Quiz 8.doc
... 1. Examples of non-vascular plants are a. ferns b. conifers c. flowering plants d. mosses and liverworts e. none of the above 2. Plant adaptations to life on land include all of these, except: a. chlorophyl b. cuticle , cork and bark c. stomata d. lignin e. xylem and phloem 3. The green, leaflike st ...
... 1. Examples of non-vascular plants are a. ferns b. conifers c. flowering plants d. mosses and liverworts e. none of the above 2. Plant adaptations to life on land include all of these, except: a. chlorophyl b. cuticle , cork and bark c. stomata d. lignin e. xylem and phloem 3. The green, leaflike st ...
Indoor Botanical Garden of Art
... on their card. Before they begin, have them plan their paper sculptures by sketching what they want their creation to look like. Give partners a section of the wall on which to build their plant. Provide construction paper and tissue paper to cut out the pieces of their plant and use colored pencils ...
... on their card. Before they begin, have them plan their paper sculptures by sketching what they want their creation to look like. Give partners a section of the wall on which to build their plant. Provide construction paper and tissue paper to cut out the pieces of their plant and use colored pencils ...
Leaf Anatomy - Lemon Bay High School
... The leaf is the primary photosynthetic organ of the plant. It consists of a flattened portion, called the blade, that is attached to the plant by a structure called the petiole. Sometimes leaves are divided into two or more sections called leaflets. Leaves with a single undivided blade are called si ...
... The leaf is the primary photosynthetic organ of the plant. It consists of a flattened portion, called the blade, that is attached to the plant by a structure called the petiole. Sometimes leaves are divided into two or more sections called leaflets. Leaves with a single undivided blade are called si ...
... up to 10 fully expanded leaves; V2: between 11 leaves and flowering; and R: after flowering. At stages V 2 and R, the highest number of leaves was recorded for S. r hombifolia , followed by S. spinosa at V 2 and S. urens at R. These results were relatively proportional to leaf area for all species. ...
Vascular tissue
... • blade – flat part of leaf • petiole – stalk connecting blade to stem • cuticle – waxy coating • veins – contain x & p ...
... • blade – flat part of leaf • petiole – stalk connecting blade to stem • cuticle – waxy coating • veins – contain x & p ...
Exotic Invasive Vegetation ID Guide
... – Multiflora rose (Rosa Multiflora) – English ivy (Hedera helix) – Japanese honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) – Kudzu (Pueria montana) ...
... – Multiflora rose (Rosa Multiflora) – English ivy (Hedera helix) – Japanese honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) – Kudzu (Pueria montana) ...
Roots, Stems, Leaves and Tissues 09
... absorption of sunlight • Photosynthesis- the bulk of leaves is made of a specialized ground tissue called mesophyll which is packed with chloroplasts • Transpiration- is the loss of water through the leaf • Gas exchange- carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged through the leaf’s surface ...
... absorption of sunlight • Photosynthesis- the bulk of leaves is made of a specialized ground tissue called mesophyll which is packed with chloroplasts • Transpiration- is the loss of water through the leaf • Gas exchange- carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged through the leaf’s surface ...
Plant structure – leaves, stems and roots
... Epiphytic plants grow on other trees using them for support. Their aerial roots rarely reach the soil so absorb water from rain or mist. ...
... Epiphytic plants grow on other trees using them for support. Their aerial roots rarely reach the soil so absorb water from rain or mist. ...
Plant Evolution
... c. Leaves- food production occurs here. Where most of the chloroplasts are located. 3. Examples of vascular plants from most primitive to most advanced (evolutionary terms) a. Seedless vascular plants- reproduce via spores (alternation of generation). Usually found in most areas. Fern is an example. ...
... c. Leaves- food production occurs here. Where most of the chloroplasts are located. 3. Examples of vascular plants from most primitive to most advanced (evolutionary terms) a. Seedless vascular plants- reproduce via spores (alternation of generation). Usually found in most areas. Fern is an example. ...
Monocots vs Dicots
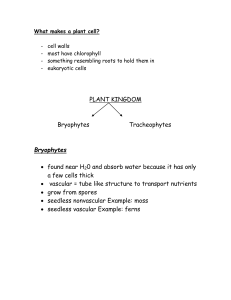
... plants. The types of plants vary in size from microscopic algae, to huge sequoia trees more than 8m (26 ft) tall. Plant Kingdom is mainly classified into two . This type of plant classification is done according to how they reproduce. 1) Spore bearing plants ( Algae, mosses, ferns and their rela ...
... plants. The types of plants vary in size from microscopic algae, to huge sequoia trees more than 8m (26 ft) tall. Plant Kingdom is mainly classified into two . This type of plant classification is done according to how they reproduce. 1) Spore bearing plants ( Algae, mosses, ferns and their rela ...
Plant TissuesMonocots, dicots, ch 23 plant cells and tissues
... Cacti depend on chlorophyll in the outer tissue of their skin and stems to conduct photosynthesis for the manufacture of food. Spines protect the plant from animals, shade the plant from the sun and also collect moisture. Extensive shallow root systems are usually radial, allowing for the quick acqu ...
... Cacti depend on chlorophyll in the outer tissue of their skin and stems to conduct photosynthesis for the manufacture of food. Spines protect the plant from animals, shade the plant from the sun and also collect moisture. Extensive shallow root systems are usually radial, allowing for the quick acqu ...
