Levels of Organization
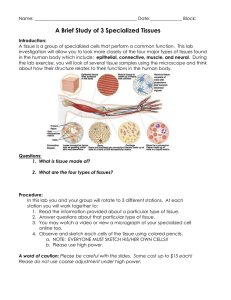
... There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. (There are other kinds of tissues besides these.) Other kinds of tissue include bone tissue (a strong solid tissue that gives you shape and support) made of bone cell ...
... There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. (There are other kinds of tissues besides these.) Other kinds of tissue include bone tissue (a strong solid tissue that gives you shape and support) made of bone cell ...
Lab 9: Adaptations for Survival in Terrestrial Environments
... modifying the basic body plan of root and shoot (with stem and leaves) and the type and distribution of specific cells. Just as plants have evolved mechanisms for survival on land, animals have adapted in several ways to a terrestrial environment. These adaptations include modifications to the gener ...
... modifying the basic body plan of root and shoot (with stem and leaves) and the type and distribution of specific cells. Just as plants have evolved mechanisms for survival on land, animals have adapted in several ways to a terrestrial environment. These adaptations include modifications to the gener ...
Life Science
... Chapter 1 – Structure of Living Things •Lesson 1 – Cells •Lesson 2 – From Cells to Organisms •Lesson 3 – Diversity of Organisms ...
... Chapter 1 – Structure of Living Things •Lesson 1 – Cells •Lesson 2 – From Cells to Organisms •Lesson 3 – Diversity of Organisms ...
Groups of Living Things Ppt
... mammary glands to produce milk for young, and have hair. ▪ Examples include ▪ Monotremes such as a platypus and echidna ▪ Marsupials such as kangaroos, koalas, and opossums. ▪ Placental such as humans, bears, and dogs. ▪ Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that lack a cell wall and chloroplasts. ...
... mammary glands to produce milk for young, and have hair. ▪ Examples include ▪ Monotremes such as a platypus and echidna ▪ Marsupials such as kangaroos, koalas, and opossums. ▪ Placental such as humans, bears, and dogs. ▪ Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that lack a cell wall and chloroplasts. ...
Intro to Biology
... to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 ...
... to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 ...
File - 8th Grade Science Ms. Neil
... to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 ...
... to environment, reproduces, need/use energy 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 ...
Chapter 4 - Tracy Jubenville Nearing
... Tissues: collection of cells that perform a specific function Epithelial tissues: cells that line every body surface (skin, inside of blood vessels) Connective tissues: type of cells that hold together, protect and support organs (fat, bone and blood) ...
... Tissues: collection of cells that perform a specific function Epithelial tissues: cells that line every body surface (skin, inside of blood vessels) Connective tissues: type of cells that hold together, protect and support organs (fat, bone and blood) ...
Unit 8-B Study Guide Questions
... 1) List and explain the six characteristics of life. 2) Give two examples of different organisms with different structures that have the same function. 3) Discuss Darwin’s species of finches and their variation in bill shape. 4) List the six of the eight main organ systems and identify the main stru ...
... 1) List and explain the six characteristics of life. 2) Give two examples of different organisms with different structures that have the same function. 3) Discuss Darwin’s species of finches and their variation in bill shape. 4) List the six of the eight main organ systems and identify the main stru ...
Developmental Biology
... organism its shape constitute morphogenesis • Differential gene expression results from genes being regulated differently in each cell type • Materials in the egg can set up gene regulation that is carried out as cells divide ...
... organism its shape constitute morphogenesis • Differential gene expression results from genes being regulated differently in each cell type • Materials in the egg can set up gene regulation that is carried out as cells divide ...
Developmental Biology
... organism its shape constitute morphogenesis • Differential gene expression results from genes being regulated differently in each cell type • Materials in the egg can set up gene regulation that is carried out as cells divide ...
... organism its shape constitute morphogenesis • Differential gene expression results from genes being regulated differently in each cell type • Materials in the egg can set up gene regulation that is carried out as cells divide ...
UNIT 3 -CELLS, HISTOLOGY, INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... a. Their products are secreted into ducts that lead either directly or indirectly to the outside of the body. b. Their products are secreted into the blood and therefore stay within the body; they are ductless glands. c. Examples are glands that secrete sweat, oil, mucus, and digestive enzymes. d. E ...
... a. Their products are secreted into ducts that lead either directly or indirectly to the outside of the body. b. Their products are secreted into the blood and therefore stay within the body; they are ductless glands. c. Examples are glands that secrete sweat, oil, mucus, and digestive enzymes. d. E ...
