color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
... the application of the inverse-square law for nearby stars. If a star is close enough to us we see it move relative to distant stars as we orbit the Sun through Parallax. By measuring how much it appears to move we can estimate the distance to the star. If we know the distance to the star, and we ca ...
... the application of the inverse-square law for nearby stars. If a star is close enough to us we see it move relative to distant stars as we orbit the Sun through Parallax. By measuring how much it appears to move we can estimate the distance to the star. If we know the distance to the star, and we ca ...
Stellarium01 Starter Part A B Doc - ASTR101
... The Bayer method is still in use today, but even it can’t account for all of the millions of stars in the sky! In the 19th and 20th centuries, various exhaustive catalogs of many hundreds of thousands of stars were made, including the BSC or Bright Star Catalog, the HD or Henry Draper Catalog, and t ...
... The Bayer method is still in use today, but even it can’t account for all of the millions of stars in the sky! In the 19th and 20th centuries, various exhaustive catalogs of many hundreds of thousands of stars were made, including the BSC or Bright Star Catalog, the HD or Henry Draper Catalog, and t ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... • In the case of the Sun, we can apply spot models to TSI data and check whether the models reproduce the observed sunspot group configurations; • Since latitude information in the rotational modulation of the TSI is very small (i ~ 90o), only total area variations and longitude distributions of act ...
... • In the case of the Sun, we can apply spot models to TSI data and check whether the models reproduce the observed sunspot group configurations; • Since latitude information in the rotational modulation of the TSI is very small (i ~ 90o), only total area variations and longitude distributions of act ...
Stars - cayugascience
... that, from Earth, resembles a recognizable form. Astronomers have officially listed a total of 88 constellations. Examples, along with Ursa Major, include Cassiopeia, Orion, Pegasus, Sagittarius, and Ursa Minor. Smaller recognizable star patterns within a larger constellation are known as asterisms. ...
... that, from Earth, resembles a recognizable form. Astronomers have officially listed a total of 88 constellations. Examples, along with Ursa Major, include Cassiopeia, Orion, Pegasus, Sagittarius, and Ursa Minor. Smaller recognizable star patterns within a larger constellation are known as asterisms. ...
Lesson 3: Calculating distances to stars
... In your exam you may be asked to calculate the distance to a star in parsecs from a given parallax angle or vice versa. The distances to stars can’t always be calculated from the parallax method. If the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to th ...
... In your exam you may be asked to calculate the distance to a star in parsecs from a given parallax angle or vice versa. The distances to stars can’t always be calculated from the parallax method. If the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to th ...
Document
... for hydrogen, helium and oxygen. Here I am convinced that there is something seriously wrong with the present theory. It is clearly impossible that hydrogen should be a million times more abundant than the metals, and I have no doubt that the number of hydrogen atoms in the two quantum state is enor ...
... for hydrogen, helium and oxygen. Here I am convinced that there is something seriously wrong with the present theory. It is clearly impossible that hydrogen should be a million times more abundant than the metals, and I have no doubt that the number of hydrogen atoms in the two quantum state is enor ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known luminosity in the galaxy. If we had this then we could make comparisons with the other stars and judge their luminosities. In other words we need a ‘standard candle’ –that is a star of known ...
... away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known luminosity in the galaxy. If we had this then we could make comparisons with the other stars and judge their luminosities. In other words we need a ‘standard candle’ –that is a star of known ...
February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
Photometry – I. “All sky”
... years, you might not even be able to get the same glass that was used previously. Detectors are also not really uniform; CCDs are much more red-sensitive than photomultipliers and different types (of either) might have significantly different responses as a function of wavelength. At the same time, ...
... years, you might not even be able to get the same glass that was used previously. Detectors are also not really uniform; CCDs are much more red-sensitive than photomultipliers and different types (of either) might have significantly different responses as a function of wavelength. At the same time, ...
