Field Star Distributions of the Hercules Thick Disk Cloud
... Wethe count all stars blueward of theby blue of sight about The expressed as number of Q1 stars divided Q4 ridge stars and the cloud is and thenvisible compare the numbers counted on lines of sight which are symmetric about l=0. readily in Figure ...
... Wethe count all stars blueward of theby blue of sight about The expressed as number of Q1 stars divided Q4 ridge stars and the cloud is and thenvisible compare the numbers counted on lines of sight which are symmetric about l=0. readily in Figure ...
Station A Star Charts I
... D6. (2 pts) When modern astronomers redesigned the magnitude system, they set the scale so that every five magnitudes is 100 times brighter (or dimmer, depending on direction). If star A is 1 magnitude brighter than star B, how many times brighter is it? Give your answer to the nearest thousandth. ...
... D6. (2 pts) When modern astronomers redesigned the magnitude system, they set the scale so that every five magnitudes is 100 times brighter (or dimmer, depending on direction). If star A is 1 magnitude brighter than star B, how many times brighter is it? Give your answer to the nearest thousandth. ...
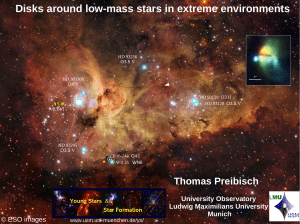
Disks around low-mass stars in extreme environments
... Problem of many injection scenarios: In most clusters (e.g., Orion Nebula Cluster), all stars formed at ~ the same time. When the first supernova happens (after > 4 Myr), most low-mass stars have already largely dispersed their disks (i.e. planetesimal formation is already finished). ...
... Problem of many injection scenarios: In most clusters (e.g., Orion Nebula Cluster), all stars formed at ~ the same time. When the first supernova happens (after > 4 Myr), most low-mass stars have already largely dispersed their disks (i.e. planetesimal formation is already finished). ...
Measuring The Parallax of Barnard's Star
... established rate of proper motion of 10.37 arcseconds per year. And, the velocity in arcseconds per year times the distance in parsecs gives the velocity in astronomical units (au) per year. Using our derived numbers we get that the projected velocity is 19.3 au/yr. A natural question to ask is: why ...
... established rate of proper motion of 10.37 arcseconds per year. And, the velocity in arcseconds per year times the distance in parsecs gives the velocity in astronomical units (au) per year. Using our derived numbers we get that the projected velocity is 19.3 au/yr. A natural question to ask is: why ...
Astronomical Toolkit
... It is interesting to note that the scale that Hipparchus selected on an intuitive basis, using just the naked eye, is already logarithmic as a result of the way our eyes respond to light. For comparison, the apparent magnitude of the full Moon is about –12.7, the magnitude of Venus can be as high as ...
... It is interesting to note that the scale that Hipparchus selected on an intuitive basis, using just the naked eye, is already logarithmic as a result of the way our eyes respond to light. For comparison, the apparent magnitude of the full Moon is about –12.7, the magnitude of Venus can be as high as ...
mufon ufo symposium -1974
... connected with lines. There are over 100 stars in the Psyche volume. Betty saw the lined pattern as a whole and the triangle as a whole but did not draw them to the same scale. The line to Alpha Mensae is an extension of the Gliese 86-Zeta Reticuli line. On this line, her conscious mind took control ...
... connected with lines. There are over 100 stars in the Psyche volume. Betty saw the lined pattern as a whole and the triangle as a whole but did not draw them to the same scale. The line to Alpha Mensae is an extension of the Gliese 86-Zeta Reticuli line. On this line, her conscious mind took control ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... 2.5 magnitudes. Antares (α Scorpius) and Betelgeuse (α AAVSO Light Curve (Z Ursae Majoris) Orionis) are two prominent examples of LPV semiregular variable stars. These stars occupy a region of instability on the H-R diagram above the Mira variables and are generally spectral class K, M, C or S. Sinc ...
... 2.5 magnitudes. Antares (α Scorpius) and Betelgeuse (α AAVSO Light Curve (Z Ursae Majoris) Orionis) are two prominent examples of LPV semiregular variable stars. These stars occupy a region of instability on the H-R diagram above the Mira variables and are generally spectral class K, M, C or S. Sinc ...
Stars part 2
... Stellar Formation and Life Cycle Stars are theorized to evolve through six stages of development… 1. Protostar Stage – the gravitational collapse of a gaseous cloud mass. • The collapse may be triggered by the passing of, the eruption of, or the explosion of a near-by star. • Energy production is d ...
... Stellar Formation and Life Cycle Stars are theorized to evolve through six stages of development… 1. Protostar Stage – the gravitational collapse of a gaseous cloud mass. • The collapse may be triggered by the passing of, the eruption of, or the explosion of a near-by star. • Energy production is d ...
18 Throughout history people around the world have looked up at
... hroughout history people around the world have looked up at the night sky and imagined stories about the stars. Early cultures used star positions and stories to teach lessons, navigate ships, and mark seasons— especially planting and harvesting times. Even though the stories might not be as accurat ...
... hroughout history people around the world have looked up at the night sky and imagined stories about the stars. Early cultures used star positions and stories to teach lessons, navigate ships, and mark seasons— especially planting and harvesting times. Even though the stories might not be as accurat ...