Unit 4 Tissue Assignment
... _____a. tissue forming most of the wall of the heart _____b. attached to bones _____c. spindle-shaped cells with ends tapering to points _____d. contain intercalated discs and gap junctions _____e. found in walls of intestine, urinary bladder, and blood vessels _____f. cells are multinucleate ...
... _____a. tissue forming most of the wall of the heart _____b. attached to bones _____c. spindle-shaped cells with ends tapering to points _____d. contain intercalated discs and gap junctions _____e. found in walls of intestine, urinary bladder, and blood vessels _____f. cells are multinucleate ...
Basic Biological Principles
... divides, grows, and divides again until it forms a layered ball of cells. At this point, the cells differentiate. That is, they specialize to become different types of cells (e.g., muscle cells, skin cells, brain cells, etc.). Eventually, all of the basic human structures form, and the embryo become ...
... divides, grows, and divides again until it forms a layered ball of cells. At this point, the cells differentiate. That is, they specialize to become different types of cells (e.g., muscle cells, skin cells, brain cells, etc.). Eventually, all of the basic human structures form, and the embryo become ...
Protostome Animals
... • There is remarkable number of different protostome species – 925,000 different arthropod species have been formally identified (80 percent of the world's species) • It has been hypothesized that the actual # may be as high as 10 mil ...
... • There is remarkable number of different protostome species – 925,000 different arthropod species have been formally identified (80 percent of the world's species) • It has been hypothesized that the actual # may be as high as 10 mil ...
Cell Structure and Function - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... microscope slide. Discard the rest of the onion piece. Trim the piece with a scalpel if necessary, and smooth any wrinkles. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of Lugol’s iodine solution and a cover slip. 4. Examine the first slide with low power and then with high power. 5. Sketch a few cells as they appear under ...
... microscope slide. Discard the rest of the onion piece. Trim the piece with a scalpel if necessary, and smooth any wrinkles. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of Lugol’s iodine solution and a cover slip. 4. Examine the first slide with low power and then with high power. 5. Sketch a few cells as they appear under ...
Slide 1
... cells, and not all viruses can pass between different species (though some can). Rabies, for instance, can be passed from animal to human. HIV is a virus that seems specific to humans. The common cold is a virus that attacks cells of the respiratory track (hence the coughing and sneezing and sniffli ...
... cells, and not all viruses can pass between different species (though some can). Rabies, for instance, can be passed from animal to human. HIV is a virus that seems specific to humans. The common cold is a virus that attacks cells of the respiratory track (hence the coughing and sneezing and sniffli ...
Biology Review PPT
... cells, and not all viruses can pass between different species (though some can). Rabies, for instance, can be passed from animal to human. HIV is a virus that seems specific to humans. The common cold is a virus that attacks cells of the respiratory track (hence the coughing and sneezing and sniffli ...
... cells, and not all viruses can pass between different species (though some can). Rabies, for instance, can be passed from animal to human. HIV is a virus that seems specific to humans. The common cold is a virus that attacks cells of the respiratory track (hence the coughing and sneezing and sniffli ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
are all made up of specialized nerve cells called neurons. Neurons
... the heart by about 20%. 3. Red cells are fully differentiated and do not require a nucleus to carry out the function of transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide. The primary function of carrying oxygen is made possible by a chemically complex protein called hemoglobin. During circulation of blood thro ...
... the heart by about 20%. 3. Red cells are fully differentiated and do not require a nucleus to carry out the function of transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide. The primary function of carrying oxygen is made possible by a chemically complex protein called hemoglobin. During circulation of blood thro ...
chromosomes
... One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromsosome). Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles (alternative form of a gene) for ...
... One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromsosome). Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles (alternative form of a gene) for ...
3 The Organization of Living Things
... The function of a cell is related to its structure. Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. The structure of a brain cell is different from the structure of a heart muscle cell. Structure includes shape and the material a part is made of. ...
... The function of a cell is related to its structure. Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. The structure of a brain cell is different from the structure of a heart muscle cell. Structure includes shape and the material a part is made of. ...
questions-2 - WordPress.com
... going to be on the test. This review is only a reflection of what I think will be on the upcoming test and may not include all the material so make sure this isn’t your only study guide* ...
... going to be on the test. This review is only a reflection of what I think will be on the upcoming test and may not include all the material so make sure this isn’t your only study guide* ...
Levels of Organization - Darlington Middle School
... There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. (There are other kinds of tissues besides these.) Other kinds of tissue include bone tissue (a strong solid tissue that gives you shape and support) made of bone cell ...
... There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. (There are other kinds of tissues besides these.) Other kinds of tissue include bone tissue (a strong solid tissue that gives you shape and support) made of bone cell ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.