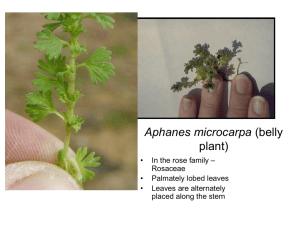
Sulphur Cinquefoil (Poten lla recta)
... flowering. Stems and leaves are covered with long, coarse, shiny hairs at right angles. Stem leaves are alternate, green on the underside, and composed of 5 to 7 leaflets with toothed margins. Leaflets appear like marijuana leaves (palmately compound). Seeds: Oval shaped dark brown seeds covered with n ...
... flowering. Stems and leaves are covered with long, coarse, shiny hairs at right angles. Stem leaves are alternate, green on the underside, and composed of 5 to 7 leaflets with toothed margins. Leaflets appear like marijuana leaves (palmately compound). Seeds: Oval shaped dark brown seeds covered with n ...
Parts of the plants and Functions
... • Leaves consist of the petiole (leaf stalk), and a blade (larger, flat portion of the leaf). • Leaves have veins and a midrib – Midrib is the large vein from which all other veins extend – Veins of the leaf form its structural framework ...
... • Leaves consist of the petiole (leaf stalk), and a blade (larger, flat portion of the leaf). • Leaves have veins and a midrib – Midrib is the large vein from which all other veins extend – Veins of the leaf form its structural framework ...
Plant Structure and Functions A26-41
... -phloem= moves food from plant’s leaves to other parts -cambium= layer of cells that separates xylem and phloem What are leaves? (p. A34-35) -simple leaves= single leaves (example: maple and oak leaves) -compound leaves= leaves come in clusters/groups (examples: chestnut and locust leaves) -epidermi ...
... -phloem= moves food from plant’s leaves to other parts -cambium= layer of cells that separates xylem and phloem What are leaves? (p. A34-35) -simple leaves= single leaves (example: maple and oak leaves) -compound leaves= leaves come in clusters/groups (examples: chestnut and locust leaves) -epidermi ...
"Scrunch," "scrunch" went the crunch of dry leaves under my feet
... nutrients the fungi need to survive. These hyphae develop into matted carpets that we sometimes see when leaf litter is moved. The speed at which decomposition occurs depends on moisture, temperature and composition of the leaf matter. Lower temperatures make decomposition occur more slowly. Leaves ...
... nutrients the fungi need to survive. These hyphae develop into matted carpets that we sometimes see when leaf litter is moved. The speed at which decomposition occurs depends on moisture, temperature and composition of the leaf matter. Lower temperatures make decomposition occur more slowly. Leaves ...
Parts of the plant File
... Root hairs • These are tiny hairs that are found near the growing tips of the roots. • They look like cotton wool • They provide a very large surface area for absorbing water from the soil ...
... Root hairs • These are tiny hairs that are found near the growing tips of the roots. • They look like cotton wool • They provide a very large surface area for absorbing water from the soil ...
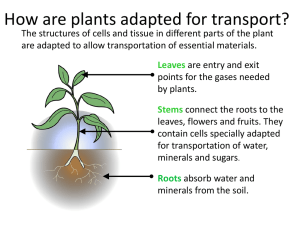
How are plants adapted for transport?
... are adapted to allow transportation of essential materials. Leaves are entry and exit points for the gases needed by plants. Stems connect the roots to the leaves, flowers and fruits. They contain cells specially adapted for transportation of water, minerals and sugars. Roots absorb water and minera ...
... are adapted to allow transportation of essential materials. Leaves are entry and exit points for the gases needed by plants. Stems connect the roots to the leaves, flowers and fruits. They contain cells specially adapted for transportation of water, minerals and sugars. Roots absorb water and minera ...
Courtesy of Wm. C. Brown Publishers
... Leaf Function • Photosynthesis – Make food (sugar “glucose”) ...
... Leaf Function • Photosynthesis – Make food (sugar “glucose”) ...
Crassulaceae species - Arizona
... Plants commonly found in Mexican gardens are often those that are easily rooted and passed on to friends. Their value is often in their beauty, but could include the utilitarian uses of food or folk medicine. Plants in the Family Crassulaceae fit into this group and are grown in abundance. HEN and C ...
... Plants commonly found in Mexican gardens are often those that are easily rooted and passed on to friends. Their value is often in their beauty, but could include the utilitarian uses of food or folk medicine. Plants in the Family Crassulaceae fit into this group and are grown in abundance. HEN and C ...
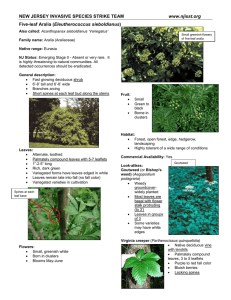
Five-leaf Aralia (Eleutherococcus sieboldianus)
... Family name: Aralia (Araliaceae) Native range: Eurasia NJ Status: Emerging Stage 0 - Absent or very rare. It is highly threatening to natural communities. All detected occurrences should be eradicated. General description: • Fast growing deciduous shrub • 6’-8’ tall and 6’-8’ wide • Branches arcing ...
... Family name: Aralia (Araliaceae) Native range: Eurasia NJ Status: Emerging Stage 0 - Absent or very rare. It is highly threatening to natural communities. All detected occurrences should be eradicated. General description: • Fast growing deciduous shrub • 6’-8’ tall and 6’-8’ wide • Branches arcing ...
Study Guide: Plants
... (Study notes! We only covered certain parts of these chapters) Important vocabulary terms: Make note cards or define the following: 28. vascular tissue 29. xylem 30. phloem 31. root 32. tap root 33. fibrous root 34. stem 35. leaf ...