Evidence for a signature of the galactic bar in the solar neighbourhood
... phenomenon has never been given until now. Two new facts allow to go more deeply into this question. At first, after the de Vaucouleurs (1964) presumption, a series of more or less direct observational evidences recently indicate that our Galaxy is definitely barred (see for example Blitz & Spergel ...
... phenomenon has never been given until now. Two new facts allow to go more deeply into this question. At first, after the de Vaucouleurs (1964) presumption, a series of more or less direct observational evidences recently indicate that our Galaxy is definitely barred (see for example Blitz & Spergel ...
Ch. 20
... Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
... Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
Basics – II. Time, Magnitudes and Spectral types
... There are two main ways of measuring time: • using the rotation of the Earth and • using the frequency of atomic oscillations. The Earth’s rotation is not uniform; the rate includes periodic and secular (long-term) changes of the order of a second per year. Atomic standards are uniform in the micros ...
... There are two main ways of measuring time: • using the rotation of the Earth and • using the frequency of atomic oscillations. The Earth’s rotation is not uniform; the rate includes periodic and secular (long-term) changes of the order of a second per year. Atomic standards are uniform in the micros ...
HR Diagram
... An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you to control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, BV, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y- ...
... An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you to control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, BV, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y- ...
Deriving the Isoradius Lines (optional, mathematical
... indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you to control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, BV, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y-axis (luminosity or absolute magnitude). One can also show the main sequence, lumi ...
... indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you to control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, BV, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y-axis (luminosity or absolute magnitude). One can also show the main sequence, lumi ...
CONSTELLATION DELPHINUS, THE DOLPHIN
... Delphinus is a constellation in the northern sky, close to the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for dolphin. Delphinus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains among the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Uni ...
... Delphinus is a constellation in the northern sky, close to the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for dolphin. Delphinus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains among the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Uni ...
CCD PHOTOMETRY OF OPEN STAR CLUSTER M67
... Colour-magnitude diagrams for the individual colour indexes (B-V), (V-R), (V-I) were created on the basis of CCD photometry. They are illustrated with theoretical isochrones in Figures 1, 2, 3, where on the vertical axis is placed the measured stellar size in the filter V and on the horizontal axis ...
... Colour-magnitude diagrams for the individual colour indexes (B-V), (V-R), (V-I) were created on the basis of CCD photometry. They are illustrated with theoretical isochrones in Figures 1, 2, 3, where on the vertical axis is placed the measured stellar size in the filter V and on the horizontal axis ...
THE CONSTELLATION OCTANS, THE OCTANT
... honour of the octant's inventor, John Hadley, who devised the navigational instrument in 1730. There is no real mythology related to Octans, partially due to its extreme southerly latitude. Octans is notable as the location of the south celestial pole. The constellation is circumpolar to the south p ...
... honour of the octant's inventor, John Hadley, who devised the navigational instrument in 1730. There is no real mythology related to Octans, partially due to its extreme southerly latitude. Octans is notable as the location of the south celestial pole. The constellation is circumpolar to the south p ...
- saspcsus
... 4. Objects in the sky move in regular and predictable patterns. As a basis for understanding this concept: A. Students know the patterns of stars stay the same, although they appear to move across the sky nightly, and different stars can be seen in different seasons. B. Students know the way in whic ...
... 4. Objects in the sky move in regular and predictable patterns. As a basis for understanding this concept: A. Students know the patterns of stars stay the same, although they appear to move across the sky nightly, and different stars can be seen in different seasons. B. Students know the way in whic ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth Where do stars form? Star
... • Our goals for learning • What is the smallest mass a newborn star can have? • What is the greatest mass a newborn star can have? • What are the typical masses of newborn stars? ...
... • Our goals for learning • What is the smallest mass a newborn star can have? • What is the greatest mass a newborn star can have? • What are the typical masses of newborn stars? ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth
... • Our goals for learning • What is the smallest mass a newborn star can have? • What is the greatest mass a newborn star can have? • What are the typical masses of newborn stars? ...
... • Our goals for learning • What is the smallest mass a newborn star can have? • What is the greatest mass a newborn star can have? • What are the typical masses of newborn stars? ...
Pulsating Variable Stars and The Hertzsprung - Chandra X
... Magellanic Cloud Galaxy Image courtesy of Chandra ...
... Magellanic Cloud Galaxy Image courtesy of Chandra ...
Constituents of the Milky Way
... For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen, helium, and one other element (lit ...
... For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen, helium, and one other element (lit ...
Astronomical Distance Determination
... E.g. the motion of the sun around the center of the Galaxy, 250 km/s, corresponds to 53 AU/yr. Most of the nearby stars are moving along with us, but not precisely. Barnard’s star “moves” 10.25 arc sec per year and hundreds of other stars move over 1 arc sec per year. The sun’s average drift over a ...
... E.g. the motion of the sun around the center of the Galaxy, 250 km/s, corresponds to 53 AU/yr. Most of the nearby stars are moving along with us, but not precisely. Barnard’s star “moves” 10.25 arc sec per year and hundreds of other stars move over 1 arc sec per year. The sun’s average drift over a ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.