10 - Keele Astrophysics Group
... grouped together stars depending on the prominence of particular spectral lines: hydrogen lines, helium lines and lines of some metallic ions. Astronomers at Harvard Observatory further developed and refined these early classification schemes and spectral types were defined to reflect a smooth chang ...
... grouped together stars depending on the prominence of particular spectral lines: hydrogen lines, helium lines and lines of some metallic ions. Astronomers at Harvard Observatory further developed and refined these early classification schemes and spectral types were defined to reflect a smooth chang ...
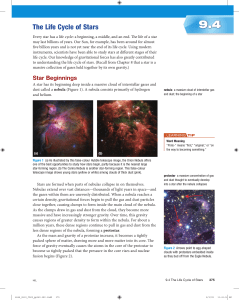
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Stars Like the Sun: Red Giant to White Dwarf After spending approximately 10 billion years as a main sequence star, a star’s available hydrogen will have been converted to helium by nuclear fusion. This results in the formation of a helium-rich core, surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. With le ...
... Stars Like the Sun: Red Giant to White Dwarf After spending approximately 10 billion years as a main sequence star, a star’s available hydrogen will have been converted to helium by nuclear fusion. This results in the formation of a helium-rich core, surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. With le ...
Enhanced lithium depletion in Sun-like stars with orbiting planets.
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
Navigating the Night Sky – Teacher Guide Argos Online Subject
... o Why are the stars different sizes on the map? -Different magnitudes (brightness). Stars whose magnitudes are larger numbers are dimmer. The Greeks labeled the brightest stars they could see as magnitude 1 and the faintest as magnitude 6. We still use this system, but it often confuses people. The ...
... o Why are the stars different sizes on the map? -Different magnitudes (brightness). Stars whose magnitudes are larger numbers are dimmer. The Greeks labeled the brightest stars they could see as magnitude 1 and the faintest as magnitude 6. We still use this system, but it often confuses people. The ...
Chapter three: The properties of Stars
... M is the apparent magnitude the star would have, if it is 10pc away from the observer on the surface of the Earth, i.e., M = m(d=10pc). Next let’s see how M is related to m at an any distance d from the observer. Image two apparent magnitude measurements are done for a star, whose luminosity is L On ...
... M is the apparent magnitude the star would have, if it is 10pc away from the observer on the surface of the Earth, i.e., M = m(d=10pc). Next let’s see how M is related to m at an any distance d from the observer. Image two apparent magnitude measurements are done for a star, whose luminosity is L On ...
Astronomy and Survey of Information
... Warning Science Content! • It is impossible to obtain the complete orbit of a spectroscopic binary unless it is also a visual or an eclipsing binary, so from these objects only a determination of the joint product of mass and the sine of the angle of inclination relative to the line of sight is poss ...
... Warning Science Content! • It is impossible to obtain the complete orbit of a spectroscopic binary unless it is also a visual or an eclipsing binary, so from these objects only a determination of the joint product of mass and the sine of the angle of inclination relative to the line of sight is poss ...
Slide 1
... scattered light. We give limits to mass and radius for XTE J1807-294 and compare these to limits determined for SAX J1808-3658 and XTE J1814-334 previously determined using similar methods. The resulting allowed region for mass-radius curves is small but consistent with a mass-radius relation with n ...
... scattered light. We give limits to mass and radius for XTE J1807-294 and compare these to limits determined for SAX J1808-3658 and XTE J1814-334 previously determined using similar methods. The resulting allowed region for mass-radius curves is small but consistent with a mass-radius relation with n ...
Properties of Stars - Montana State University Extended University
... 7. What are two reasons why determining a star's temperature from Wien's law (see the electromagnetic radiation chapter) is usually not as accurate as using the spectral lines? 8. What are the 7 basic spectral types in order of temperature (hottest to coldest)? 9. If our Sun has a surface temperatur ...
