Document
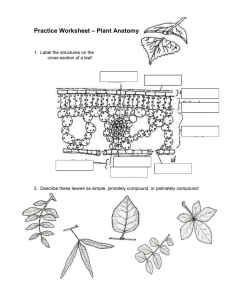
... leaflets. Leaves with a single undivided blade are called simple, those with two or more leaflets are called compound. The outer surface of the leaf has a thin waxy covering called the cuticle (A), this layer’s primary function is to prevent water loss within the leaf. (Plants that leave entirely wi ...
... leaflets. Leaves with a single undivided blade are called simple, those with two or more leaflets are called compound. The outer surface of the leaf has a thin waxy covering called the cuticle (A), this layer’s primary function is to prevent water loss within the leaf. (Plants that leave entirely wi ...
INFORMATION CARD COMMON NAME: Madrone SCIENTIFIC
... the green inner bark produces food through photosynthesis. FACTS: Madrones stump sprout and are able to recover quickly after a fire. They have a beautiful cinnamon wood similar to Manzanita which is used to make ornamental objects. NATIVE USES: The Indians and early settlers used the tree for utens ...
... the green inner bark produces food through photosynthesis. FACTS: Madrones stump sprout and are able to recover quickly after a fire. They have a beautiful cinnamon wood similar to Manzanita which is used to make ornamental objects. NATIVE USES: The Indians and early settlers used the tree for utens ...
Botique Fungus Pharm RTU 35oz 8-12-06.cdr
... top and bottom and in case of trees, the entire trunk where eggs are wintering over. Please test on seedlings before full application. Please do not over spray, do not spray to drip. There should not be a soapy residue on the leaves. For Regular Maintenance: Mix 8 parts water to 1 part concentrate s ...
... top and bottom and in case of trees, the entire trunk where eggs are wintering over. Please test on seedlings before full application. Please do not over spray, do not spray to drip. There should not be a soapy residue on the leaves. For Regular Maintenance: Mix 8 parts water to 1 part concentrate s ...
51. Poison Ivy - Friess Lake School District
... What are the leaves like? The leaves are compound with three almond-shaped leaves centered at the end of one stalk. Each leaf is rounded at the base with a sharp point at the tip. The upper leaf is conspicuously-stemmed. The leaves are glossy green during summer and bright red in the fall. They can ...
... What are the leaves like? The leaves are compound with three almond-shaped leaves centered at the end of one stalk. Each leaf is rounded at the base with a sharp point at the tip. The upper leaf is conspicuously-stemmed. The leaves are glossy green during summer and bright red in the fall. They can ...
Kingdom Plantae - Porterville Unified School District
... Flowering plants • The ovary of the flower ripens and becomes a fruit ...
... Flowering plants • The ovary of the flower ripens and becomes a fruit ...
Kingdom Plantae - Cloudfront.net
... Flowering plants • The ovary of the flower ripens and becomes a fruit ...
... Flowering plants • The ovary of the flower ripens and becomes a fruit ...
Seed
... from leaves; support/structure Roots: Absorbs water and nutrients from soil; anchors plant to the ground ...
... from leaves; support/structure Roots: Absorbs water and nutrients from soil; anchors plant to the ground ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... Which color of light is absorbed by chlorophyll? • Chlorophyll absorb blue and red light ...
... Which color of light is absorbed by chlorophyll? • Chlorophyll absorb blue and red light ...
Botany Chapter 6 leaves
... – Provides a structure for vascular tissue to and from leaf. – **Monocots often have leaf sheath instead of petiole** ...
... – Provides a structure for vascular tissue to and from leaf. – **Monocots often have leaf sheath instead of petiole** ...
Unit 14 Plants Angiosperms Notes
... = produce flowers and develop seeds that are enclosed in a fruit Advantage = added protection the fruit provides Anthophytes = division 2 classes 1. Monocotyledons = one seed leaf 60,000 species Familiar: grasses, orchids, lilies, and palms 2. Dicotyledons = two seed leaves Majority 170,000 species ...
... = produce flowers and develop seeds that are enclosed in a fruit Advantage = added protection the fruit provides Anthophytes = division 2 classes 1. Monocotyledons = one seed leaf 60,000 species Familiar: grasses, orchids, lilies, and palms 2. Dicotyledons = two seed leaves Majority 170,000 species ...
