
Anatomy and Physiology notes - Introduction, Cell
... What are emergent properties? give some individual organism examples. organ system organ tissue cell cell organelle molecule What is a very important emergent atom property at the cell level? ...
... What are emergent properties? give some individual organism examples. organ system organ tissue cell cell organelle molecule What is a very important emergent atom property at the cell level? ...
Cells And Systems Notes
... lining of the respiratory system causing extra mucus to be produced, which is removed by coughing. Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, if prolonged over time can cause emphysema. Lung Cancer: Caused by tar in smoke, which makes certain cells grow out of control. ...
... lining of the respiratory system causing extra mucus to be produced, which is removed by coughing. Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, if prolonged over time can cause emphysema. Lung Cancer: Caused by tar in smoke, which makes certain cells grow out of control. ...
Cellular Hierarchy
... microscopic differences between plant and animal cells translate into macroscopic (larger) differences in organisms. This fact is explained by the cellular hierarchy. As we will discover during this chapter, differences in cells mean differences in larger structures like tissues or organs. You can t ...
... microscopic differences between plant and animal cells translate into macroscopic (larger) differences in organisms. This fact is explained by the cellular hierarchy. As we will discover during this chapter, differences in cells mean differences in larger structures like tissues or organs. You can t ...
Cells to Body Systems vocab and notes
... 1. Cell: smallest unit of living things that can carry out basic processes of life 2. Unicellular: organism made of one cell that carries out all of its life processes 3. Multicellular: organisms made of many cells that work together to carry out life processes 4. Organelle: tiny structure within a ...
... 1. Cell: smallest unit of living things that can carry out basic processes of life 2. Unicellular: organism made of one cell that carries out all of its life processes 3. Multicellular: organisms made of many cells that work together to carry out life processes 4. Organelle: tiny structure within a ...
Levels of Organization - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Second Level: Tissues In any multi-cellular organism, cells rarely work alone. Cells that are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues. Tissues are the second level of organization. There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue, ne ...
... Second Level: Tissues In any multi-cellular organism, cells rarely work alone. Cells that are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues. Tissues are the second level of organization. There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue, ne ...
Section 1: Human Body
... 27. In humans, the allele for Widow’s peak is dominant (W) to the allele for a Straight hair line (w). If both parents have a Widow’s peak, how is it possible that one of their children has a Straight hairline? USE A PUNNETT SQUARE!! W w Both parents must be heterozygous so they have a “w”. W ...
... 27. In humans, the allele for Widow’s peak is dominant (W) to the allele for a Straight hair line (w). If both parents have a Widow’s peak, how is it possible that one of their children has a Straight hairline? USE A PUNNETT SQUARE!! W w Both parents must be heterozygous so they have a “w”. W ...
Outline
... _________________ tissue Connective tissue ________________ tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue - Covering and Lining Tissue that covers the surface of body and lining of intestinal, respiratory, urinary tract and forms thin sheets, not very strong. Also functions as protection, for example skin ...
... _________________ tissue Connective tissue ________________ tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue - Covering and Lining Tissue that covers the surface of body and lining of intestinal, respiratory, urinary tract and forms thin sheets, not very strong. Also functions as protection, for example skin ...
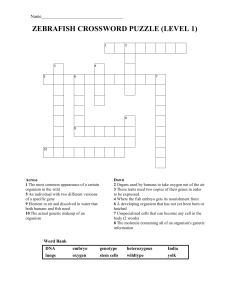
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... 3 These traits need two copies of their genes in order to be expressed 4 Where the fish embryo gets its nourishment from 6 A developing organism that has not yet been born or hatched 7 Unspecialized cells that can become any cell in the body (2 words) 8 The molecule containing all of an organism's g ...
... 3 These traits need two copies of their genes in order to be expressed 4 Where the fish embryo gets its nourishment from 6 A developing organism that has not yet been born or hatched 7 Unspecialized cells that can become any cell in the body (2 words) 8 The molecule containing all of an organism's g ...
Fertilization and Development
... • In humans, this typically lasts 40 weeks • Premature birth – babies born prior to completing 37 weeks of development – Increase chance of lung and brain problems – Typically, the earliest survivable birth is 24 weeks ...
... • In humans, this typically lasts 40 weeks • Premature birth – babies born prior to completing 37 weeks of development – Increase chance of lung and brain problems – Typically, the earliest survivable birth is 24 weeks ...
SAT Biology Review: Diversity of Life
... Most are multicellular, absorptive heterotrophs with chitin cell walls. Composed of long threads called hyphae, which may weave together into a mycelium. Reproduce using spores. Alternation of generations: mainly haploid, only diploid to form spores. Primary ecological role: decomposer. Examples: ye ...
