UNIT 2 PART 5 PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONhighlighted
... which are irregularly shaped, have large air ...
... which are irregularly shaped, have large air ...
Nestronia umbellula - Wildlife Resources Division
... locations in Georgia. The genus Nestronia consists of only this species. Like many of its relatives in the Santalaceae (e.g., buffalo nut), Nestronia is a hemiparasite. Such plants contain chlorophyll and make their own food, but are capable of parasitizing the roots of certain other plants when the ...
... locations in Georgia. The genus Nestronia consists of only this species. Like many of its relatives in the Santalaceae (e.g., buffalo nut), Nestronia is a hemiparasite. Such plants contain chlorophyll and make their own food, but are capable of parasitizing the roots of certain other plants when the ...
Leaf FAQ
... plants the same? That is, if we make something happen in one plant species, will it happen in another? ...
... plants the same? That is, if we make something happen in one plant species, will it happen in another? ...
Plants
... Autotrophs that store food as starch and have cellulose cell walls. Ancestral to land plants (depend on water). They are not classified under Kingdom Plantae - belong to the Kingdom Protista ...
... Autotrophs that store food as starch and have cellulose cell walls. Ancestral to land plants (depend on water). They are not classified under Kingdom Plantae - belong to the Kingdom Protista ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... o Allow for transpiration (water loss from the plant by evaporation) o More on the bottom surface of leaf to minimize water loss ...
... o Allow for transpiration (water loss from the plant by evaporation) o More on the bottom surface of leaf to minimize water loss ...
intro_to_plant_names_tanner
... Leaf Morphology • Venation refers to the pattern in which the veins are distributed in the leaf blade • Parallel or Net-veined ...
... Leaf Morphology • Venation refers to the pattern in which the veins are distributed in the leaf blade • Parallel or Net-veined ...
Leaves- a plant`s food factory Photosynthesis
... Leaves- a plant’s food factory Animals are Consumers- we have to eat other things to survive. Plants are Producers- they make their own food using Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide and Water to create the sugar (Glucose) they eat. This is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. ...
... Leaves- a plant’s food factory Animals are Consumers- we have to eat other things to survive. Plants are Producers- they make their own food using Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide and Water to create the sugar (Glucose) they eat. This is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. ...
Dendrology - Delaware ENVIROTHON
... Keying takes practice • Most tree keys use characters such as leaf shape and seed descriptions to create groups, the user must be familiar with the terminology used to describe these characters to be successful. ...
... Keying takes practice • Most tree keys use characters such as leaf shape and seed descriptions to create groups, the user must be familiar with the terminology used to describe these characters to be successful. ...
Floriculture Disorders - Talbot County School District
... or at tips of stems. The mature plant may form a mat or grow up to a foot tall. The plant branches at the base and along the stems. Purslane seeds are very tiny and produced in abundance. ...
... or at tips of stems. The mature plant may form a mat or grow up to a foot tall. The plant branches at the base and along the stems. Purslane seeds are very tiny and produced in abundance. ...
Note on the Growing of Xeronema Callistemon
... date some 50 plants about a year and a quarter old, 4 or 5 inches high, with seven leaves in a fan. They take 2 i to 3 months to germinate, have grown most noticeably in the last six months and are still growing slowly. These seedlings are in boxes, some under glass, some in the open. Both are growi ...
... date some 50 plants about a year and a quarter old, 4 or 5 inches high, with seven leaves in a fan. They take 2 i to 3 months to germinate, have grown most noticeably in the last six months and are still growing slowly. These seedlings are in boxes, some under glass, some in the open. Both are growi ...
slide presentation
... Grows upon another plant (such as tree) non-parasitically or sometimes upon other objects ( such as a building or telegraph wire). Derives its moisture and nutrients from the air and rain and sometimes from debris accumulating around it. ...
... Grows upon another plant (such as tree) non-parasitically or sometimes upon other objects ( such as a building or telegraph wire). Derives its moisture and nutrients from the air and rain and sometimes from debris accumulating around it. ...
word
... Bulliform cells - enlarged epidermal cells (can be found in other species) a) Enable rolling of the leaf - common to bambusoid grasses ...
