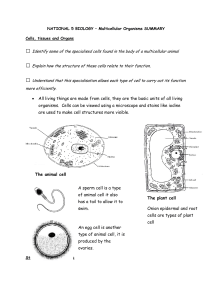
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the hae ...
... body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the hae ...
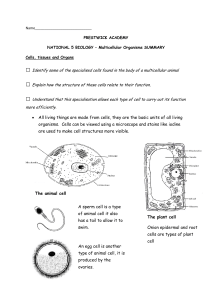
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the hae ...
... body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the hae ...
Development Reading Guide File
... placenta. The placenta develops inside the uterus and surrounds the embryo. This structure enables nutrients and waste products to be transferred between the mother and developing baby (Figure 33-14). By the end of the third month, the placenta is fully formed and functional. In the wall of the plac ...
... placenta. The placenta develops inside the uterus and surrounds the embryo. This structure enables nutrients and waste products to be transferred between the mother and developing baby (Figure 33-14). By the end of the third month, the placenta is fully formed and functional. In the wall of the plac ...
Do not write on this paper
... The body plan of the organism shown above is A radially symmetrical. B asymmetrical. C bilaterally symmetrical. D complex. 5. Which of the following work together to form tissues? A organs B organ systems C cells 1. Every living thing is made from a tiny building D muscles block called a(n) ___ . 2. ...
... The body plan of the organism shown above is A radially symmetrical. B asymmetrical. C bilaterally symmetrical. D complex. 5. Which of the following work together to form tissues? A organs B organ systems C cells 1. Every living thing is made from a tiny building D muscles block called a(n) ___ . 2. ...
Practice Exam
... The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water. Would individuals who are suffering from diarrhoea absorb more or less water in their large intestine? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________ ...
... The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water. Would individuals who are suffering from diarrhoea absorb more or less water in their large intestine? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________ ...
Tissues and Membranes
... Matrix—calcium salts and collagen Arranged into haversian systems Skeletal support, organ protection, red bone marrow in femur head, pelvis, sternum—produce blood cells Good blood supply—fast healing o Cartilage (Fig 4-5 B) Cells—chondrocytes Matrix—protein Joint surfaces—decreases fri ...
... Matrix—calcium salts and collagen Arranged into haversian systems Skeletal support, organ protection, red bone marrow in femur head, pelvis, sternum—produce blood cells Good blood supply—fast healing o Cartilage (Fig 4-5 B) Cells—chondrocytes Matrix—protein Joint surfaces—decreases fri ...
Connective Tissues
... Single, centrally located nucleus Makes up walls of hollow internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, uterus, and blood vessels ...
... Single, centrally located nucleus Makes up walls of hollow internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, uterus, and blood vessels ...
Unit 2 Revision List Topic Key Questions Key Words Plant and
... ➔ Can you identify how cells are specialised from diagrams? ➔ Can you explain how the following cells are specialised? ◆ red blood cells ◆ nerve cells ◆ muscle cells ◆ sperm cells ◆ ciliated cells ◆ palisade cells ◆ root hair cells ...
... ➔ Can you identify how cells are specialised from diagrams? ➔ Can you explain how the following cells are specialised? ◆ red blood cells ◆ nerve cells ◆ muscle cells ◆ sperm cells ◆ ciliated cells ◆ palisade cells ◆ root hair cells ...
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... Cell differentiation - Cells differentiate to form different types of cells. Animal cells differentiate at an early stage, whereas many plant cells can differentiate throughout life. ...
... Cell differentiation - Cells differentiate to form different types of cells. Animal cells differentiate at an early stage, whereas many plant cells can differentiate throughout life. ...
Getting to Know: Cell Theory
... There certainly is an amazing diversity of life forms on Earth. It would be difficult to imagine them all made of the same cell. In fact, there are many different kinds of cells. Unicellular organisms consist of just one cell. These cells go through life cycles just like more complex organisms. They ...
... There certainly is an amazing diversity of life forms on Earth. It would be difficult to imagine them all made of the same cell. In fact, there are many different kinds of cells. Unicellular organisms consist of just one cell. These cells go through life cycles just like more complex organisms. They ...
PLACE IN THE ANIMAL KINGDOM
... a) Study of body structures using X-rays III. LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION A. Chemical 1. Atoms compounds monomers macromolecules B. Cellular 1. The smallest unit of life C. Tissue 1. A group of cells with common function and structure D. Organs 1. An organ is a structure that is composed ...
... a) Study of body structures using X-rays III. LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION A. Chemical 1. Atoms compounds monomers macromolecules B. Cellular 1. The smallest unit of life C. Tissue 1. A group of cells with common function and structure D. Organs 1. An organ is a structure that is composed ...
B2 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... Increase in size, length or height as well as an increase in the number of cells A base in DNA that pairs with cytosine The place where an organism lives The red iron-containing pigment found in red blood cells Having one set of chromosomes, as in gametes Chemical that kills plants, usually used on ...
... Increase in size, length or height as well as an increase in the number of cells A base in DNA that pairs with cytosine The place where an organism lives The red iron-containing pigment found in red blood cells Having one set of chromosomes, as in gametes Chemical that kills plants, usually used on ...
Cells of the Respiratory System
... Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses from the alveoli to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. In order to do so, it has to diffuse through the alveolar epithelial cell, the capillary endothelial cell, plasma in the capillary, and into the red blood cell. ...
... Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses from the alveoli to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. In order to do so, it has to diffuse through the alveolar epithelial cell, the capillary endothelial cell, plasma in the capillary, and into the red blood cell. ...
Cell Unit
... protists live in moist surroundings. In general, the protist kingdom includes organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane and who do not fit into the other kingdoms. ...
... protists live in moist surroundings. In general, the protist kingdom includes organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane and who do not fit into the other kingdoms. ...
Document
... Zygote: A single sperm penetrates the mother's egg cell, and the resulting cell is called a zygote. The zygote is a single cell. The zygote contains all of the genetic information (DNA) necessary to become a child. Half of the genetic information comes from the mother' s egg (23 chromosomes) and hal ...
... Zygote: A single sperm penetrates the mother's egg cell, and the resulting cell is called a zygote. The zygote is a single cell. The zygote contains all of the genetic information (DNA) necessary to become a child. Half of the genetic information comes from the mother' s egg (23 chromosomes) and hal ...
Pregnancy PPT
... By the eighth month the fetus opens its eyes By the end of the third trimester, the fetus has grown to an average length of 500mm and an average weight between 2700 and 4100 grams ...
... By the eighth month the fetus opens its eyes By the end of the third trimester, the fetus has grown to an average length of 500mm and an average weight between 2700 and 4100 grams ...
Diffusion and Osmosis in plant and animal cells
... hypotonic solution it will burst • If a red blood cell is placed in an isotonic solution there is no net movement of water and the cell remains unchanged • If a red blood cell is placed in a hypertonic solution is will shrink ...
... hypotonic solution it will burst • If a red blood cell is placed in an isotonic solution there is no net movement of water and the cell remains unchanged • If a red blood cell is placed in a hypertonic solution is will shrink ...
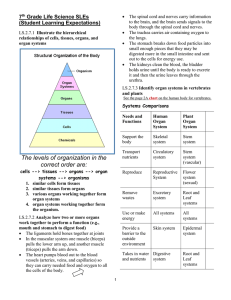
Levels of Organization
... of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other parts. The arrangement of specialized parts within a living thing is sometimes referred to as levels of organization. Cells of course, are the first level of organization. ...
... of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other parts. The arrangement of specialized parts within a living thing is sometimes referred to as levels of organization. Cells of course, are the first level of organization. ...
Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems
... Include: red blood cells carry oxygen; white blood cells fight infection; platelets clot blood; plasma is the liquid part of blood that transports blood cells, dissolved material, nutrients, and ...
... Include: red blood cells carry oxygen; white blood cells fight infection; platelets clot blood; plasma is the liquid part of blood that transports blood cells, dissolved material, nutrients, and ...
Click Here for Science Words in Word DOC format
... Aerobe – any organism that uses oxygen for respiration. Allele – an alternate form that a gene may have for a single trait; can be dominant or recessive. Amino acids – building blocks of proteins. Anaerobe – any organism that is able to live without organism. Anus – opening at the end of the digesti ...
... Aerobe – any organism that uses oxygen for respiration. Allele – an alternate form that a gene may have for a single trait; can be dominant or recessive. Amino acids – building blocks of proteins. Anaerobe – any organism that is able to live without organism. Anus – opening at the end of the digesti ...
Specialized Cells - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... cells becoming specialized for the tissue they form and the function they serve. These cells are referred to as specialized cells: i.e. cells that have physical and chemical differences that allow them to perform one job/ one function. specialized cell: a cell that can perform a specific function. C ...
... cells becoming specialized for the tissue they form and the function they serve. These cells are referred to as specialized cells: i.e. cells that have physical and chemical differences that allow them to perform one job/ one function. specialized cell: a cell that can perform a specific function. C ...
Science Words in Adobe Reader PDF format
... Aerobe – any organism that uses oxygen for respiration. Allele – an alternate form that a gene may have for a single trait; can be dominant or recessive. Amino acids – building blocks of proteins. Anaerobe – any organism that is able to live without organism. Anus – opening at the end of the digesti ...
... Aerobe – any organism that uses oxygen for respiration. Allele – an alternate form that a gene may have for a single trait; can be dominant or recessive. Amino acids – building blocks of proteins. Anaerobe – any organism that is able to live without organism. Anus – opening at the end of the digesti ...
File
... • analyze similarities and differences between single-celled and multicelled organisms (e.g., compare, in general terms, an amoeba and a grizzly bear, a single-celled alga and a poplar tree) • distinguish between plant and animal cells (e.g., distinguish between cell walls and cell membranes) • desc ...
... • analyze similarities and differences between single-celled and multicelled organisms (e.g., compare, in general terms, an amoeba and a grizzly bear, a single-celled alga and a poplar tree) • distinguish between plant and animal cells (e.g., distinguish between cell walls and cell membranes) • desc ...
Unit C Section Review
... Unit C: Biology (Cycling of Matter in Living Systems) – Assignment Answer Key Section Review Questions #1 – 5, 7, 8, 10 – 12, 14 – 22 1. The benefits of being multicellular are that different functions can be performed by specialized groups of cells. Each cell is not responsible for carrying out all ...
... Unit C: Biology (Cycling of Matter in Living Systems) – Assignment Answer Key Section Review Questions #1 – 5, 7, 8, 10 – 12, 14 – 22 1. The benefits of being multicellular are that different functions can be performed by specialized groups of cells. Each cell is not responsible for carrying out all ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.