New Zealand Pigmyweed
... northwards, though much less common in Scotland. Very common in the south-east of England. ...
... northwards, though much less common in Scotland. Very common in the south-east of England. ...
New Zealand Pigmyweed - GB non
... northwards, though much less common in Scotland. Very common in the south-east of England. ...
... northwards, though much less common in Scotland. Very common in the south-east of England. ...
Land Plants vs. Aquatic Plants
... • the stem holds up and support the plant; it also has vascular bundles of xylem and phloem • roots anchor the plant in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the ground ...
... • the stem holds up and support the plant; it also has vascular bundles of xylem and phloem • roots anchor the plant in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the ground ...
Handout #2 - Thirteen.org
... The stem carries water and nutrients. 4. What type of cells would one find inside a stem? The two types of cells are xylem and phloem. 5. What is the purpose of leaves on a plant? The leaves serve as the food-making factories of the plant. 6. How are leaves arranged? The leaves can be simple or sing ...
... The stem carries water and nutrients. 4. What type of cells would one find inside a stem? The two types of cells are xylem and phloem. 5. What is the purpose of leaves on a plant? The leaves serve as the food-making factories of the plant. 6. How are leaves arranged? The leaves can be simple or sing ...
Kingdom Plantae
... • Contain xylem & phloem (vascular tissue) – Xylem – carries water up from the roots – Phloem – transports products of photosynthesis ...
... • Contain xylem & phloem (vascular tissue) – Xylem – carries water up from the roots – Phloem – transports products of photosynthesis ...
Document
... • Above ground plant organ specialized for photosynthesis • Leaves are the site where transpiration and guttation takes place • Leaves can store food and water, in other plants they can serve different purposes ...
... • Above ground plant organ specialized for photosynthesis • Leaves are the site where transpiration and guttation takes place • Leaves can store food and water, in other plants they can serve different purposes ...
Seed Plants (Pg 262-271)
... 1. What are the two characteristics of seed plants? They have vascular tissue (tubes), and they both use pollen and seeds to reproduce. 2. What are the two kinds of vascular tissue (tubes) in seed plants? Phloem and xylem 3. Vascular tissue Job Xylem the tubes where water enter and move upward into ...
... 1. What are the two characteristics of seed plants? They have vascular tissue (tubes), and they both use pollen and seeds to reproduce. 2. What are the two kinds of vascular tissue (tubes) in seed plants? Phloem and xylem 3. Vascular tissue Job Xylem the tubes where water enter and move upward into ...
Plant adaptation PowerPoint Resource
... All plants have features (adaptations) which help them to survive and reproduce in the places where they live (their habitat) ...
... All plants have features (adaptations) which help them to survive and reproduce in the places where they live (their habitat) ...
All plants have features (adaptations) which help them to survive
... All plants have features (adaptations) which help them to survive and reproduce in the places where they live (their habitat) ...
... All plants have features (adaptations) which help them to survive and reproduce in the places where they live (their habitat) ...
Plants
... Pollen contains plant sperm, and fills the air during the springtime, which often causes seasonal allergies. ...
... Pollen contains plant sperm, and fills the air during the springtime, which often causes seasonal allergies. ...
Parts of a plant
... *anchor plant and hold upright *absorb water and minerals form soil and conduct to stem *store food, & propagation ...
... *anchor plant and hold upright *absorb water and minerals form soil and conduct to stem *store food, & propagation ...
Root and Shoot Systems
... anchor a plant into the soil and absorb water and nutrients. They comprise a root system with a large surface area. Shoots – the aboveground portion of plants that consist of stems and leaves and function in absorption of light energy and carbon dioxide. ...
... anchor a plant into the soil and absorb water and nutrients. They comprise a root system with a large surface area. Shoots – the aboveground portion of plants that consist of stems and leaves and function in absorption of light energy and carbon dioxide. ...
Floriculture Disorders Eddie McKie
... • It may grow upright to a height of 2 feet. It will not tolerate close mowing as well as smooth crabgrass. • True leaves are generally 3 inches long and hairy on the upper surface of the leaf and leaf sheath. • The branches are l about 2 to 5 inches at the end of the stalk. ...
... • It may grow upright to a height of 2 feet. It will not tolerate close mowing as well as smooth crabgrass. • True leaves are generally 3 inches long and hairy on the upper surface of the leaf and leaf sheath. • The branches are l about 2 to 5 inches at the end of the stalk. ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.