CrystEngComm
... furan-2,5-dicarboxylate (Cu(FDC)(H2O)) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/m (no. 12) with one Cu-center on a mirror plane and one Cu-center on a general position. The asymmetric unit contains 1.5 Cu2+ ions, 1.5 FDC ligands and 1.5 coordinated H2O molecules (Fig. 1). Cu1 and water oxygen O ...
... furan-2,5-dicarboxylate (Cu(FDC)(H2O)) crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/m (no. 12) with one Cu-center on a mirror plane and one Cu-center on a general position. The asymmetric unit contains 1.5 Cu2+ ions, 1.5 FDC ligands and 1.5 coordinated H2O molecules (Fig. 1). Cu1 and water oxygen O ...
Post Print Electronic structure and chemical bonding in Ti2AlC
... by weaker Ti-Al bonds with a cost of energy. Thus, in Ti2AlC, every second single monolayer of C atoms has been replaced by Al layers. The TiC layers surrounding the Al monolayers are then twinned with the Al layer as a mirror plane. Figure 1 shows the crystal structure of Ti2AlC 共211兲 with the ther ...
... by weaker Ti-Al bonds with a cost of energy. Thus, in Ti2AlC, every second single monolayer of C atoms has been replaced by Al layers. The TiC layers surrounding the Al monolayers are then twinned with the Al layer as a mirror plane. Figure 1 shows the crystal structure of Ti2AlC 共211兲 with the ther ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical explanations
... This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In the present case all answers are relevant and complementary since they partially address the question. This example insists on the cultural differences between scientific communities. Chemical explanations of the s ...
... This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In the present case all answers are relevant and complementary since they partially address the question. This example insists on the cultural differences between scientific communities. Chemical explanations of the s ...
CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND
... ionic solid, molecules for molecular solids) under standard conditions is called lattice enthalpy (∆lHo). The lattice enthalpy is a positive quantity. ELECTRO VALENCY: The number of electrons lost or gain by an atom of an element is called as electrovalency. The element which give up electrons to fo ...
... ionic solid, molecules for molecular solids) under standard conditions is called lattice enthalpy (∆lHo). The lattice enthalpy is a positive quantity. ELECTRO VALENCY: The number of electrons lost or gain by an atom of an element is called as electrovalency. The element which give up electrons to fo ...
O - gearju.com
... (a) The electronegativity difference between H and Cl is 0.9, which is appreciable but not large enough (by the 2.0 rule) to qualify HCl as an ionic compound. Therefore, the bond between H and Cl is polar covalent. (b) The electronegativity difference between K and F is 3.2, which is well above the ...
... (a) The electronegativity difference between H and Cl is 0.9, which is appreciable but not large enough (by the 2.0 rule) to qualify HCl as an ionic compound. Therefore, the bond between H and Cl is polar covalent. (b) The electronegativity difference between K and F is 3.2, which is well above the ...
O - gearju.com
... (a) The electronegativity difference between H and Cl is 0.9, which is appreciable but not large enough (by the 2.0 rule) to qualify HCl as an ionic compound. Therefore, the bond between H and Cl is polar covalent. (b) The electronegativity difference between K and F is 3.2, which is well above the ...
... (a) The electronegativity difference between H and Cl is 0.9, which is appreciable but not large enough (by the 2.0 rule) to qualify HCl as an ionic compound. Therefore, the bond between H and Cl is polar covalent. (b) The electronegativity difference between K and F is 3.2, which is well above the ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical
... unifies the phenomena better than any other. In the causal model the explanation will trace the causal processes and interactions leading to the event (i.e. the causal history) , or at least a subset of these, as well as describing the processes and interactions that make up the event itself. Except ...
... unifies the phenomena better than any other. In the causal model the explanation will trace the causal processes and interactions leading to the event (i.e. the causal history) , or at least a subset of these, as well as describing the processes and interactions that make up the event itself. Except ...