... Bulliform cells - enlarged epidermal cells (can be found in other species) a) Enable rolling of the leaf - common to bambusoid grasses ...
Northern bayberry, Myrica pensylvanica
... Look for oval leaves that alternate and have fine teeth near the tip. The waxy leaves are very fragrant with a sweet smell when crushed. Leaves are crowded toward the end of the branch. ...
... Look for oval leaves that alternate and have fine teeth near the tip. The waxy leaves are very fragrant with a sweet smell when crushed. Leaves are crowded toward the end of the branch. ...
Plant project
... • Because the plant is from the desert it can cope with entence heat, but they need full sun little water and good drainage and they hold water for a very long time…. ...
... • Because the plant is from the desert it can cope with entence heat, but they need full sun little water and good drainage and they hold water for a very long time…. ...
Dicentra cucullaria – Dutchman`s Breeches
... SUGGESTED CARE: The corms (bulbs) should be planted close to the surface and well watered. Allow a cluster of showy patches to develop before thinning. Digging the corms should happen after the ...
... SUGGESTED CARE: The corms (bulbs) should be planted close to the surface and well watered. Allow a cluster of showy patches to develop before thinning. Digging the corms should happen after the ...
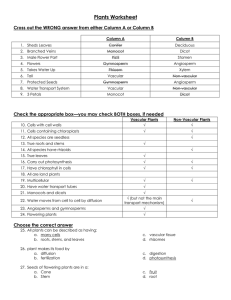
Plants Worksheet_answer key - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Check the appropriate box—you may check BOTH boxes, if needed 10. Cells with cell walls 11. Cells containing chloroplasts ...
... Check the appropriate box—you may check BOTH boxes, if needed 10. Cells with cell walls 11. Cells containing chloroplasts ...
leaves - SBI3USylviaFall2010
... • Angiosperms used to fall into two major groups – dicots and monocots depending on how many cotyledons the seeds contained. Now there are four groups but the main two are monocots and eudicots (true dicots) • More than 2/3 of angiosperms are eudicots (e.g. Dandelions) and ¼ are monocots (e.g. Grass ...
... • Angiosperms used to fall into two major groups – dicots and monocots depending on how many cotyledons the seeds contained. Now there are four groups but the main two are monocots and eudicots (true dicots) • More than 2/3 of angiosperms are eudicots (e.g. Dandelions) and ¼ are monocots (e.g. Grass ...
Autumn Leaf - Reiman Gardens
... possible to find adults year round while in the southern parts they are primarily found September – June with the highest populations in both areas at the end of the rainy season. Fun Facts: Whether it is the leaf like shape of the Autumn Leaf when it closes its wings, the color and pattern of the o ...
... possible to find adults year round while in the southern parts they are primarily found September – June with the highest populations in both areas at the end of the rainy season. Fun Facts: Whether it is the leaf like shape of the Autumn Leaf when it closes its wings, the color and pattern of the o ...
how grass grows - British Grassland Society
... occurs when the evaporation of water through the leaves is faster than the rate of uptake from the soil. Leaf expansion is first restricted during day time hours when the evaporative demand is at its highest. During a dry period, plant cells continue to be formed, but they need water to expand. When ...
... occurs when the evaporation of water through the leaves is faster than the rate of uptake from the soil. Leaf expansion is first restricted during day time hours when the evaporative demand is at its highest. During a dry period, plant cells continue to be formed, but they need water to expand. When ...
BioD Exam Plants Structure and Function
... b. Gas exchange. c. Collecting water. 27. Which drawing showed a compound leaf? a. A b. B c. C 28. Which drawing showed a simple leaf? a. A b. B c. C Roots 29. Root hairs anchor plants and help them absorb water by a. Protecting the growing part of the root. b. Increasing the root’s surface area. c. ...
... b. Gas exchange. c. Collecting water. 27. Which drawing showed a compound leaf? a. A b. B c. C 28. Which drawing showed a simple leaf? a. A b. B c. C Roots 29. Root hairs anchor plants and help them absorb water by a. Protecting the growing part of the root. b. Increasing the root’s surface area. c. ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.