... Most are multicellular, absorptive heterotrophs with chitin cell walls. Composed of long threads called hyphae, which may weave together into a mycelium. Reproduce using spores. Alternation of generations: mainly haploid, only diploid to form spores. Primary ecological role: decomposer. Examples: ye ...
SAT Biology Review: Diversity of Life
... Most are multicellular, absorptive heterotrophs with chitin cell walls. Composed of long threads called hyphae, which may weave together into a mycelium. Reproduce using spores. Alternation of generations: mainly haploid, only diploid to form spores. Primary ecological role: decomposer. Examples: ye ...
... Most are multicellular, absorptive heterotrophs with chitin cell walls. Composed of long threads called hyphae, which may weave together into a mycelium. Reproduce using spores. Alternation of generations: mainly haploid, only diploid to form spores. Primary ecological role: decomposer. Examples: ye ...
Levels of Organization Notes (pg 418-427)
... Lesson 10.3 Levels of Organization Life's Organization All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is not made of one cell. Instead, it is made of trillions of cells working together. The skin of the Komodo dragon, ...
... Lesson 10.3 Levels of Organization Life's Organization All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is not made of one cell. Instead, it is made of trillions of cells working together. The skin of the Komodo dragon, ...
1.1 Cells – structure and function
... 1.2 Specialised cells You, like many other organisms including plants, started life as a single cell – a fertilised egg. This divides and forms an embryo. Cells become specialised to perform different functions. This is called differentiation (becoming different). Some examples of specialised cells ...
... 1.2 Specialised cells You, like many other organisms including plants, started life as a single cell – a fertilised egg. This divides and forms an embryo. Cells become specialised to perform different functions. This is called differentiation (becoming different). Some examples of specialised cells ...
Human Body Test 12/16 [1388442]
... D. Humans have many systems that perform the same function. 11. Which best describes a single-celled organism? A. an organism with one cell that uses other cells to survive B. an organism with many cells that work together to survive C. an organism with many cells that battle each other to survive D ...
... D. Humans have many systems that perform the same function. 11. Which best describes a single-celled organism? A. an organism with one cell that uses other cells to survive B. an organism with many cells that work together to survive C. an organism with many cells that battle each other to survive D ...
function - mselder
... from the parent cell coils and condenses to form pairs of chromosomes with identical chromatids Differences: During meiosis cell divides twice instead of only once, in meiosis the four daughter cells end up with only half the genetic material while in mitosis the two daughter cells have the same gen ...
... from the parent cell coils and condenses to form pairs of chromosomes with identical chromatids Differences: During meiosis cell divides twice instead of only once, in meiosis the four daughter cells end up with only half the genetic material while in mitosis the two daughter cells have the same gen ...
8838083
... Club cells, also known as bronchiolar exocrine cells, and originally known as Clara cells , are dome-shaped cells with short microvilli, found in the small airways (bronchioles) of the lungs. Club cells are found in the ciliated simple epithelium. These cells may secrete glycosaminoglycans to protec ...
... Club cells, also known as bronchiolar exocrine cells, and originally known as Clara cells , are dome-shaped cells with short microvilli, found in the small airways (bronchioles) of the lungs. Club cells are found in the ciliated simple epithelium. These cells may secrete glycosaminoglycans to protec ...
Levels of Organization
... Division of Labor & The First Level Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, i ...
... Division of Labor & The First Level Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, i ...
Nicole`s teacher asked her to make a diagram of a good chain for a
... the ozone layer is damaged, how will Earth be most affected? A. The ultraviolet radiation may result in damage to living things B. The ultraviolet radiation may cause air conditioning systems to overheat C. The ultraviolet radiation may rapidly increase the water temperature of the Pacific Ocean D. ...
... the ozone layer is damaged, how will Earth be most affected? A. The ultraviolet radiation may result in damage to living things B. The ultraviolet radiation may cause air conditioning systems to overheat C. The ultraviolet radiation may rapidly increase the water temperature of the Pacific Ocean D. ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... Every living things is made up of one or more cells • Prokaryotes are unicellular. This means that all functions of life happen within that one cell • Eukaryotes are unicellular (protists) and multicellular. If the organism is multicellular, different cells have different jobs and they all work tog ...
... Every living things is made up of one or more cells • Prokaryotes are unicellular. This means that all functions of life happen within that one cell • Eukaryotes are unicellular (protists) and multicellular. If the organism is multicellular, different cells have different jobs and they all work tog ...
6.2 workbook - Fetal Development
... Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Use each term only once. You will not need to use every term. ...
... Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Use each term only once. You will not need to use every term. ...
Cells1 - ClickBiology
... cell membrane semi-permeable, so will allow water and mineral ions into the cell ...
... cell membrane semi-permeable, so will allow water and mineral ions into the cell ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.













![Human Body Test 12/16 [1388442]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020444861_1-5f310fa9844f0b2fa5e006a0adbe59b7-300x300.png)