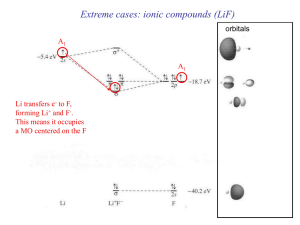
The Role of Hydrogen Bond in Designing Molecular Optical Materials
... coefficients may be used to compute atomic electrostatic moments. However, there are two main limitations: (a) the multipole expansion is a fitting procedure that therefore returns only approximated quantities; and (b) the atomic multipole parameters may strongly correlate within a refinement proced ...
... coefficients may be used to compute atomic electrostatic moments. However, there are two main limitations: (a) the multipole expansion is a fitting procedure that therefore returns only approximated quantities; and (b) the atomic multipole parameters may strongly correlate within a refinement proced ...
UN1001: Section 11: Hydrogen Effects
... Note that the reaction can occur with atomic H in the metal lattice . . . C + 4H CH4 May crack the steel from high internal pressure. ...
... Note that the reaction can occur with atomic H in the metal lattice . . . C + 4H CH4 May crack the steel from high internal pressure. ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structure
... Interactive Figure 8.1.1 shows a demonstration of Coulomb’s law using a gold leaf electroscope in which a narrow metal plate and a thin sheet of gold are connected to a conducting rod. The plastic pen held above the electroscope carries a static charge, which is transferred to the metals via inducta ...
... Interactive Figure 8.1.1 shows a demonstration of Coulomb’s law using a gold leaf electroscope in which a narrow metal plate and a thin sheet of gold are connected to a conducting rod. The plastic pen held above the electroscope carries a static charge, which is transferred to the metals via inducta ...
127 - Chimica
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
Detailed characterization of anodic bonding process between glass
... using low pressure chemical vapour deposition ŽLPCVD. process, and silicon oxide Ž100 nm. was grown by dry thermal oxidation. Process conditions for the preparation of these surfaces are detailed in Table 1. For glass materials, three types of which were investigated including Corning 7740 glass Ž50 ...
... using low pressure chemical vapour deposition ŽLPCVD. process, and silicon oxide Ž100 nm. was grown by dry thermal oxidation. Process conditions for the preparation of these surfaces are detailed in Table 1. For glass materials, three types of which were investigated including Corning 7740 glass Ž50 ...
Lecture 2
... that do not change =1; and orbitals that remain in the same position but change sign = -1) 4. Find the irreducible representations (they correspond to the symmetry of group orbitals, also called Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations SALC’s of the orbitals). 5. Find AO’s in central atom with the same ...
... that do not change =1; and orbitals that remain in the same position but change sign = -1) 4. Find the irreducible representations (they correspond to the symmetry of group orbitals, also called Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations SALC’s of the orbitals). 5. Find AO’s in central atom with the same ...
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
... Solve NaF consists of Na+ and F− ions, CsI of Cs+ and I− ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2− ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of Equation 8.4, the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2− ions, to ...
... Solve NaF consists of Na+ and F− ions, CsI of Cs+ and I− ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2− ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of Equation 8.4, the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2− ions, to ...
Synthesis and Characterization of Four Energetic Transition Metal
... nitrogen-rich heterocyclic ligands [3], because these ligands have the characters of both high nitrogen content and positive heats of formation. 1,2,4-triazole and its derivates are a kind of nitrogen-rich heterocyclic ligand with fascinating explosive properties [4], due to their diverse coordinati ...
... nitrogen-rich heterocyclic ligands [3], because these ligands have the characters of both high nitrogen content and positive heats of formation. 1,2,4-triazole and its derivates are a kind of nitrogen-rich heterocyclic ligand with fascinating explosive properties [4], due to their diverse coordinati ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... form a triatomic (three-atom) molecule (O3) which is called ozone. Sulfur is the most common nonmetal in the oxygen family. Sulfur is used in the making of rubber for rubber bands and car tires. Group 17 contains four nonmetals – fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The elements in group 17 are ...