... 7. What are two reasons why determining a star's temperature from Wien's law (see the electromagnetic radiation chapter) is usually not as accurate as using the spectral lines? 8. What are the 7 basic spectral types in order of temperature (hottest to coldest)? 9. If our Sun has a surface temperatur ...
Guidestar: February, 2015 - Houston Astronomical Society
... February 6th meeting to get your 2015 code. We will soon be putting the site orientation program on the website. In doing so we are going to ask everyone who already has taken the course to take a refresher course. When you complete the course and pass the 10 or so question quiz the data base will a ...
... February 6th meeting to get your 2015 code. We will soon be putting the site orientation program on the website. In doing so we are going to ask everyone who already has taken the course to take a refresher course. When you complete the course and pass the 10 or so question quiz the data base will a ...
Open access - ORBi
... disk. The photospheric model is fixed using the estimated limb-darkened diameter from surface-brightness relationships and the linear limb-darkening coefficients of Claret.16 Furthermore, we account for a possible oblateness of the photosphere, based on the measured v sin i, as described in a previous ...
... disk. The photospheric model is fixed using the estimated limb-darkened diameter from surface-brightness relationships and the linear limb-darkening coefficients of Claret.16 Furthermore, we account for a possible oblateness of the photosphere, based on the measured v sin i, as described in a previous ...
Cepheus (constellation)
... δ Cephei is the prototype Cepheid variable, a yellow-hued supergiant star 980 light-years from Earth. It was discovered to be variable by John Goodricke in 1784. It varies between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei ha ...
... δ Cephei is the prototype Cepheid variable, a yellow-hued supergiant star 980 light-years from Earth. It was discovered to be variable by John Goodricke in 1784. It varies between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei ha ...
5 Understanding stars and star ClUsters
... Understanding Stars and Star Clusters Stars are formed from gas and dust compressed together by various forces. Star clusters are formed in several different ways. In what are called open clusters, it is usually the sweeping wave action of the spiral arms of the galaxy thrusting vast stretches of th ...
... Understanding Stars and Star Clusters Stars are formed from gas and dust compressed together by various forces. Star clusters are formed in several different ways. In what are called open clusters, it is usually the sweeping wave action of the spiral arms of the galaxy thrusting vast stretches of th ...
Measuring the Stars Section 29.2
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
iaf2001_paper (doc - 1.8 MB)
... a main target, some additional stars, brighter than a magnitude 9 and belonging to an extended range of stellar types ( Dor, Ceph, peculiar metallic stars…), will also be studied. COROT is designed to acquire up to 10 stars simultaneously. ...
... a main target, some additional stars, brighter than a magnitude 9 and belonging to an extended range of stellar types ( Dor, Ceph, peculiar metallic stars…), will also be studied. COROT is designed to acquire up to 10 stars simultaneously. ...
Pulsating variable stars and the Hertzsprung
... In the early XX century, astronomers began photographing the spectra of stars, but the diversity of spectral features was too confusing and complex to explain. Edward Pickering (1846-1919) re-arranged the spectral sequence, taking into consideration the changes in other lines. Building upon this ide ...
... In the early XX century, astronomers began photographing the spectra of stars, but the diversity of spectral features was too confusing and complex to explain. Edward Pickering (1846-1919) re-arranged the spectral sequence, taking into consideration the changes in other lines. Building upon this ide ...
– 1 – 1. Historical Notes for Ay 123 1.1.
... actually are. It is now clear that there are some problems specific to certain situations in the catalog. GAIA – another ESA project, to be launched in 2012, collecting area 30 × that of Hipparcos, position measurements 200 × more accurate than Hipparcos. SIM (space interferometry mission) – JPL pro ...
... actually are. It is now clear that there are some problems specific to certain situations in the catalog. GAIA – another ESA project, to be launched in 2012, collecting area 30 × that of Hipparcos, position measurements 200 × more accurate than Hipparcos. SIM (space interferometry mission) – JPL pro ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.