18 are exactly the same ones as for galactic star clusters of early
... ations of radial velocity and spectral type have been made in NGC 4755 from 102 spectra of 35 stars. Full details are published elsewhere (Feast 1963). These results were combined with the three-colour photometry of Arp and van Sant (1958). The cluster has a nearly-vertical evolved main sequence at ...
... ations of radial velocity and spectral type have been made in NGC 4755 from 102 spectra of 35 stars. Full details are published elsewhere (Feast 1963). These results were combined with the three-colour photometry of Arp and van Sant (1958). The cluster has a nearly-vertical evolved main sequence at ...
Chandra Emission Line Diagnostics of Sco
... The wind shock model theorizes that a small amount of the wind material is shock heated to x-ray temperatures. The source of these shocks is thought to be self-excited instabilities or clumps of material moving at different speeds running into each other (Owocki, Castor, Rybicki 1988). In this model ...
... The wind shock model theorizes that a small amount of the wind material is shock heated to x-ray temperatures. The source of these shocks is thought to be self-excited instabilities or clumps of material moving at different speeds running into each other (Owocki, Castor, Rybicki 1988). In this model ...
20_LectureOutline
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
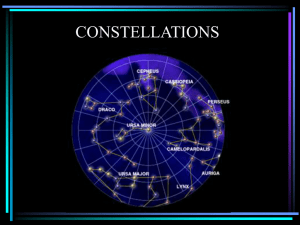
Constellations Overview
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
Studying Variable stars using Small Telescopes Observational
... Stars which vary their light output, hence their brightness, by some change within the star itself. Provide a wealth of information about the internal structure of stars, models of stellar evolution and distance determination. Further classified as: Pulsating Variables – Cepheids, RR Lyrae, RV Tauri ...
... Stars which vary their light output, hence their brightness, by some change within the star itself. Provide a wealth of information about the internal structure of stars, models of stellar evolution and distance determination. Further classified as: Pulsating Variables – Cepheids, RR Lyrae, RV Tauri ...
... their ratio is larger than 1/3 but less than 3). These systems are dynamically unstable, and either evolve towards hierarchical configurations or dissolve by successive ejections of components until only a close pair remains. Internal motions in trapezium-type systems were studied by Allen et al. (1 ...
Document
... • Standard candles → identify them → know their distance (with ~6% uncertainty) • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
... • Standard candles → identify them → know their distance (with ~6% uncertainty) • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
Lecture 8: The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 1882: Henry Draper’ widow makes a large donation to Harvard College Observatory with the goal of continuing his work. Observatory directory Edward Pickering used give to hire numerous assistants, which he called “calculators”. ...
... 1882: Henry Draper’ widow makes a large donation to Harvard College Observatory with the goal of continuing his work. Observatory directory Edward Pickering used give to hire numerous assistants, which he called “calculators”. ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... FIGURE 5: Simulated field of stars of magnitudes 1 through 6 (larger circles representing brighter stars). Top left -- numbers of each magnitude in proportions found in Bright Star Catalog (i.e. real sky). Top right -numbers calculated via equation 3. Bottom left, equal numbers of each magnitude. B ...
... FIGURE 5: Simulated field of stars of magnitudes 1 through 6 (larger circles representing brighter stars). Top left -- numbers of each magnitude in proportions found in Bright Star Catalog (i.e. real sky). Top right -numbers calculated via equation 3. Bottom left, equal numbers of each magnitude. B ...
Core-collapse supernovae and their massive progenitors
... Type Ic (H and He-poor) supernovae, respectively, whose circumstellar environment matches that of a WR star. Observationally, SN 2002ap (Type Ic) so far provides the most stringent constraints upon a potential WR progenitor, revealing an upper limit of MB = –4 mag, in common with a subset of Magella ...
... Type Ic (H and He-poor) supernovae, respectively, whose circumstellar environment matches that of a WR star. Observationally, SN 2002ap (Type Ic) so far provides the most stringent constraints upon a potential WR progenitor, revealing an upper limit of MB = –4 mag, in common with a subset of Magella ...
Carolina Kehrig
... ■ “template” systems → understand the evolution and feedback from massive stars in distant starburst galaxies which cannot be studied to the same depth and to constrain models for metal-poor massive stars ...
... ■ “template” systems → understand the evolution and feedback from massive stars in distant starburst galaxies which cannot be studied to the same depth and to constrain models for metal-poor massive stars ...
Constellations, Looking Far Away, and Stars/Stellar Evolution
... Read aloud. The graph of how the temperatures and luminosities of stars are related is known as the Hertzsprung-Russell or H-R diagram. From this graph, we can also get an estimate of the size of a star, its radius. Astronomers worked with this graph long before they knew why stars varied in this wa ...
... Read aloud. The graph of how the temperatures and luminosities of stars are related is known as the Hertzsprung-Russell or H-R diagram. From this graph, we can also get an estimate of the size of a star, its radius. Astronomers worked with this graph long before they knew why stars varied in this wa ...
Surveying the Stars
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? A. B. C. D. ...
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? A. B. C. D. ...
MS Word version
... (B) Is this “cosmic landmark” useful to everyone? On what parts of the earth is it always available, sometimes available, or never available? ...
... (B) Is this “cosmic landmark” useful to everyone? On what parts of the earth is it always available, sometimes available, or never available? ...
