HR DIAGRAM (Page 1) - McDonald Observatory
... instance, the faintest stars our eyes alone may see are apparent magnitude 6. A fairly bright star like Sirius is magnitude -1.4, while the sun is a blinding -26. For each single step up or down on the magnitude scale, the brightness changes by a factor of 2.512. And for every five steps, the bright ...
... instance, the faintest stars our eyes alone may see are apparent magnitude 6. A fairly bright star like Sirius is magnitude -1.4, while the sun is a blinding -26. For each single step up or down on the magnitude scale, the brightness changes by a factor of 2.512. And for every five steps, the bright ...
Lesson 3 - The Life Cycle of Stars - Hitchcock
... • Although black holes are invisible, they can be observed by the gravitational effect they have on their surroundings. • Matter swirls around a black hole just before being pulled in. The matter becomes so hot that it emits X-rays. • Astronomers use X-rays and other means to locate black holes, eve ...
... • Although black holes are invisible, they can be observed by the gravitational effect they have on their surroundings. • Matter swirls around a black hole just before being pulled in. The matter becomes so hot that it emits X-rays. • Astronomers use X-rays and other means to locate black holes, eve ...
Hertzsprung Rusell Diagram KLT
... Stars that look to us as though they are near each other, may intact be very far away from each other. Distant but very bright stars look similar to close but dim stars. ...
... Stars that look to us as though they are near each other, may intact be very far away from each other. Distant but very bright stars look similar to close but dim stars. ...
What is the life cycle of a star?
... • Although black holes are invisible, they can be observed by the gravitational effect they have on their surroundings. • Matter swirls around a black hole just before being pulled in. The matter becomes so hot that it emits X-rays. • Astronomers use X-rays and other means to locate black holes, eve ...
... • Although black holes are invisible, they can be observed by the gravitational effect they have on their surroundings. • Matter swirls around a black hole just before being pulled in. The matter becomes so hot that it emits X-rays. • Astronomers use X-rays and other means to locate black holes, eve ...
CONSTELLATIONS
... Autumnal Equinox / September 21 THE PLANETS As you have seen, the dashed line on the planisphere marks the ecliptic. As our Earth moves around in its orbit, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets also appear along this line. The ecliptic therefore represents the plane of the solar system. Of the nine pl ...
... Autumnal Equinox / September 21 THE PLANETS As you have seen, the dashed line on the planisphere marks the ecliptic. As our Earth moves around in its orbit, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets also appear along this line. The ecliptic therefore represents the plane of the solar system. Of the nine pl ...
preliminary version - University of Exeter
... Periods for CTTs from photometric monitoring: The most efficient method of determining large numbers of periods for young stars is via photometric monitoring. Unfortunately, this method has proved insensitive to periods amongst CTTs in the past, largely due to the irregular variability shown by CTTs ...
... Periods for CTTs from photometric monitoring: The most efficient method of determining large numbers of periods for young stars is via photometric monitoring. Unfortunately, this method has proved insensitive to periods amongst CTTs in the past, largely due to the irregular variability shown by CTTs ...
Section 1.2 Astrometric Data
... (extragalactic) radio reference system. Providing proper motions within the ICRS means that they are consistent with the best present realisations of a quasi-inertial reference system (i.e. non-rotating with respect to distant galaxies); • since parallax is explicitly derived in the data reduction, ...
... (extragalactic) radio reference system. Providing proper motions within the ICRS means that they are consistent with the best present realisations of a quasi-inertial reference system (i.e. non-rotating with respect to distant galaxies); • since parallax is explicitly derived in the data reduction, ...
The double-degenerate, super-Chandrasekhar nucleus of the
... further discussion. A 0.88 M⊙ helium star approaching core helium exhaustion20 , produced by the hydrogen shell of a massive star being stripped off during RLOF, would have a compatible luminosity of 422 L⊙ , although its radius, 0.16 R⊙ is still lower than the 0.68 R⊙ radius found in this work, an ...