Adaptations of Common Daisy (Bellis perrenis)
... Grows from rhizomes (growing stem found underground). Small rounded spoon shaped leaves, that grow in a rosette formation are evergreen. Leaves are 2-5cm long. Leaves may be hairy The flower heads are 2-3cm wide, with white petals often with a red tip. They are produced on a leafless stem, 210cm tal ...
... Grows from rhizomes (growing stem found underground). Small rounded spoon shaped leaves, that grow in a rosette formation are evergreen. Leaves are 2-5cm long. Leaves may be hairy The flower heads are 2-3cm wide, with white petals often with a red tip. They are produced on a leafless stem, 210cm tal ...
Sulphur Cinquefoil (Potentilla recta)
... This perennial herb is a tufted plant growing from a woody taproot or caudex. It produces upright to erect leafy stems up to 80 centimeters tall. The leaves are palmate, divided into usually 6 or 7 leaflets, sometimes up to nine. The green to yellowgreen leaves may be up to 15 centimeters long, with ...
... This perennial herb is a tufted plant growing from a woody taproot or caudex. It produces upright to erect leafy stems up to 80 centimeters tall. The leaves are palmate, divided into usually 6 or 7 leaflets, sometimes up to nine. The green to yellowgreen leaves may be up to 15 centimeters long, with ...
ID Honeysuckle shrub species (L. morrowii & L. tatarica)
... Stems light brown changing to gray, with hollowed out brown pith, & bark often shredding. Flowers creamy white, tubular, in pairs in the leaf axils, late May to early June. Turn yellow with age. Fruit red, ¼”, mid-summer to early fall. ...
... Stems light brown changing to gray, with hollowed out brown pith, & bark often shredding. Flowers creamy white, tubular, in pairs in the leaf axils, late May to early June. Turn yellow with age. Fruit red, ¼”, mid-summer to early fall. ...
Chinese boxthorn
... Erect perennial, deciduous; stems thick, 0.5-1(-2) m tall; branches long arching or prostrate, with thorns; leaves alternate, ovate or ovate-lanceolate, up to 7 cm long, in tight clusters; leaf blades thick and grayish; flowers usually 2-8 at a node, 1 cm long, funnel-form, corolla purplish; fruit ( ...
... Erect perennial, deciduous; stems thick, 0.5-1(-2) m tall; branches long arching or prostrate, with thorns; leaves alternate, ovate or ovate-lanceolate, up to 7 cm long, in tight clusters; leaf blades thick and grayish; flowers usually 2-8 at a node, 1 cm long, funnel-form, corolla purplish; fruit ( ...
PLANTS
... reproduce (sperm and egg swim) • Asexual does not • Rhiziods instead of roots • Flat broad tissues instead of leaves ...
... reproduce (sperm and egg swim) • Asexual does not • Rhiziods instead of roots • Flat broad tissues instead of leaves ...
Yellow woodsorrel Oxalis stricta L.
... Life cycle: Perennial/annual depending upon climate Habitat: Poorly maintained turf; waste areas General description: Young plants are erect, but as age they become spreading. Leaves are light‐green, trifoliolate with heart‐shaped leaflets. Yellow flowers with five petals; fruit is a 5‐ridge ...
... Life cycle: Perennial/annual depending upon climate Habitat: Poorly maintained turf; waste areas General description: Young plants are erect, but as age they become spreading. Leaves are light‐green, trifoliolate with heart‐shaped leaflets. Yellow flowers with five petals; fruit is a 5‐ridge ...
Plant Organs
... Herbaceous Stems – green and do not develop tough, woody tissues. Their sizes are limited because their soft stem tissues cannot support much weight. Woody Stems – Vascular plants that live for more than one year often have woody stems. The roots and stems of these plants increase in diameter every ...
... Herbaceous Stems – green and do not develop tough, woody tissues. Their sizes are limited because their soft stem tissues cannot support much weight. Woody Stems – Vascular plants that live for more than one year often have woody stems. The roots and stems of these plants increase in diameter every ...
Burning bush, Euonymus alatus
... Similar Species Euonymus atropurpureus (Wahoo) is also called burning bush because it has leaves that turn red in the fall. Differences between the two include that the Wahoo has larger leaves than E. alatus and Wahoo leaves have fine hairs on their underside which E. alatus leaves do not. ...
... Similar Species Euonymus atropurpureus (Wahoo) is also called burning bush because it has leaves that turn red in the fall. Differences between the two include that the Wahoo has larger leaves than E. alatus and Wahoo leaves have fine hairs on their underside which E. alatus leaves do not. ...
Horticulture Crop Weeds
... Galinsoga ciliata Asteraceae Summer annual, upright, branching Pubescent stems & leaves (upper surface of blades) Opposite leaves with toothed margins White flowers – both disk and ray flowers (toothed) present ...
... Galinsoga ciliata Asteraceae Summer annual, upright, branching Pubescent stems & leaves (upper surface of blades) Opposite leaves with toothed margins White flowers – both disk and ray flowers (toothed) present ...
Kingdom
... _____________________ leaf has one blade. ________________________ leaves have many leaflets. When leaves grow in an alternating arrangement it is called _________________. When three or more leaves grow around the stem in the same position it is called a ______________________ arrangement. Most pho ...
... _____________________ leaf has one blade. ________________________ leaves have many leaflets. When leaves grow in an alternating arrangement it is called _________________. When three or more leaves grow around the stem in the same position it is called a ______________________ arrangement. Most pho ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.