: XY has only one X, disoder more likely to be in phenotype ...
Asexual Reproduction - Effingham County Schools
... 3. What is a zygote and when is it formed? 3. A zygote is the first cell of a person. It is formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg during reproduction. ...
... 3. What is a zygote and when is it formed? 3. A zygote is the first cell of a person. It is formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg during reproduction. ...
B3 Intervention and Revision Higher B3a Molecules for
... conditions including Parkinsons disease and paralysis. Discuss issues arising from stem cell research in animals. Explain the difference between adult and embryonic stem cells. Human embryos (embryonic stem cells) Adult bone marrow (adult stem cells) ...
... conditions including Parkinsons disease and paralysis. Discuss issues arising from stem cell research in animals. Explain the difference between adult and embryonic stem cells. Human embryos (embryonic stem cells) Adult bone marrow (adult stem cells) ...
INTRODUCTORY QUESTIONS
... C. Living things require energy. Different organisms obtain their food from different sources. Give an example. What is autotrophic? Autotrophic organisms such as green plants make their own food through photosynthesis. What is photosynthesis? This is a process where green plants use sun energy to m ...
... C. Living things require energy. Different organisms obtain their food from different sources. Give an example. What is autotrophic? Autotrophic organisms such as green plants make their own food through photosynthesis. What is photosynthesis? This is a process where green plants use sun energy to m ...
Page 1
... Order of least to most complex (smallest to largest): organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism Animals have cells that are alike and plants will have cells that are similar too. Tissues are groups of similar cells that all do the same sort of work. For example, nerve tissue is mad ...
... Order of least to most complex (smallest to largest): organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism Animals have cells that are alike and plants will have cells that are similar too. Tissues are groups of similar cells that all do the same sort of work. For example, nerve tissue is mad ...
I. Organization of Living Things TISSUE CELL
... a special job. Planaria have several organs, including eyespots and reproductive organs. Finally, organs may work together to form an organ system. In the earthworm as well as in the most complex animal, man, the circulatory system carries food and oxygen to all parts of the body. Organs such as the ...
... a special job. Planaria have several organs, including eyespots and reproductive organs. Finally, organs may work together to form an organ system. In the earthworm as well as in the most complex animal, man, the circulatory system carries food and oxygen to all parts of the body. Organs such as the ...
Cells - St. Ambrose School
... They are organized structures that help living things carry on the activities of life, such as digestion, movement, growth and reproduction ...
... They are organized structures that help living things carry on the activities of life, such as digestion, movement, growth and reproduction ...
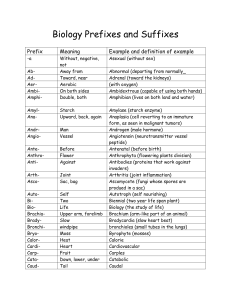
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyp ...
... heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyp ...
Hello!!! - Elida Local Schools
... Cells are the structural and functional units of all living organisms. Some organisms, such as bacteria, are each made up of only one cell. Other organisms, such as animals, are each made up of many cells. Cells in many-celled organisms specialize depending upon their location and function in the bo ...
... Cells are the structural and functional units of all living organisms. Some organisms, such as bacteria, are each made up of only one cell. Other organisms, such as animals, are each made up of many cells. Cells in many-celled organisms specialize depending upon their location and function in the bo ...
6.2 Sexual Reproduction
... In sexual reproduction, a male provides sperm which fertilizes one or more eggs of a female. To make an offspring, one sperm fuses with one egg to form a fertilized egg or zygote. ...
... In sexual reproduction, a male provides sperm which fertilizes one or more eggs of a female. To make an offspring, one sperm fuses with one egg to form a fertilized egg or zygote. ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review 2016
... Haploid - Haploid contain single set of chromosomes (half the number of diploid cells, example: sex cells such as sperm and egg) c. Diploid - Diploid cells contain pairs of chromosomes (cells throughout the body EXCEPT sex cells) d. Regeneration - the process that uses cell division to regrow body p ...
... Haploid - Haploid contain single set of chromosomes (half the number of diploid cells, example: sex cells such as sperm and egg) c. Diploid - Diploid cells contain pairs of chromosomes (cells throughout the body EXCEPT sex cells) d. Regeneration - the process that uses cell division to regrow body p ...
End of Chapter 23 Questions
... embryonic disk. It forms blood cells in the early stages of development and gives rise to the cells that later become sex cells. The allantois forms during the third week as a tube extending from the early yolk sac into the connecting stalk of the embryo. It also forms blood cells and gives rise to ...
... embryonic disk. It forms blood cells in the early stages of development and gives rise to the cells that later become sex cells. The allantois forms during the third week as a tube extending from the early yolk sac into the connecting stalk of the embryo. It also forms blood cells and gives rise to ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.