... (Study notes! We only covered certain parts of these chapters) Important vocabulary terms: Make note cards or define the following: 28. vascular tissue 29. xylem 30. phloem 31. root 32. tap root 33. fibrous root 34. stem 35. leaf ...
Plant Science - Review
... 20. The tubes that carry water and minerals from the roots up to where photosynthesis will occur are called ______________________. 21. The tubes that carry sugar and water down from where they are produced to where they will be used or stored are called _____________________________. 22. Short day ...
... 20. The tubes that carry water and minerals from the roots up to where photosynthesis will occur are called ______________________. 21. The tubes that carry sugar and water down from where they are produced to where they will be used or stored are called _____________________________. 22. Short day ...
LEAVES
... • FUNCTION OF LEAVES – Leaves are the solar energy and CO2 collectors of plants. – In some plants, leaves have become adapted for specialized functions. ...
... • FUNCTION OF LEAVES – Leaves are the solar energy and CO2 collectors of plants. – In some plants, leaves have become adapted for specialized functions. ...
Rhizogoniaceae
... to ovate-lanceolate; margin simple or comprised of elongated cells, ±thickened, entire, dentate, serrate, or with single or paired multicellular teeth; costa strong, ending just below the apex to excurrent, often toothed abaxially; laminal cells usually small and isodiametric, ±thick-walled, smooth. ...
... to ovate-lanceolate; margin simple or comprised of elongated cells, ±thickened, entire, dentate, serrate, or with single or paired multicellular teeth; costa strong, ending just below the apex to excurrent, often toothed abaxially; laminal cells usually small and isodiametric, ±thick-walled, smooth. ...
Plant Structure and Taxonomy - BROADUS
... A shorter version is called the binomial system in which only the Genus and Species of a plant is used to identify it. ...
... A shorter version is called the binomial system in which only the Genus and Species of a plant is used to identify it. ...
croomia - Florida Natural Areas Inventory
... Field Description: Perennial herb with an erect, somewhat fleshy stem to 1 foot tall, occuring in patches of several plants. Leaves heart-shaped, 4 - 6 clustered at the top of the stem, alternate but appearing whorled or spiraled when viewed from above; with conspicuous, parallel veins strongly curv ...
... Field Description: Perennial herb with an erect, somewhat fleshy stem to 1 foot tall, occuring in patches of several plants. Leaves heart-shaped, 4 - 6 clustered at the top of the stem, alternate but appearing whorled or spiraled when viewed from above; with conspicuous, parallel veins strongly curv ...
Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet
... Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet chlorophyll xylem embryo cellulose seed flowers ...
... Kingdom Plantae: Review Sheet chlorophyll xylem embryo cellulose seed flowers ...
Name - Fairfield Public Schools
... Ch. 28 Plant Evolution: Describe the basic physical characteristics, the environment in which they are found and examples for each of the following: o bryophytes o pteridophytes o gymnosperms o angiosperms How are the 4 groups of plants related to one another in terms of evolution? Which group ...
... Ch. 28 Plant Evolution: Describe the basic physical characteristics, the environment in which they are found and examples for each of the following: o bryophytes o pteridophytes o gymnosperms o angiosperms How are the 4 groups of plants related to one another in terms of evolution? Which group ...
Anomodon longifolius
... Similar species The far commoner A. viticulosus (p. 694) – with which A. longifolius often grows – is much bigger (shoots 2–8 cm long; leaves 2–3 mm long), and has a blunter leaf tip. The very rare A. attenuatus (Smith, p. 744) is also larger (shoots up to 5 cm long; leaves 1–2 mm long), with a blun ...
... Similar species The far commoner A. viticulosus (p. 694) – with which A. longifolius often grows – is much bigger (shoots 2–8 cm long; leaves 2–3 mm long), and has a blunter leaf tip. The very rare A. attenuatus (Smith, p. 744) is also larger (shoots up to 5 cm long; leaves 1–2 mm long), with a blun ...
Lesson 2 Tree Anatomy
... 2. The leaf carries out transpiration which is the loss of water and the gas exchange of CO2. 3. The leaf can store some food, which can be transferred to other areas of the plant. Leaves Leaves contain cells full of chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are the ultimate energy factories of the tree. Chl ...
... 2. The leaf carries out transpiration which is the loss of water and the gas exchange of CO2. 3. The leaf can store some food, which can be transferred to other areas of the plant. Leaves Leaves contain cells full of chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are the ultimate energy factories of the tree. Chl ...
Lesson 2 Tree Anatomy
... 2. The leaf carries out transpiration which is the loss of water and the gas exchange of CO2. 3. The leaf can store some food, which can be transferred to other areas of the plant. Leaves Leaves contain cells full of hloroplasts. Chloroplasts are the ultimate energy factories of the tree. Chlo ...
... 2. The leaf carries out transpiration which is the loss of water and the gas exchange of CO2. 3. The leaf can store some food, which can be transferred to other areas of the plant. Leaves Leaves contain cells full of hloroplasts. Chloroplasts are the ultimate energy factories of the tree. Chlo ...
LAB 3
... The cotyledons are opposite but later leaves are alternate, i.e., with a single leaf at each node. The alternation becomes more pronounced as the inflorescence develops. In what way do the cotyledons differ from the other leaves on the plant? Note the difference in size and texture between the old ...
... The cotyledons are opposite but later leaves are alternate, i.e., with a single leaf at each node. The alternation becomes more pronounced as the inflorescence develops. In what way do the cotyledons differ from the other leaves on the plant? Note the difference in size and texture between the old ...
Supermarket Angiosperm
... Chili, bell pepper or eggplant (foods Usually referred to as vegetables, but are true fruits because they develop from the ovary of a flower) ...
... Chili, bell pepper or eggplant (foods Usually referred to as vegetables, but are true fruits because they develop from the ovary of a flower) ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.