PHYSICS – Astrophysics Section I
... This formula requires either the distance (in parsecs) or the parallax angle (in arc seconds) to work. Shouldn’t be hard. Discuss the limitations of trigonometric parallax measurements Trigonometric parallax, although useful, has several limitations on its usefulness in finding distances to other st ...
... This formula requires either the distance (in parsecs) or the parallax angle (in arc seconds) to work. Shouldn’t be hard. Discuss the limitations of trigonometric parallax measurements Trigonometric parallax, although useful, has several limitations on its usefulness in finding distances to other st ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... Cygnus X-1 is a well-known black hole and galactic Xray source in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the m ...
... Cygnus X-1 is a well-known black hole and galactic Xray source in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the m ...
CONSTELLATIONS OF THE SOUTHERN SKY VOLANS
... Created by Bayer in 1603, this constellation used to be called PiscisVolans, the Flying Fish, before it was shortened to Volans. Volans was one of the 12 new constellations introduced at the end of the 16th century by the Dutch navigators Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Volans repr ...
... Created by Bayer in 1603, this constellation used to be called PiscisVolans, the Flying Fish, before it was shortened to Volans. Volans was one of the 12 new constellations introduced at the end of the 16th century by the Dutch navigators Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Volans repr ...
Using Photometric Data to Derive an HR Diagram
... All the stars in a cluster are at the same distance from us (neglecting the depth of the cluster itself, which is tiny compared with its overall distance from us). All the stars in a cluster are the same absolute age, although at different stages of evolution, depending on their rate of fuel consump ...
... All the stars in a cluster are at the same distance from us (neglecting the depth of the cluster itself, which is tiny compared with its overall distance from us). All the stars in a cluster are the same absolute age, although at different stages of evolution, depending on their rate of fuel consump ...
Observational properties of stars
... To make things a bit more complicated, astronomers may not know the composition of the stars in the cluster, or they may want to study many different clusters, so isochrones are usually constructed for quite a few different metallicities as well as ages. The generated isochrones can then be matched ...
... To make things a bit more complicated, astronomers may not know the composition of the stars in the cluster, or they may want to study many different clusters, so isochrones are usually constructed for quite a few different metallicities as well as ages. The generated isochrones can then be matched ...
Star Types - College of Engineering and Computer Science
... Up the red giant branch As hydrogen in the core is being used up, it starts to contract, raising temperature in the surrounding. Eventually, hydrogen will burn only in a shell. There is less gravity from above to balance this pressure. The Sun will then swell to enormous size and luminosity, and it ...
... Up the red giant branch As hydrogen in the core is being used up, it starts to contract, raising temperature in the surrounding. Eventually, hydrogen will burn only in a shell. There is less gravity from above to balance this pressure. The Sun will then swell to enormous size and luminosity, and it ...
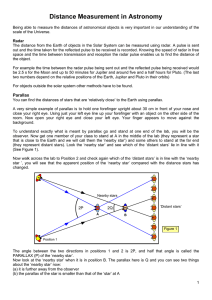
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
... For example the time between the radar pulse being sent out and the reflected pulse being received would be 2.5 s for the Moon and up to 50 minutes for Jupiter and around five and a half hours for Pluto. (The last two numbers depend on the relative positions of the Earth, Jupiter and Pluto in their ...
... For example the time between the radar pulse being sent out and the reflected pulse being received would be 2.5 s for the Moon and up to 50 minutes for Jupiter and around five and a half hours for Pluto. (The last two numbers depend on the relative positions of the Earth, Jupiter and Pluto in their ...
Why Star Positions?
... Arcturus and Sirius had moved significantly from their positions given by Ptolemy in his great mathematical and astronomical treatise, the Almagest. Sirius, for example, Earth in orbit around Sun had moved nearly half a degree southwards, about the diameter of the Moon, over the intervening two thou ...
... Arcturus and Sirius had moved significantly from their positions given by Ptolemy in his great mathematical and astronomical treatise, the Almagest. Sirius, for example, Earth in orbit around Sun had moved nearly half a degree southwards, about the diameter of the Moon, over the intervening two thou ...
Lecture 12
... The magnitude system • Astronomers quantify the intensity of light produced by a source with the unit magnitudes • Magnitudes are a logarithmic representation of the spectral flux density of a source. – Allows for easy comparison of sources with immense ranges in ...
... The magnitude system • Astronomers quantify the intensity of light produced by a source with the unit magnitudes • Magnitudes are a logarithmic representation of the spectral flux density of a source. – Allows for easy comparison of sources with immense ranges in ...
click here
... • Stars of given type of spectrum and the same colors have the same absolute magnitude (99.9%) • Stars have different apparent magnitudes depending on their distance. • Stars behind dust clouds look redder than they are intrinsically, so… m-M=5 log d1 –5+ A(l) (i.e., the star looks fainter) ...
... • Stars of given type of spectrum and the same colors have the same absolute magnitude (99.9%) • Stars have different apparent magnitudes depending on their distance. • Stars behind dust clouds look redder than they are intrinsically, so… m-M=5 log d1 –5+ A(l) (i.e., the star looks fainter) ...
Lecture18
... The period is easy to measure and give the astronomer the luminosity of the star Using the luminosity and the apparent brightness, the astronomer can calculate the distance to the star The relationship between period and luminosity was discovered by Henrietta Leavit in 1908 Leavit found that the bri ...
... The period is easy to measure and give the astronomer the luminosity of the star Using the luminosity and the apparent brightness, the astronomer can calculate the distance to the star The relationship between period and luminosity was discovered by Henrietta Leavit in 1908 Leavit found that the bri ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.