... form a triatomic (three-atom) molecule (O3) which is called ozone. Sulfur is the most common nonmetal in the oxygen family. Sulfur is used in the making of rubber for rubber bands and car tires. Group 17 contains four nonmetals – fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The elements in group 17 are ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... of its electrons (-1 charge) is equal to the number of protons (+1 charge) in its atomic nuclei. However while electrically neutral molecules have no electrical charge, many of them such as haloalkanes (R-X), alcohols (R-OH), and amines (RNH2 ) have polar bonds. [graphic 3.7] Electron Distribution i ...
... of its electrons (-1 charge) is equal to the number of protons (+1 charge) in its atomic nuclei. However while electrically neutral molecules have no electrical charge, many of them such as haloalkanes (R-X), alcohols (R-OH), and amines (RNH2 ) have polar bonds. [graphic 3.7] Electron Distribution i ...
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
Part 3 Answers Only for Questions, Exercises, and Problems in The
... 8. The particles in a solid occupy fixed positions relative to each other and cannot be poured, but different pieces of solids can move relative to each other. The slogan emphasizes that this brand of table salt has solid pieces small enough to move freely relative to one another, but not so small t ...
... 8. The particles in a solid occupy fixed positions relative to each other and cannot be poured, but different pieces of solids can move relative to each other. The slogan emphasizes that this brand of table salt has solid pieces small enough to move freely relative to one another, but not so small t ...
Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature
... chemically bonded together are called diatomic elements. The diatomic elements are hydrogen, bromine, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, iodine, and fluorine. (You need to memorize the diatomic elements.) What type of chemical bond exists between the diatomic elements? Nonpolar covalent Back to main menu ...
... chemically bonded together are called diatomic elements. The diatomic elements are hydrogen, bromine, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, iodine, and fluorine. (You need to memorize the diatomic elements.) What type of chemical bond exists between the diatomic elements? Nonpolar covalent Back to main menu ...
3: Haloalkanes, Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
... The relative magnitudes of these electronegativity differences reflect the relative magnitudes of the polarity of each bond. The negative (-) electronegativity difference for a C-H bond suggests that C is (δ-) while H is (δ+), however the magnitude of the electronegativity difference is so small tha ...
Document
... Self-organization of metal complexes through noncovalent interactions including electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding has great potential for creating supramolecular architectures with well-defined shapes and functions.1-10 Aromatic π-π stacking interactions also play vital roles in highly ...
... Self-organization of metal complexes through noncovalent interactions including electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding has great potential for creating supramolecular architectures with well-defined shapes and functions.1-10 Aromatic π-π stacking interactions also play vital roles in highly ...
Crystal Structure of Mixed-metal Phosphite, Pb2Ga(HPIIIO3)3(PVO3)
... c=12.544(3) Å and α=β=γ=90°. The crystal structure of Pb2Ga(HPO3)3(PO3) exhibits a complicated 3D framework based on PbO6 and GaO6 octahedral connected by HPO3 and H2PO3 anions via corner- or edge-sharing. Keywords: Crystal structure; Hydrothermal reactions; Mixed-metal phosphites; 3D framework; Sin ...
... c=12.544(3) Å and α=β=γ=90°. The crystal structure of Pb2Ga(HPO3)3(PO3) exhibits a complicated 3D framework based on PbO6 and GaO6 octahedral connected by HPO3 and H2PO3 anions via corner- or edge-sharing. Keywords: Crystal structure; Hydrothermal reactions; Mixed-metal phosphites; 3D framework; Sin ...
George Facer`s A level Chemistry
... under reflux because ammonia gas would be liberated. This would then escape because it would not be condensed by the reflux condenser. The halogenoalkane and the ammonia solution must therefore be heated in a sealed container. Alternatively, a concentrated ammonia solution can be used and the mixtur ...
... under reflux because ammonia gas would be liberated. This would then escape because it would not be condensed by the reflux condenser. The halogenoalkane and the ammonia solution must therefore be heated in a sealed container. Alternatively, a concentrated ammonia solution can be used and the mixtur ...
Halogen bond

Halogen bonding (XB) is the non-covalent interaction that occurs between a halogen atom (Lewis acid) and a Lewis base. Although halogens are involved in other types of bonding (e.g. covalent), halogen bonding specifically refers to when the halogen acts as an electrophilic species.