... further discussion. A 0.88 M⊙ helium star approaching core helium exhaustion20 , produced by the hydrogen shell of a massive star being stripped off during RLOF, would have a compatible luminosity of 422 L⊙ , although its radius, 0.16 R⊙ is still lower than the 0.68 R⊙ radius found in this work, an ...
chapter16StarBirth
... • Without CO molecules to provide cooling, the clouds that formed the first stars had to be considerably warmer than today’s molecular clouds • The first stars must therefore have been more massive than most of today’s stars, for gravity to overcome pressure ...
... • Without CO molecules to provide cooling, the clouds that formed the first stars had to be considerably warmer than today’s molecular clouds • The first stars must therefore have been more massive than most of today’s stars, for gravity to overcome pressure ...
Stellar Evolution
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a ...
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a ...
3P15.pdf
... the photosphere to the total surface flux emitted by the star. Fig. 4a to 7a show, for all the stars of the sample, the mean value of the excess emission of the Hα line vs. the mean value of the excess emission of other chromospheric lines (Ca II λ8542Å, Ca II K, Hβ and Hγ). Fig. 4b to 7b show the s ...
... the photosphere to the total surface flux emitted by the star. Fig. 4a to 7a show, for all the stars of the sample, the mean value of the excess emission of the Hα line vs. the mean value of the excess emission of other chromospheric lines (Ca II λ8542Å, Ca II K, Hβ and Hγ). Fig. 4b to 7b show the s ...
From the reviews - Astrofoto Portugal
... "Navigating the Night Sky is an easy to read book that is essential for all those taking their first steps in finding their w ay around the night sky. Whilst the book is aimed at beginners it also provides information for the more advanced stargazer. The book is arranged into chapters on the Constel ...
... "Navigating the Night Sky is an easy to read book that is essential for all those taking their first steps in finding their w ay around the night sky. Whilst the book is aimed at beginners it also provides information for the more advanced stargazer. The book is arranged into chapters on the Constel ...
Orion - Starry Starry Night!
... Taurus Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth ...
... Taurus Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth ...
Hall Scorpius constellation (11) Jacob Hall Physics 1040, sec 002
... is the same color as the planet Mars. Antares is a red supergiant with a radius about 800 times that of the Sun. It is classified as a variable star; its apparent magnitude varies between 0.9 and 1.8. It has a hot blue companion star about 2.9 arcseconds away. (2) Antares is the 16th brightest star ...
... is the same color as the planet Mars. Antares is a red supergiant with a radius about 800 times that of the Sun. It is classified as a variable star; its apparent magnitude varies between 0.9 and 1.8. It has a hot blue companion star about 2.9 arcseconds away. (2) Antares is the 16th brightest star ...
Physics- HSC- Module 9.7 Astrophysics
... During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers obtained spectra and parallax distances for many stars, a powerful tool was discovered for classifying and understanding stars. Around 1911-13, Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell independently found that stars could be divided into t ...
... During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers obtained spectra and parallax distances for many stars, a powerful tool was discovered for classifying and understanding stars. Around 1911-13, Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell independently found that stars could be divided into t ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... 17.1 The Solar Neighborhood Next nearest neighbor: Barnard’s Star Barnard’s Star has the largest proper motion of any star—proper motion is the actual shift of the star in the sky, after correcting for parallax These pictures were taken 22 years apart: ...
... 17.1 The Solar Neighborhood Next nearest neighbor: Barnard’s Star Barnard’s Star has the largest proper motion of any star—proper motion is the actual shift of the star in the sky, after correcting for parallax These pictures were taken 22 years apart: ...
sa`d al-malik - WordPress.com
... Greek legend, however, tells of Ganymede, an exceptionally handsome, young prince of Troy. He was spotted by Zeus, who immediately decided that he would make a perfect cup-bearer. The story then differs - one version telling how Zeus sent his pet eagle, Aquila, to carry Ganymede to Olympus, another ...
... Greek legend, however, tells of Ganymede, an exceptionally handsome, young prince of Troy. He was spotted by Zeus, who immediately decided that he would make a perfect cup-bearer. The story then differs - one version telling how Zeus sent his pet eagle, Aquila, to carry Ganymede to Olympus, another ...
common constellations
... explosion of this type is called a supernova. The explosion was so large and so bright that it was visible in broad daylight for at least twenty-three days. It must have been amazing! You can still see the remnants of this explosion in Taurus. It is called the Crab Nebula. The Crab Nebula is one of ...
... explosion of this type is called a supernova. The explosion was so large and so bright that it was visible in broad daylight for at least twenty-three days. It must have been amazing! You can still see the remnants of this explosion in Taurus. It is called the Crab Nebula. The Crab Nebula is one of ...
13.5 The HR Diagram By the early 1900s, astronomers had learned
... In 1912, the Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell working independently found that if stars are plotted on a diagram according to their luminosity and their temperature (or, equivalently, spectral type), then most of them lie along a smooth curve. The ...
... In 1912, the Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell working independently found that if stars are plotted on a diagram according to their luminosity and their temperature (or, equivalently, spectral type), then most of them lie along a smooth curve. The ...
Good Vibrations and Stellar Pulsations - Physics
... a 2nd magnitude star in the constellation Cetus. As it declined in brightness, the star vanished by October. Later it reappeared, and was renamed Mira (“the Wonderful”) By 1660 its 11-month period had been established. The light variations were believed to be caused by “blotches” on the surface of a ...
... a 2nd magnitude star in the constellation Cetus. As it declined in brightness, the star vanished by October. Later it reappeared, and was renamed Mira (“the Wonderful”) By 1660 its 11-month period had been established. The light variations were believed to be caused by “blotches” on the surface of a ...
L87 THE b PICTORIS MOVING GROUP B. ZUCkERMAN AND
... Based on averaged proper motions from PPM and Hipparcos catalogs. UVW are positive in the directions of the Galactic center, Galactic rotation, and the north Galactic pole. Errors in UVW are all smaller than 2.0 km s!1 in all components except for HIP 88399, 88726, and 92024, where poor radial veloc ...
... Based on averaged proper motions from PPM and Hipparcos catalogs. UVW are positive in the directions of the Galactic center, Galactic rotation, and the north Galactic pole. Errors in UVW are all smaller than 2.0 km s!1 in all components except for HIP 88399, 88726, and 92024, where poor radial veloc ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... To derive the density distribution from the star counts, the luminosity function needs to be determined. In principle one can then invert the integral equation for D(r). In practice, one assumes certain functional forms for D(r), and tries to determine which one provides the best fit. ...
... To derive the density distribution from the star counts, the luminosity function needs to be determined. In principle one can then invert the integral equation for D(r). In practice, one assumes certain functional forms for D(r), and tries to determine which one provides the best fit. ...
RS Oph
... mechanism but nothing so far has proved to be conclusive. This makes the next outburst an important target for the sensitive multi-wavelength measuring devices that were not available for use during the previous outbursts. Outbursts in RS Oph have been seen in 1933, 1958, 1967 & 1985. Another outbur ...
... mechanism but nothing so far has proved to be conclusive. This makes the next outburst an important target for the sensitive multi-wavelength measuring devices that were not available for use during the previous outbursts. Outbursts in RS Oph have been seen in 1933, 1958, 1967 & 1985. Another outbur ...
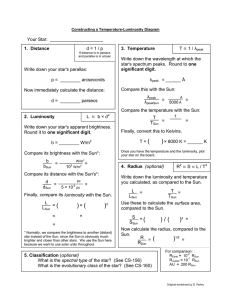
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Evolution of a Planetary System
... 1. Review. Remind the students that in the last Mission, they learned how planets may form around a star. But are all stars the same? Now we will study how stars can vary in their color and temperature. Star types were first invented to identify stars with different colors. For example, our Sun is a ...
... 1. Review. Remind the students that in the last Mission, they learned how planets may form around a star. But are all stars the same? Now we will study how stars can vary in their color and temperature. Star types were first invented to identify stars with different colors. For example, our Sun is a ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.